Anat Cell Biol.
2018 Mar;51(1):7-13. 10.5115/acb.2018.51.1.7.
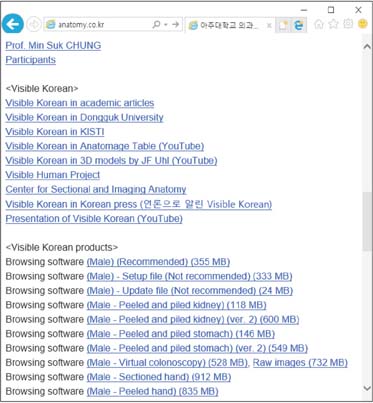
Homepage to distribute the anatomy learning contents including Visible Korean products, comics, and books
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. dissect@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2418389
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2018.51.1.7
Abstract
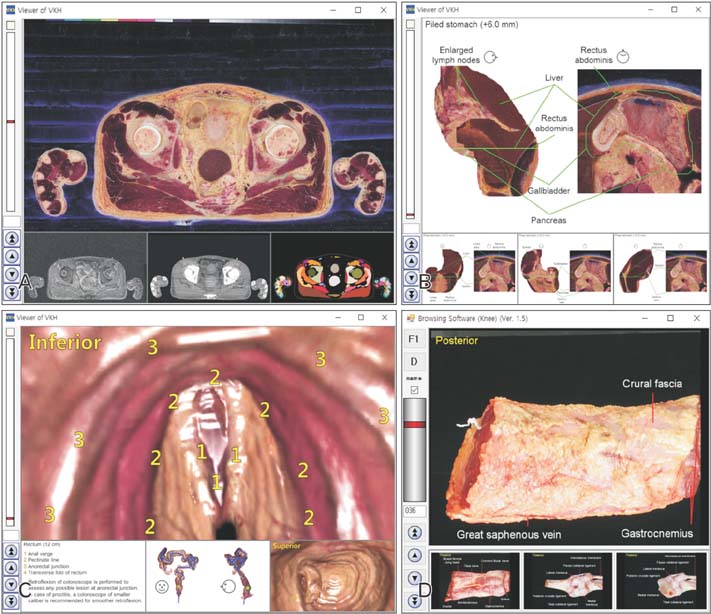
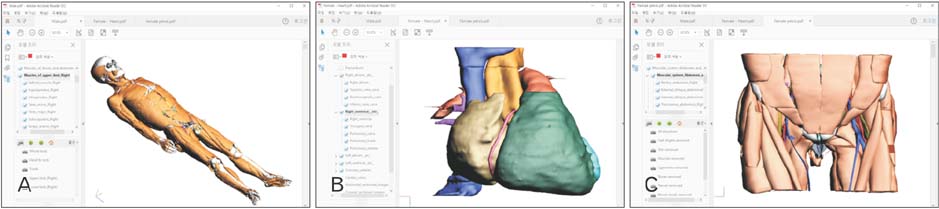
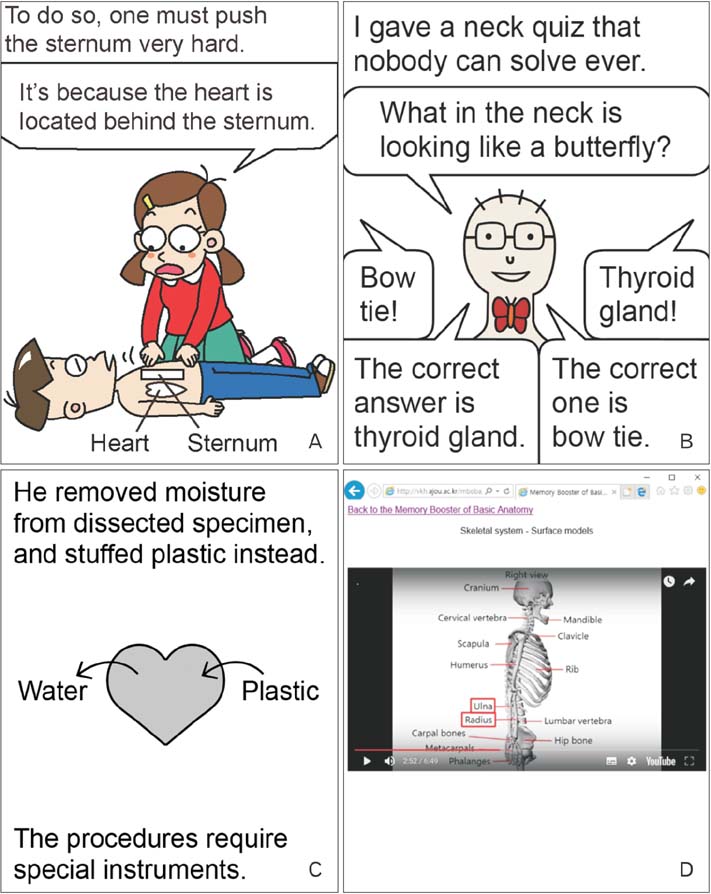
- The authors have operated the homepage (http://anatomy.co.kr) to provide the learning contents of anatomy. From the homepage, sectioned images, volume models, and surface models"”all Visible Korean products"”can be downloaded. The realistic images can be interactively manipulated, which will give rise to the interest in anatomy. The various anatomy comics (learning comics, comic strips, plastination comics, etc.) are approachable. Visitors can obtain the regional anatomy book with concise contents, mnemonics, and schematics as well as the simplified dissection manual and the pleasant anatomy essay. Medical students, health allied professional students, and even laypeople are expected to utilize the easy and comforting anatomy contents. It is hoped that other anatomists successively produce and distribute their own informative contents.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Portable Document Format File Containing the Schematics and Operable Surface Models of the Head Structures
Beom Sun Chung, Min Suk Chung, Jin Seo Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(27):e212. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e212.New Viewpoint of Surface Anatomy Using the Curved Sectional Planes of a Male Cadaver
Koojoo Kwon, Byeong-Seok Shin, Min Suk Chung, Beom Sun Chung
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(3):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e15.Effects of Reading a Free Electronic Book on Regional Anatomy with Schematics and Mnemonics on Student Learning
Beom Sun Chung, Ki Seok Koh, Chang-Seok Oh, Jin Seo Park, Jae-Ho Lee, Min Suk Chung
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(6):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e42.
Reference
-
1. Park JS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Lee YS, Har DH, Park HS. Visible Korean Human: improved serially sectioned images of the entire body. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005; 24:352–360.2. Park JS, Chung MS, Shin DS, Har DH, Cho ZH, Kim YB, Han JY, Chi JG. Sectioned images of the cadaver head including the brain and correspondences with ultrahigh field 7.0 T MRIs. Proc IEEE. 2009; 97:1988–1996.3. Park HS, Choi DH, Park JS. Improved sectioned images and surface models of the whole female body. Int J Morphol. 2015; 33:1323–1332.
Article4. Hwang SB, Chung MS, Hwang YI, Park HS, Har DH, Shin DS, Shin BS, Park JS. Improved sectioned images of the female pelvis showing detailed urogenital and neighboring structures. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2010; 23:187–198.
Article5. Shin DS, Chung MS, Park HS, Park JS, Hwang SB. Browsing software of the Visible Korean data used for teaching sectional anatomy. Anat Sci Educ. 2011; 4:327–332.
Article6. Shin DS, Chung MS, Park JS, Park HS, Lee S, Moon YL, Jang HG. Portable document format file showing the surface models of cadaver whole body. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:849–856.
Article7. Shin DS, Lee S, Park HS, Lee SB, Chung MS. Segmentation and surface reconstruction of a cadaver heart on Mimics software. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2015; 74:372–377.
Article8. Chung BS, Chung MS, Park HS, Shin BS, Kwon K. Colonoscopy tutorial software made with a cadaver's sectioned images. Ann Anat. 2016; 208:19–23.
Article9. Chung BS, Chung MS, Shin BS, Kwon K. Peeled and piled volume models of the kidney that show actual morphology. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:1514–1515.
Article10. Chung BS, Kwon K, Shin BS, Chung MS. Peeled and piled volume models of the stomach made from a cadaver's sectioned images. Int J Morphol. 2016; 34:939–944.
Article11. Chung BS, Kwon K, Shin BS, Chung MS. Surface models and gradually peeled volume model to explore hand structures. Ann Anat. 2017; 211:202–206.
Article12. Shin DS, Kim DH, Park JS, Jang HG, Chung MS. Evaluation of anatomy comic strips for further production and applications. Anat Cell Biol. 2013; 46:210–216.
Article13. Kim J, Chung MS, Jang HG, Chung BS. The use of educational comics in learning anatomy among multiple student groups. Anat Sci Educ. 2017; 10:79–86.
Article14. Chung BS, Chung MS. Free manual of cadaver dissection modifiable by other anatomists. Anat Sci Int. 2015; 90:201–202.
Article15. Park JS, Kim DH, Chung MS. Anatomy comic strips. Anat Sci Educ. 2011; 4:275–279.
Article16. Gao H, Liu J, Yu S, Sui H. A new polyester technique for sheet plastination. J Int Soc Plastination. 2006; 21:7–10.17. Chung BS, Sui HJ, Chung MS. Comics for laypeople interested in plastination. Int J Morphol. 2016; 34:1105–1108.
Article18. Chung BS, Kim J, Chung MS. Integrated comics and Visible Korean movies for laypeople's learning of systemic anatomy. Int J Morphol. 2017; 35:883–887.
Article19. Kelc R. 2012. Zygote body: a new interactive 3-dimensional didactical tool for teaching anatomy. WebmedCentral Anat. 2012; 3:WMC002889.20. Kwon K, Chung MS, Park JS, Shin BS, Chung BS. Improved software to browse the serial medical images for learning. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:1195–1201.
Article21. Chung BS, Park JS, Jang HG, Chung MS. Software to browse the pictures of two knees in diverse states of dissection, flexion and rotation. Int J Morphol. 2015; 33:1009–1015.
Article22. Veneri D. The role and effectiveness of computer-assisted learning in physical therapy education: a systematic review. Physiother Theory Pract. 2011; 27:287–298.
Article23. Evans DJ. The role of the anatomist in communicating anatomy to a lay audience. Eur J Anat. 2007; 11:Suppl 1. S79–S83.24. Evans DJ. Connecting with different audiences: the anatomy of communication is essential. Anat Sci Educ. 2013; 6:134–137.
Article25. Chung BS, Park EM, Kim SH, Cho SK, Chung MS. Comic strips to accompany science museum exhibits. J Educ Learn. 2016; 5:141–146.
Article26. Lewis TL, Burnett B, Tunstall RG, Abrahams PH. Complementing anatomy education using three-dimensional anatomy mobile software applications on tablet computers. Clin Anat. 2014; 27:313–320.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Reading a Free Electronic Book on Regional Anatomy with Schematics and Mnemonics on Student Learning
- Establishing Homepage for Basic Nursing Science Education: in the Nervous System of Human Body
- Evaluation of anatomy comic strips for further production and applications
- Portable Document Format File Showing the Surface Models of Cadaver Whole Body
- Real-Color Volume Models Made from Real-Color Sectioned Images of Visible Korean