J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg.
2018 Jun;24(1):1-4. 10.13029/jkaps.2018.24.1.1.
Congenital Esophageal Stenosis in Children: From Etiology to Prognosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Surgery, Pusan National University Children's Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. spkhy02@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2415878
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13029/jkaps.2018.24.1.1
Abstract
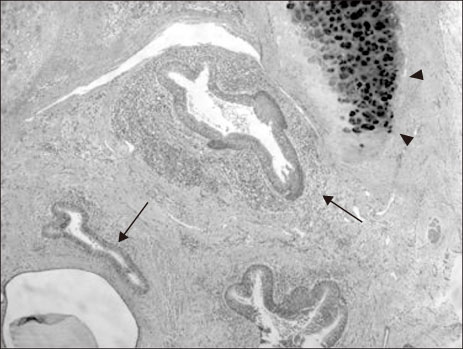
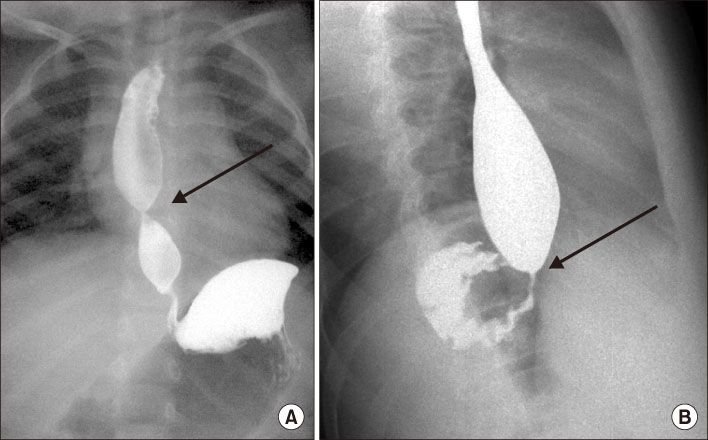
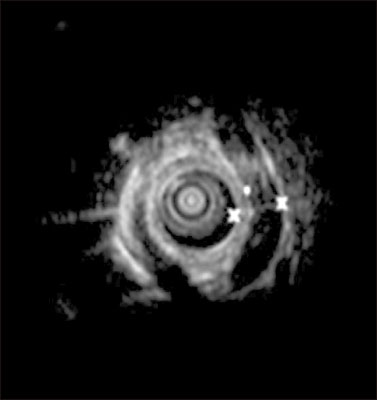
- Congenital esophageal stenosis (CES) is a rare disease that has been reported to occur once in every 25,000 to 50,000 births. According to its etiology, CES is divided into 3 subtypes, tracheobronchial remnants (TBR), fibromuscular hypertrophy (FMH) and membranous diaphragm (MD). Symptoms begin at the weaning period and the introduction of solid food around 6 months with dysphagia and vomiting. Esophagography is first screening test and endoscopic ultrasonography plays important roles to diagnose subtypes deciding therapeutic plan. TBRs were generally treated with surgical resection and end-to-end anasotomosis, whereas FMH and MD had good response rate to endoscopic or radiologic guided dilatation. This article reviews the literature on the etiology, clinical course, diagnosis and management of CES including recent opinion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nihoul-Fékété C, De Backer A, Lortat-Jacob S, Pellerin D. Congenital esophageal stenosis. Pediatr Surg Int. 1987; 2:86–92.
Article2. Ramesh JC, Ramanujam TM, Jayaram G. Congenital esophageal stenosis: report of three cases, literature review, and a proposed classification. Pediatr Surg Int. 2001; 17:188–192.
Article3. Nemolato S, De Hertogh G, Van Eyken P, Faa G, Geboes K. Oesophageal tracheobronchial remnants. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2008; 32:779–781.
Article4. Valerio D, Jones PF, Stewart AM. Congenital oesophageal stenosis. Arch Dis Child. 1977; 52:414–416.
Article5. Zhao LL, Hsieh WS, Hsu WM. Congenital esophageal stenosis owing to ectopic tracheobronchial remnants. J Pediatr Surg. 2004; 39:1183–1187.
Article6. Nishina T, Tsuchida Y, Saito S. Congenital esophageal stenosis due to tracheobronchial remnants and its associated anomalies. J Pediatr Surg. 1981; 16:190–193.
Article7. Harmon CM, Coran AG. Congenital anomalies of the esophagus. In : Coran AG, Adzick NS, Krummel TM, Laberge J, Shamberger RC, Caldmone AA, editors. Pediatric surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2012. p. 915–916.8. Nam SH, Kim DY, Kim SC, Kim IK. The diagnosis and treatment of congenital esophageal stenosis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009; 76:383–387.
Article9. Oh CH, Levine MS, Katzka DA, Rubesin SE, Pinheiro LW, Amygdalos MA, et al. Congenital esophageal stenosis in adults: clinical and radiographic findings in seven patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:1179–1182.10. Younes Z, Johnson DA. Congenital esophageal stenosis: clinical and endoscopic features in adults. Dig Dis. 1999; 17:172–177.
Article11. Kim SH, Kim HY, Jung SE, Lee SC, Park KW. Clinical study of congenital esophageal stenosis: comparison according to association of esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2017; 20:79–86.
Article12. Amae S, Nio M, Kamiyama T, Ishii T, Yoshida S, Hayashi Y, et al. Clinical characteristics and management of congenital esophageal stenosis: a report on 14 cases. J Pediatr Surg. 2003; 38:565–570.
Article13. Trappey AF 3rd, Hirose S. Esophageal duplication and congenital esophageal stenosis. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2017; 26:78–86.
Article14. Murphy SG, Yazbeck S, Russo P. Isolated congenital esophageal stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 1995; 30:1238–1241.
Article15. Yoo HJ, Kim WS, Cheon JE, Yoo SY, Park KW, Jung SE, et al. Congenital esophageal stenosis associated with esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula: clinical and radiologic features. Pediatr Radiol. 2010; 40:1353–1359.
Article16. Lee KS. Preoperative diagnosis of congenital esophageal stenosis caused by tracheobronchial remnants using miniprobe endoscopic ultrasonography in a child. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012; 15:52–56.
Article17. Takamizawa S, Tsugawa C, Mouri N, Satoh S, Kanegawa K, Nishijima E, et al. Congenital esophageal stenosis: therapeutic strategy based on etiology. J Pediatr Surg. 2002; 37:197–201.
Article18. Quiros JA, Hirose S, Patino M, Lee H. Esophageal tracheobronchial remnant, endoscopic ultrasound diagnosis, and surgical management. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013; 56:e14.
Article19. Suzuhigashi M, Kaji T, Noguchi H, Muto M, Goto M, Mukai M, et al. Current characteristics and management of congenital esophageal stenosis: 40 consecutive cases from a multicenter study in the Kyushu area of Japan. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017; 33:1035–1040.
Article20. Romeo E, Foschia F, de Angelis P, Caldaro T, Federici di Abriola G, Gambitta R, et al. Endoscopic management of congenital esophageal stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 2011; 46:838–841.
Article21. Vasudevan SA, Kerendi F, Lee H, Ricketts RR. Management of congenital esophageal stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 2002; 37:1024–1026.
Article22. Saka R, Okuyama H, Sasaki T, Nose S, Oue T. Thoracoscopic resection of congenital esophageal stenosis. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2017; 10:321–324.
Article23. Kawahara H, Oue T, Okuyama H, Kubota A, Okada A. Esophageal motor function in congenital esophageal stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 2003; 38:1716–1719.
Article24. Elhalaby EA, Elbarbary MM, Hashish AA, Kaddah SN, Hamza AF. Congenital esophageal stenosis: to dilate or to resect. Ann Pediatr Surg. 2006; 2:2–9.25. Michaud L, Coutenier F, Podevin G, Bonnard A, Becmeur F, Khen-Dunlop N, et al. Characteristics and management of congenital esophageal stenosis: findings from a multicenter study. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013; 8:186.
Article26. Terui K, Saito T, Mitsunaga T, Nakata M, Yoshida H. Endoscopic management for congenital esophageal stenosis: a systematic review. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 7:183–191.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Congenital Esophageal Stenosis Presented with Esophageal Foreign Body
- Esophageal stenosis due to tracheobronchial remnants: a case report
- Balloon dilatation of the esophageal strictures in infants and children
- Preoperative Diagnosis of Congenital Esophageal Stenosis Caused by Tracheobronchial Remnants Using Miniprobe Endoscopic Ultrasonography in a Child
- Congenital Esophageal Stenosis due to Tracheobronchial Remnants: A case report