Ann Rehabil Med.
2018 Jun;42(3):473-476. 10.5535/arm.2018.42.3.473.
Optimal Placement of Needle Electromyography in Extensor Indicis: A Cadaveric Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rmkdh@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2417840
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.3.473
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To identify the center of extensor indicis (EI) muscle through cadaver dissection and compare the accuracy of different techniques for needle electromyography (EMG) electrode insertion.
METHODS
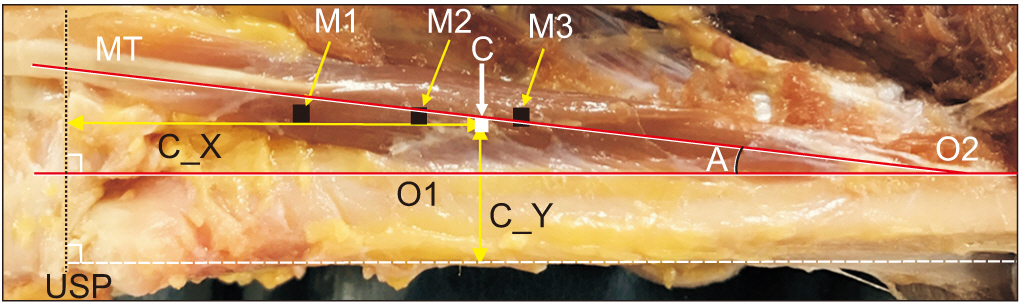
Eighteen upper limbs of 10 adult cadavers were dissected. The center of trigonal EI muscle was defined as the point where the three medians of the triangle intersect. Three different needle electrode insertion techniques were introduced: M1, 2.5 cm above the lower border of ulnar styloid process (USP), lateral aspect of the ulna; M2, 2 finger breadths (FB) proximal to USP, lateral aspect of the ulna; and M3, distal fourth of the forearm, lateral aspect of the ulna. The distance from USP to the center (X) parallel to the line between radial head to USP, and from medial border of ulna to the center (Y) were measured. The distances between 3 different points (M1- M3) and the center were measured (marked as D1, D2, and D3, respectively).
RESULTS
The median value of X was 48.3 mm and that of Y was 7.2 mm. The median values of D1, D2 and D3 were 23.3 mm, 13.3 mm and 9.0 mm, respectively.
CONCLUSION
The center of EI muscle is located approximately 4.8 cm proximal to USP level and 7.2 mm lateral to the medial border of the ulna. Among the three methods, the technique placing the needle electrode at distal fourth of the forearm and lateral to the radial side of the ulna bone (M3) is the most accurate and closest to the center of the EI muscle.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ultrasonographic Analysis of Optimal Needle Placement for Extensor Indicis
Jin Young Kim, Hyun Seok, Sang-Hyun Kim, Yoon-Hee Choi, Jun Young Ahn, Seung Yeol Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2020;44(6):450-458. doi: 10.5535/arm.20035.
Reference
-
1. Leis AA, Trapani VC. Atlas of electromyography. New York: Oxford University Press;2000. p. 46.2. Komiyama M, Nwe TM, Toyota N, Shimada Y. Variations of the extensor indicis muscle and tendon. J Hand Surg Br. 1999; 24:575–8.
Article3. Pandey S. A practical approach to management of focal hand dystonia. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2015; 18:146–53.
Article4. Gray H, Standring S, Ellis H, Berkovitz BK. Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 40th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone;2008. p. 851.5. Chu-Andrews J, Johnson RJ. Electrodiagnosis: an anatomical and clinical approach. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1986. p. 144.6. Perotto A, Delagi EF. Anatomical guide for the electromyographer: the limbs and trunk. 3rd ed. Springfield: Charles C. Thomas;1994. p. 45–6.7. Lee HJ, DeLisa JA. Surface anatomy for clinical needle electromyography. New York: Demos Medical Pub;2000. p. 178–9.8. Karvelas K, Ziegler C, Rho ME. Resident accuracy of electromyography needle electrode placement using ultrasound verification. PM R. 2016; 8:748–53.
Article9. Goodmurphy C, Chiodo A, Haig A. The accuracy of needle placement in extremity muscles: a blinded study. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007; 24:366–78.
Article10. Cheong IY, Kim DK, Oh YJ, Park BK, Kim KH, Kim DH. Optimal needle placement for extensor hallucis longus muscle: a cadaveric study. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016; 40:457–62.
Article11. Preston DC, Shapiro BE. Electromyography and neuromuscular disorders: clinical-electrophysiologic correlations. 3rd ed. London: Elsevier;2013. p. 148.12. Safwat MD, Abdel-Meguid EM. Distribution of terminal nerve entry points to the flexor and extensor groups of forearm muscles: an anatomical study. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2007; 66:83–93.13. Molloy FM, Shill HA, Kaelin-Lang A, Karp BI. Accuracy of muscle localization without EMG: implications for treatment of limb dystonia. Neurology. 2002; 58:805–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Congenital Absence of Extensor Indicis Proprius Tendon, Bilateral: A Case Report
- Ultrasonographic Analysis of Optimal Needle Placement for Extensor Indicis
- Extensor Indicis Brevis: A Case Report
- Optimal Needle Placement for Extensor Hallucis Longus Muscle: A Cadaveric Study
- Reconstruction of the Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon by Tendon Graft or Tendon Transfer