J Korean Fract Soc.
2018 Jul;31(3):87-93. 10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.87.
A Comparison of the Results between Internal Fixation and External Fixation in AO C Type Distal Radius Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. simba0415@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2417150
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.87
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the radiological and clinical results of plate fixation and external fixation with additional devices for treating distal radius fracture in AO type C subtypes, and propose a treatment method according to the subtypes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
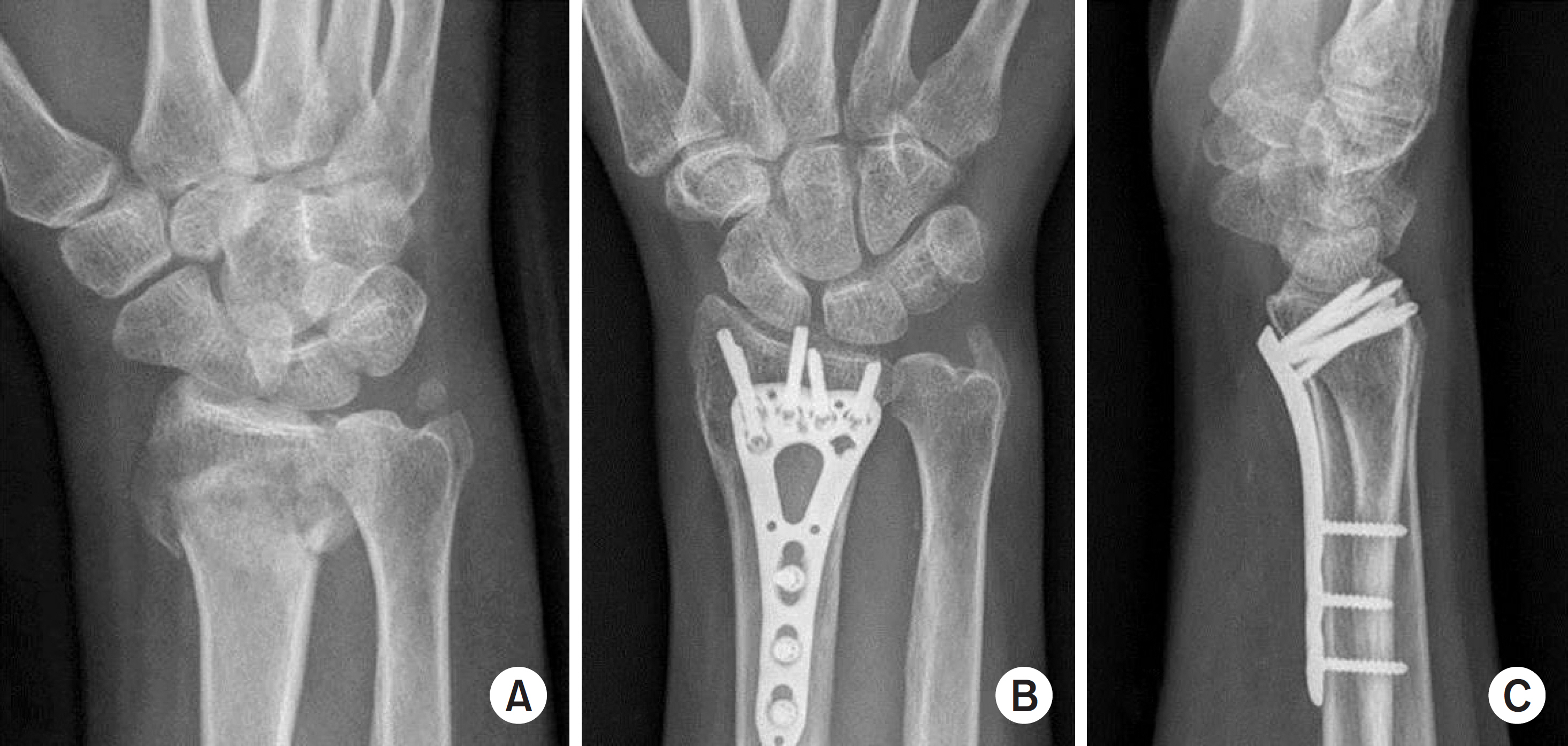
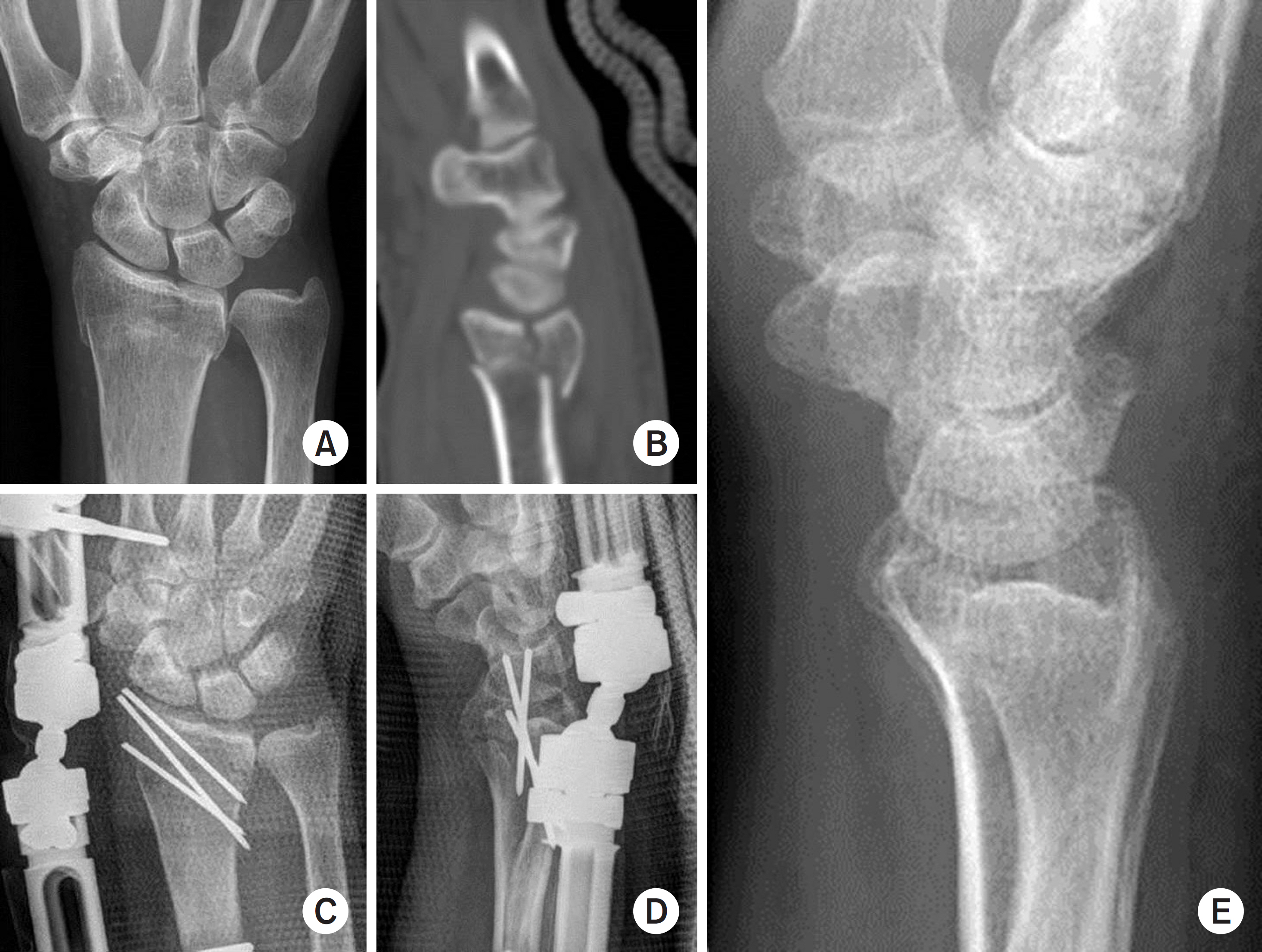
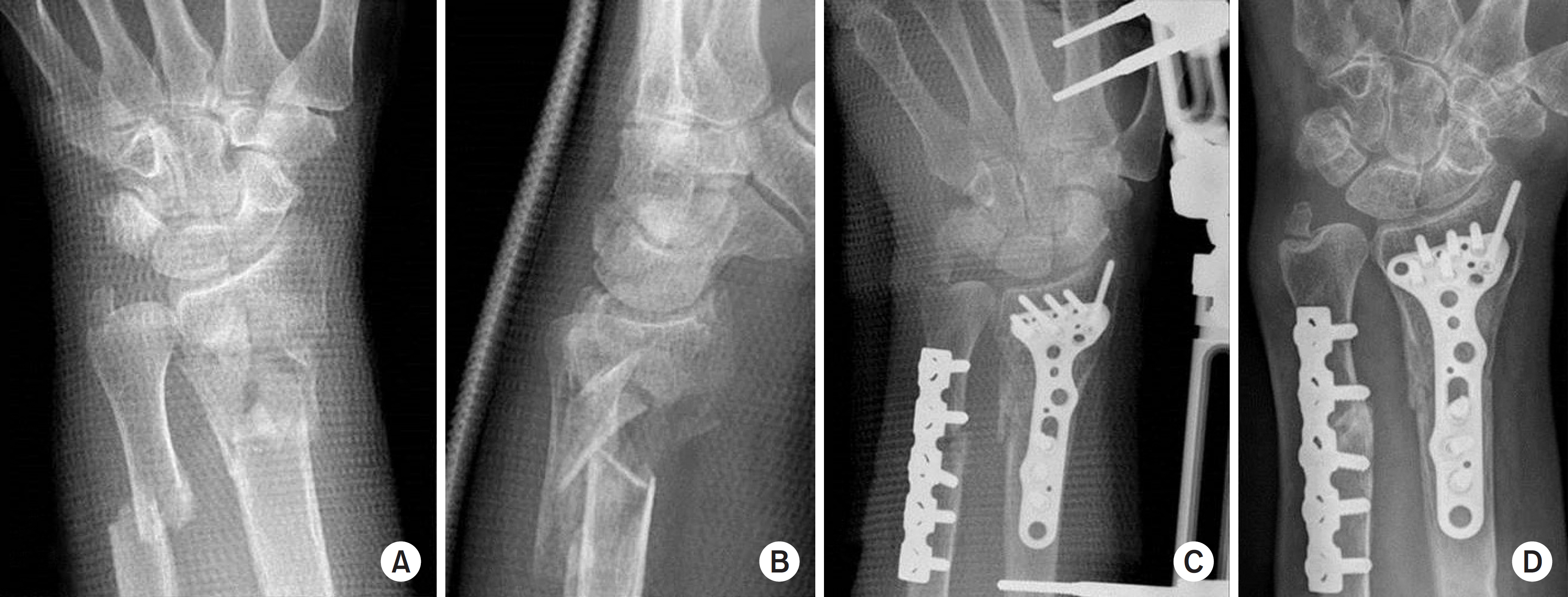
Two hundred and one AO type C distal radius fracture patients were retrospectively reviewed. Eighty-five patients in group 1 were treated with volar or dorsal plate, and 116 patients in group 2, were treated with external fixation with additional fixation devices. Clinical (range of mtion, Green and O'Brien's score) and radiological outcomes were evaluated.
RESULTS
At the 12-month follow-up, group 1 showed flexion of 64.4°, extension of 68.3°, ulnar deviation of 30.6°, radial deviation of 20.8°, supination of 76.1°, and pronation of 79.4° in average; group 2 showed flexion of 60.5°, extension of 66.9°, ulnar deviation of 25.5°, radial deviation of 18.6°, supination of 73.5°, and pronation of 75.0° in average. The mean Green and O'Brien score was 92.2 in group 1 and 88.6 in group 2. The radial height of group 1 and group 2 was 11.6/11.4 mm; radial inclination was 23.2°/22.5°; volar tilt was 11.6°/8.7°; and the ulnar displacement was 1.27/0.93 mm.
CONCLUSION
Judicious surgical techniques during device application and tips for postoperative management during external fixation can produce similar clinical results compared with internal fixation patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Singer BR, McLauchlan GJ, Robinson CM, Christie J. Epidemiology of fractures in 15,000 adults: the influence of age and gender. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 80:243–248. 1998.2. Mattila VM, Huttunen TT, Sillanpää P, Niemi S, Pihlajamäki H, Kannus P. Significant change in the surgical treatment of distal radius fractures: a nationwide study between 1998 and 2008 in Finland. J Trauma. 71:939–942. discussion 942–943,. 2011.
Article3. Cooney WP. External fixation of distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 180:44–49. 1983.
Article4. Kapoor H, Agarwal A, Dhaon BK. Displaced intraarticular fractures of distal radius: a comparative evaluation of results following closed reduction, external fixation and open reduction with internal fixation. Injury. 31:75–79. 2000.
Article5. Kapandji A. Intrafocal pinning of fractures of the distal end of the radius 10 yeasr later. Ann Chir Main. 6:57–63. 1987.6. Penning D, Gausepohl T. External fixation of the wrist. Injury. 27:1–15. 1996.
Article7. Leung F, Tu YK, Chew WY, Chow SP. Comparison of external and percutaneous pin fixation with plate fixation for intraarticular distal radial fractures. A randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 90:16–22. 2008.8. Xie X, Xie X, Qin H, Shen L, Zhang C. Comparison of internal and external fixation of distal radius fractures. Acta Orthop. 84:286–291. 2013.
Article9. Wang J, Yang Y, Ma J, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation versus external fixation for unstable distal radial fractures: a metaanalysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 99:321–331. 2013.
Article10. Esposito J, Schemitsch EH, Saccone M, Sternheim A, Kuzyk PR. External fixation versus open reduction with plate fixation for distal radius fractures: a metaanalysis of randomised controlled trials. Injury. 44:409–416. 2013.
Article11. Hegeman JH, Oskam J, Vierhout PA, Ten Duis HJ. External fixation for unstable intraarticular distal radial fractures in women older than 55 years. Acceptable functional end results in the majority of the patients despite significant secondary displacement. Injury. 36:339–344. 2005.12. Zollinger PE, Kreis RW, van der Meulen HG, van der Elst M, Breederveld RS, Tuinebreijer WE. No higher risk of CRPS after external fixation of distal radial fractures-subgroup analysis under randomised vitamin C prophylaxis. Open Orthop J. 4:71–75. 2010.13. Roh YH, Lee BK, Baek JR, Noh JH, Gong HS, Baek GH. A randomized comparison of volar plate and external fixation for intraarticular distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 40:34–41. 2015.14. Shukla R, Jain RK, Sharma NK, Kumar R. External fixation versus volar locking plate for displaced intraarticular distal radius fractures: a prospective randomized comparative study of the functional outcomes. J Orthop Traumatol. 15:265–270. 2014.
Article15. Margaliot Z, Haase SC, Kotsis SV, Kim HM, Chung KC. A metaanalysis of outcomes of external fixation versus plate osteosynthesis for unstable distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 30:1185–1199. 2005.
Article16. Brogan DM, Richard MJ, Ruch D, Kakar S. Management of severely comminuted distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 40:1905–1914. 2015.
Article17. Gausepohl T, Pennig D, Mader PK. Principles of external fixation and supplementary techniques in distal radius fractures. Injury, 31 Suppl. 1:56–70. 2000.
Article18. Capo JT, Rossy W, Henry P, Maurer RJ, Naiu S, Chen L. External fixation of distal radius fractures: effect of distraction and duration. J Hand Surg Am. 34:1605–1611. 2009.
Article19. Weber SC, Szabo RM. Severely comminuted distal radial fracture as an unsolved problem: complications associated with external fixation and pins and plaster techniques. J Hand Surg Am. 11:157–165. 1986.
Article20. McQueen MM, Michie M, Court-Brown CM. Hand and wrist function after external fixation of unstable distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 285:200–204. 1992.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Results According to the Type and Procedure in Unstable Fracture of the Distal Radius
- Treatment of Comminuted Distal Radius Fracutures with External Skeletal Fixation
- External fixation of distal radius fracture
- External Fixation for Distal Radius Fractures
- Surgical Treatment for Unstable Intra-articular Fracture of Distal Radius