J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2018 Jul;56(3):179-187. 10.4047/jkap.2018.56.3.179.
The effect of heat to remove cement on implant titanium abutment and screw
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry and Institute of Oral Bio-Science, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Republic of Korea. jmseo@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2416809
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2018.56.3.179
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of heat applied to disintegrate cement on the removal torque value and fracture strength of titanium abutment and abutment screw.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Implants, titanium abutments and abutment screws were prepared for each 20 piece. Implant abutments and screws were classified as the control group in which no heat was applied and the experimental group was heated in a vacuum furnace to 450℃ for 8 minutes and cooled in air. The abutments and screws were connected to the implants with 30 Ncm tightening torque at interval 10 minutes and the removal torque value was measured 15 minutes later. And the fracture strength of abutment screw was measured using universal testing machine.
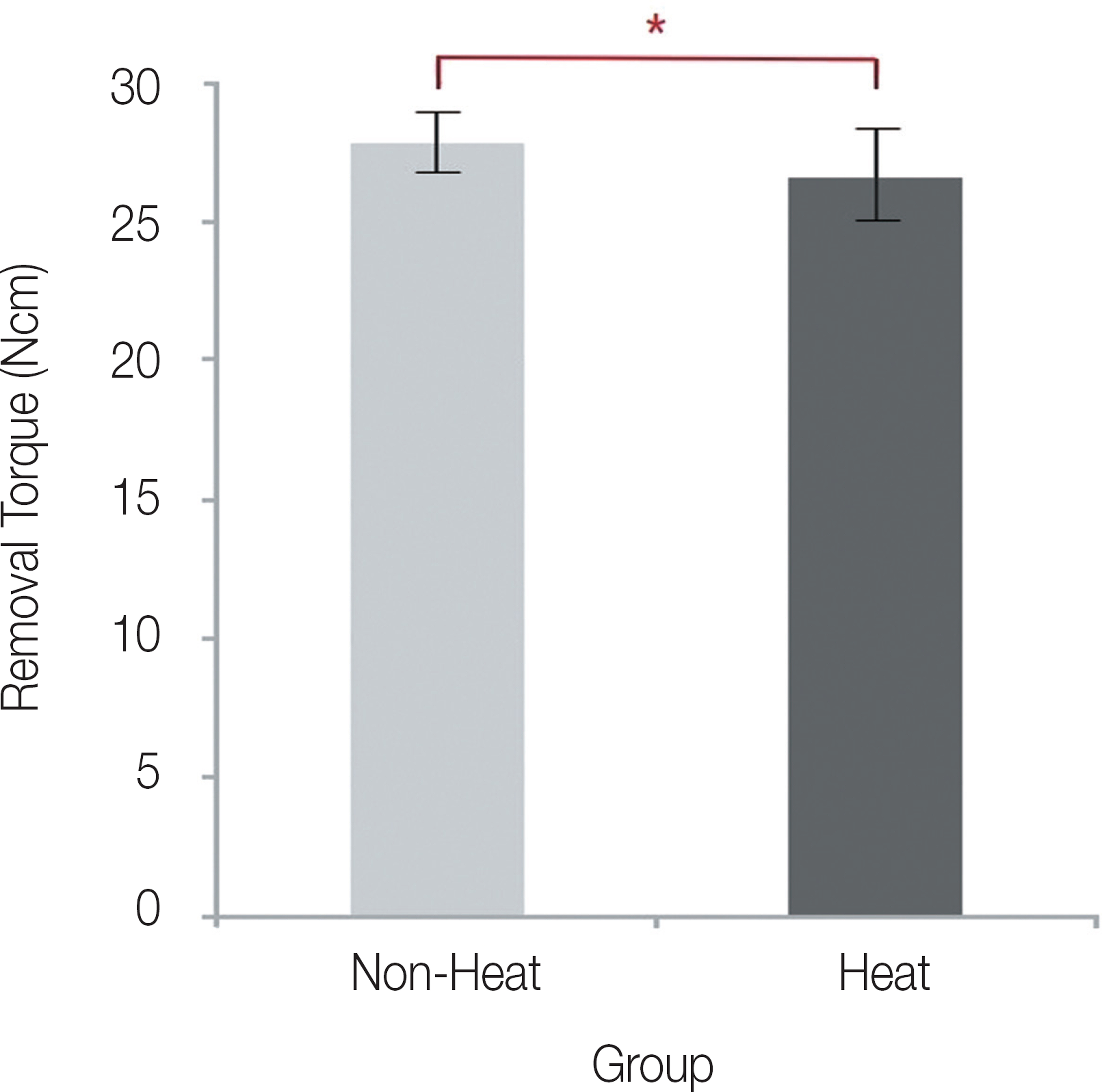
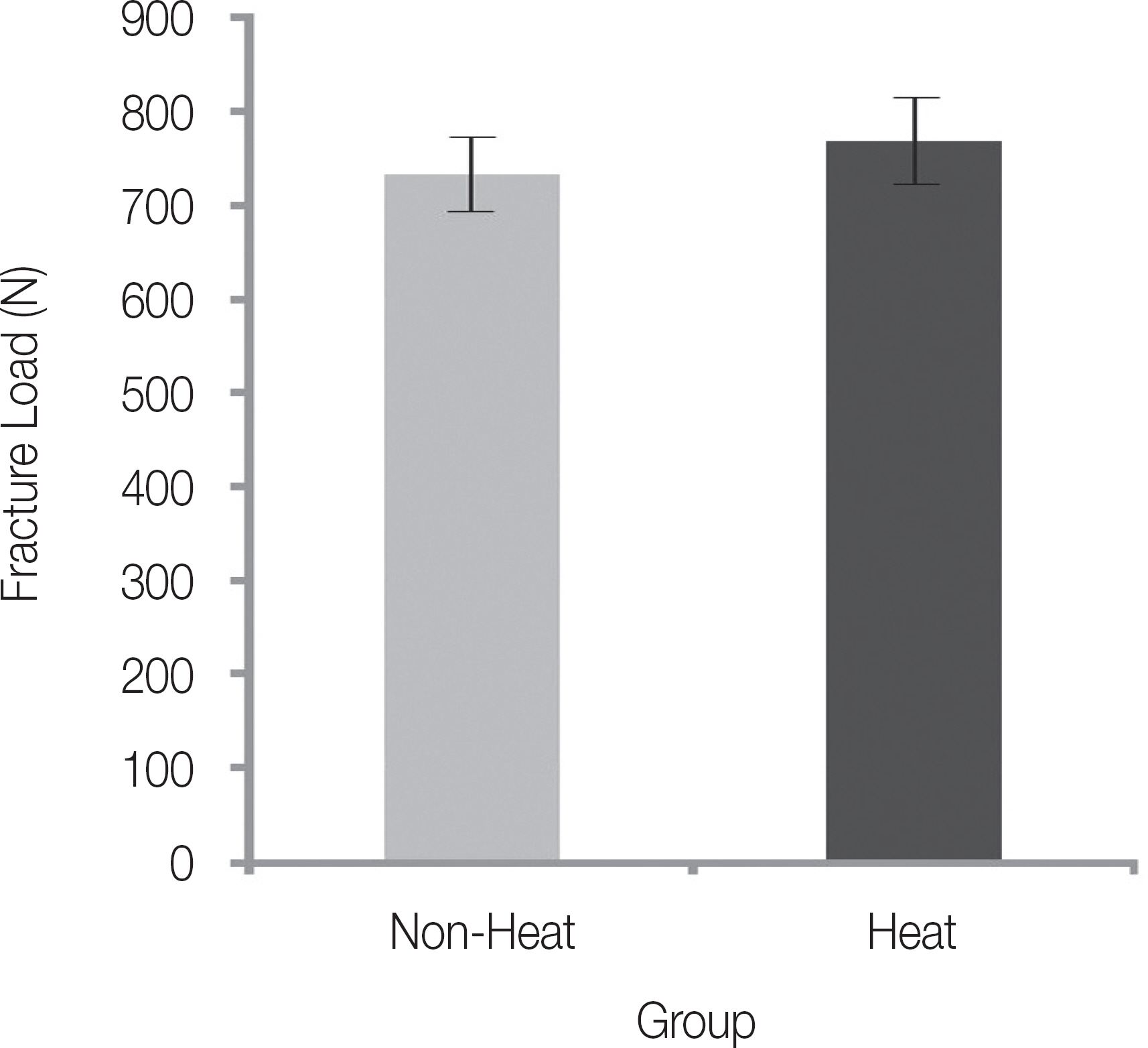
RESULTS
The mean removal torque value was 27.84 ± 1.07 Ncm in the control group and 26.55 ± 1.56 Ncm in the experimental group and showed statistically significant difference (P < .05). The mean fracture strength was 731.47 ± 39.46 N in the control group and 768.58 ± 46.73 N in the experimental group and showed statistically no significant difference (P > .05).
CONCLUSION
The heat applied for cement disintegration significantly reduced the removal torque value of the abutment screw and did not significantly affect fracture strength of the abutment screw. Therefore, in the case of applying heat to disintegrate cement it is necessary to separate the abutment screw or pay attention to the reuse of the heated screw. However further studies are needed to evaluate the clinical reuse of the heated screw.
Figure
Reference
-
1.Misch CE. Contemporary implant dentistry. 3rd ed.St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier;2008.2.Chung CH., Son MK. The classification and comparison of implant prosthesis according to types of retention. Part I: screw retained prosthesis vs cement retained prosthesis. Implantology. 2010. 14:138–51.3.Kim JH., Yun BH., Jang JE., Huh JB., Jeong CM. Retrievable SCP (screw-cement prosthesis) implant-supported fixed partial dentures in a fully edentulous patient: a case report. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2012. 50:318–23.
Article4.Chung CH., Son MK. The classification and comparison of implant prosthesis according to types of retention. Part II: Screw-cement retained prosthesis. Implantology. 2011. 15:58–70.5.Taylor TD. Prosthodontic problems and limitations associated with osseointegration. J Prosthet Dent. 1998. 79:74–8.
Article6.Rangert B., Jemt T., Jörneus L. Forces and moments on Brane-mark implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1989. 4:241–7.7.Pauletto N., Lahiffe BJ., Walton JN. Complications associated with excess cement around crowns on osseointegrated implants: a clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999. 14:865–8.8.Arora A., Upadhayaya V., Mittal S., Goyal I. Techniques for retrievability of cement retained implant prosthesis. J Dent Implant. 2014. 4:161–4.
Article9.Aparicio C. A new method for achieving passive flt of an interim restoration supported by Brånemark implants: a technical note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995. 10:614–8.10.Jung RE., Pjetursson BE., Glauser R., Zembic A., Zwahlen M., Lang NP. A systematic review of the 5-year survival and complication rates of implant-supported single crowns. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008. 19:119–30.
Article11.Shin SY. Prosthodontic problems and complications associated with osseointegration. J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci. 2015. 31:349–57.
Article12.Hong JY., Chae GJ., Jung UW., Kim CS., Cho KS., Chai JK., Kim CK., Choi SH. Implant-related complications and treatment of the ailing implants. Implantology. 2007. 11:44–54.13.Rosenstiel SF., Land MF., Fujimoto J. Contemporary fixed prosthodontics. 5th ed.St. Louis: USA; Elsevier;2016.14.Krishnan V., Tony Thomas C., Sabu I. Management of abutment screw loosening: review of literature and report of a case. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014. 14:208–14.
Article15.Linkevicius T., Vindasiute E., Puisys A., Linkeviciene L., Svedi-ene O. In‡uence of the temperature on the cement disintegration in cement-retained implant restorations. Stomatologija. 2012. 14:114–7.16.Veiga C., Davim JP., Loureiro AJR. Properties and applications of titanium alloys: A brief review. Rev Adv Mater Sci. 2012. 32:133–48.17.ISO 14801: 2016. Dentistry implants - dynamic fatigue test for endosseous dental implants. Geneva (Switzerland): International Organization for Standardization;2016.18.Leelanarathiwat K., Asvanund P., Anunmana C. Removal torque of screw-and cement-retained cantilever flxed prosthesis on angled abutment after cyclic loading. Mahidol Dent J. 2016. 36:269–77.19.Gracis S., Michalakis K., Vigolo P., Vult von Steyern P., Zwahlen M., Sailer I. Internal vs. external connections for abutments/reconstructions: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012. 23:202–16.
Article20.Theoharidou A., Petridis HP., Tzannas K., Garefls P. Abutment screw loosening in single-implant restorations: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008. 23:681–90.21.Im SM., Kim DG., Park CJ., Cha MS., Cho LR. Biomechanical considerations for the screw of implant prosthesis: A literature review. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2010. 48:61–8.
Article22.Al Jabbari YS., Fournelle R., Ziebert G., Toth J., Iacopino AM. Mechanical behavior and failure analysis of prosthetic retaining screws after long-term use in vivo. Part 4: Failure analysis of 10 fractured retaining screws retrieved from three patients. J Prosthodont. 2008. 17:201–10.
Article23.Gupta S., Gupta H., Tandan A. Technical complications of implant-causes and management: A comprehensive review. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2015. 6:3–8.
Article24.Haack JE., Sakaguchi RL., Sun T., Coffey JP. Elongation and preload stress in dental implant abutment screws. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995. 10:529–36.25.Winkler S., Ring K., Ring JD., Boberick KG. Implant screw mechanics and the settling effect: overview. J Oral Implantol. 2003. 29:242–5.26.Kyung KY., Cha HS., Lee JH. The effect of a titanium socket with a zirconia abutment on screw loosening after thermocy-cling in an internally connected implant: a preliminary study. J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci. 2017. 33:114–8.
Article27.Cantwell A., Hobkirk JA. Preload loss in gold prosthesis-retaining screws as a function of time. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:124–32.28.Huh YH., Cho LR., Kim DG., Park CJ. Comparison of implant torque controllers using detorque value. J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci. 2010. 26:419–32.29.Lang LA., Kang B., Wang RF., Lang BR. Finite element analysis to determine implant preload. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. 90:539–46.
Article30.Stüker RA., Teixeira ER., Beck JC., da Costa NP. Preload and torque removal evaluation of three different abutment screws for single standing implant restorations. J Appl Oral Sci. 2008. 16:55–8.
Article31.Hong SY., Markus I., Jeong WC. New cooling approach and tool life improvement in cryogenic machining of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Mach Tools Manuf. 2001. 41:2245–60.
Article32.Zherebtsov S., Salishchev G., Galeyev R., Maekawa K. Mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy with submi-crocrystalline structure produced by severe plastic deformation. Mater Trans. 2005. 46:2020–5.33.Ming Q., Yongzhen Z., Jun Z., Jianheng Y. Dry friction characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V alloy under high sliding velocity. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mat Sci. 2007. 22:582.34.Revankar GD., Shetty R., Rao SS., Gaitonde VN. Wear resistance enhancement of titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) by ball burnishing process. J Mater Res Technol. 2017. 6:13–32.
Article35.Swarnakar AK., van der Biest O., Baufeld B. Young's modulus and damping in dependence on temperature of Ti-6Al-4V components fabricated by shaped metal deposition. J Mater Sci. 2011. 46:3802–11.
Article36.da Rocha SS., Adabo GL., Henriques GE., Nóbilo MA. Vickers hardness of cast commercially pure titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloy submitted to heat treatments. Braz Dent J. 2006. 17:126–9.37.Meyers MA., Benavides HAC., Bruhl SP., Colorado HA., Dal-gaard E., Elias CN., Figueiredo RB., Garcia Rincon O., Kawasaki M., Langdeon TG., Mangalaraja RV., Marroquin MCG., da Cunha Rocha A., Schoenung J., Costa e Silva A., Wells M., Yang W. (Eds.) Proceedings of the 3rd Pan American Materials Congress. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer;2017. p. 381–91.38.Liu G., Zhu D., Jian Shang. Enhanced fatigue crack growth resistance at elevated temperature in TiC/Ti-6Al-4V composite: Microcrack-induced crack closure. Metall Mater Trans A. 1995. 26:159–66.39.Lee KA., Kim YK., Yu JH., Park SH., Kim MC. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and impact toughness of Ti-6Al-4V manufactured by selective laser melting process. Arch Metall Mater. 2017. 62:1341–6.
Article40.Tan BF., Tan KB., Nicholls JI. Critical bending moment of implant-abutment screw joint interfaces: effect of torque levels and implant diameter. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:648–58.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of cement washout on loosening of abutment screws and vice versa in screw- and cement- retained implant-supported dental prosthesis
- The effect of a titanium socket with a zirconia abutment on screw loosening after thermocycling in an internally connected implant: a preliminary study
- Corrosion Characteristics Between Implant Fixture And Abutment Screw
- SINGLE TOOTH IMPLANT RESTORATION USING COMBINATION IMPLANT CROWN : A CASE REPORT
- A study on surface of various abutment screws