Korean Circ J.
2018 Jul;48(7):552-564. 10.4070/kcj.2018.0167.
White-Coat Hypertension: the Neglected Subgroup in Hypertension
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Science, Clinica Medica, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milano, Italy. guido.grassi@unimib.it
- 2Istituto Auxologico Italiano IRCCS, Milano, Italy.
- 3Department of Cardiology, Charité-University-Medicine Campus Virchow Klinikum, Berlin, Germany.
- 4IRCCS Multimedica, Sesto San Giovanni, Milan, Italy.
- KMID: 2414891
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2018.0167
Abstract
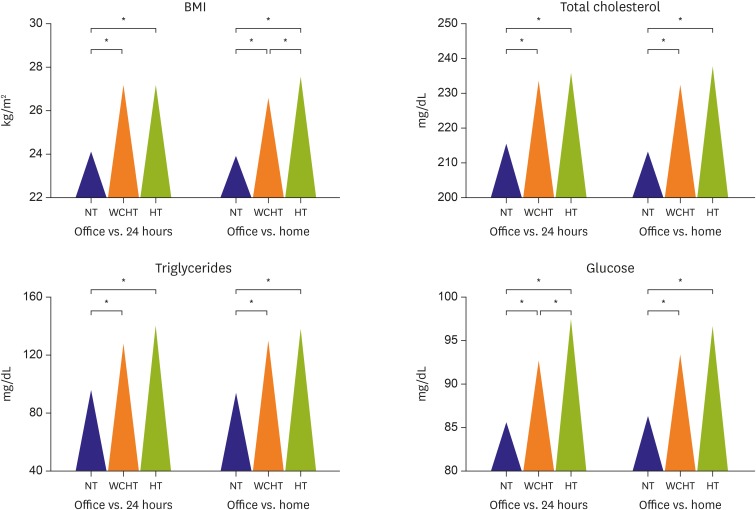
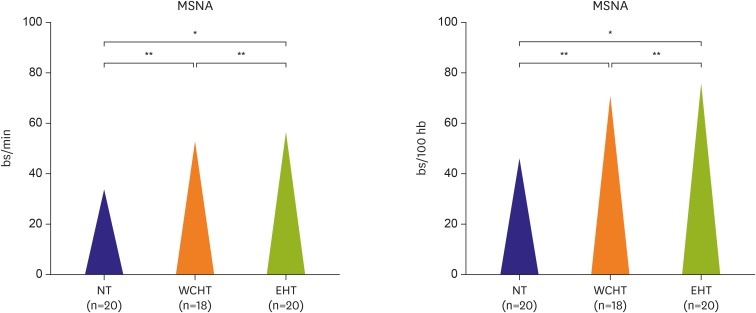
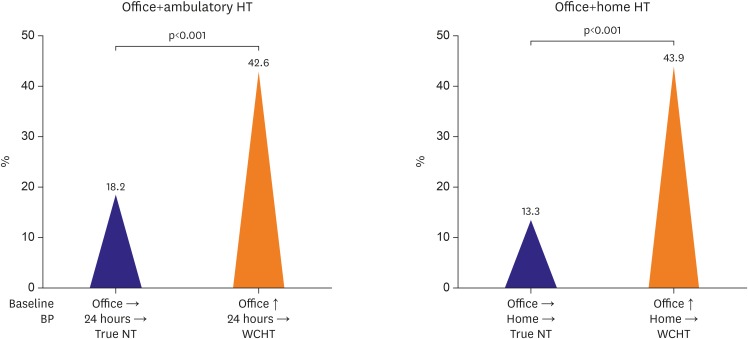
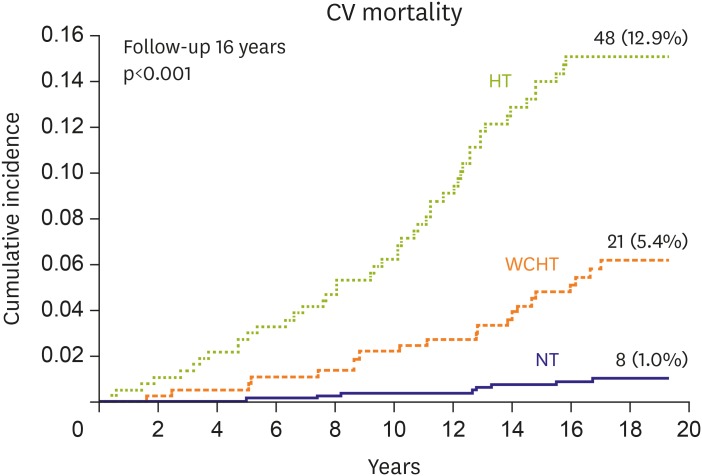
- The clinical prognostic importance of white coat hypertension (WCH), that is, the clinical condition characterized by an increase of office but a normal ambulatory or home blood pressure (BP) is since a long time matter of considerable debate. WCH accounts for a consistent portion of hypertensive patients (up to 30-40%), particularly when hypertension is mild or age is more advanced. Although scanty and inconsistent information is available on the response of office and out-office BP to antihypertensive treatment and the cardiovascular (CV) protection provided by treatment, an increasing body of evidence focusing on the association of WCH with CV risk factors, subclinical cardiac and extra-cardiac organ damage and, more importantly, with CV events indicates that the risk entailed by this condition is intermediate between true normotension and sustained hypertension. This review will address a number of issues concerning WCH with particular attention to prevalence and clinical correlates, relation with subclinical target organ damage and CV morbidity/mortality, therapeutic perspectives. Several topics covered in this review are based on data acquired over the past 20 years by the Pressioni Arteriose Monitorate E Loro Associazioni (PAMELA) study, a longitudinal survey performed by our group on the general population living in the surroundings of Milan area in the north part of Italy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013; 31:1281–1357. PMID: 23817082.2. Hermida RC, Smolensky MH, Ayala DE, Portaluppi F. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) as the reference standard for diagnosis of hypertension and assessment of vascular risk in adults. Chronobiol Int. 2015; 32:1329–1342. PMID: 26587588.3. Pickering TG, James GD, Boddie C, Harshfield GA, Blank S, Laragh JH. How common is white coat hypertension? JAMA. 1988; 259:225–228. PMID: 3336140.4. Mancia G, Sega R, Bravi C, et al. Ambulatory blood pressure normality: results from the PAMELA study. J Hypertens. 1995; 13:1377–1390. PMID: 8866899.5. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2018; 71:e13–e115. PMID: 29133356.6. O'Brien E, Parati G, Stergiou G, et al. European Society of Hypertension position paper on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. J Hypertens. 2013; 31:1731–1768. PMID: 24029863.7. Sega R, Trocino G, Lanzarotti A, et al. Alterations of cardiac structure in patients with isolated office, ambulatory, or home hypertension: data from the general population (Pressione Arteriose Monitorate E Loro Associazioni [PAMELA] study). Circulation. 2001; 104:1385–1392. PMID: 11560854.8. Afsar B. Comparison of demographic, clinical, and laboratory parameters between patients with sustained normotension, white coat hypertension, masked hypertension, and sustained hypertension. J Cardiol. 2013; 61:222–226. PMID: 23294898.9. Mulè G, Nardi E, Cottone S, et al. Metabolic syndrome in subjects with white-coat hypertension: impact on left ventricular structure and function. J Hum Hypertens. 2007; 21:854–860. PMID: 17541385.10. Tocci G, Presta V, Figliuzzi I, et al. Prevalence and clinical outcomes of white-coat and masked hypertension: analysis of a large ambulatory blood pressure database. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018; 20:297–305. PMID: 29370477.11. de la Sierra A, Vinyoles E, Banegas JR, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of white-coat hypertension based on different definition criteria in untreated and treated patients. J Hypertens. 2017; 35:2388–2394. PMID: 28723880.12. Vyssoulis G, Karpanou E, Adamopoulos D, et al. Nocturnal blood pressure fall and metabolic syndrome score in patients with white coat hypertension. Blood Press Monit. 2008; 13:251–256. PMID: 18799949.13. Mancia G, Bombelli M, Facchetti R, et al. Increased long-term risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus in white-coat and masked hypertension. J Hypertens. 2009; 27:1672–1678. PMID: 19417688.14. Grassi G, Seravalle G, Trevano FQ, et al. Neurogenic abnormalities in masked hypertension. Hypertension. 2007; 50:537–542. PMID: 17620522.15. Grassi G, Mark A, Esler M. The sympathetic nervous system alterations in human hypertension. Circ Res. 2015; 116:976–990. PMID: 25767284.16. Cuspidi C, Facchetti R, Bombelli M, et al. Risk of new onset metabolic syndrome associated with white coat and masked hypertension: data from a general population. J Hypertens. 2018.17. Sivén SS, Niiranen TJ, Kantola IM, Jula AM. White-coat and masked hypertension as risk factors for progression to sustained hypertension: the Finn-Home study. J Hypertens. 2016; 34:54–60. PMID: 26630213.18. Mancia G, Bombelli M, Facchetti R, et al. Long-term risk of sustained hypertension in white-coat or masked hypertension. Hypertension. 2009; 54:226–232. PMID: 19564548.19. Palatini P, Dorigatti F, Roman E, et al. White-coat hypertension: a selection bias? Harvest Study Investigators. Hypertension and Ambulatory Recording Venetia Study. J Hypertens. 1998; 16:977–984. PMID: 9794738.20. Cuspidi C, Meani S, Sala C, et al. How reliable is isolated clinical hypertension defined by a single 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring? J Hypertens. 2007; 25:315–320. PMID: 17211238.21. Mancia G, Grassi G. The heterogeneous nature of white-coat hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016; 68:2044–2046. PMID: 27810042.22. Bombelli M, Facchetti R, Carugo S, et al. Left ventricular hypertrophy increases cardiovascular risk independently of in-office and out-of-office blood pressure values. J Hypertens. 2009; 27:2458–2464. PMID: 19654559.23. Høegholm A, Kristensen KS, Bang LE, Nielsen JW, Nielsen WB, Madsen NH. Left ventricular mass and geometry in patients with established hypertension and white coat hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1993; 6:282–286. PMID: 8507447.24. Cuspidi C, Rescaldani M, Tadic M, Sala C, Grassi G, Mancia G. White-coat hypertension, as defined by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, and subclinical cardiac organ damage: a meta-analysis. J Hypertens. 2015; 33:24–32. PMID: 25380162.25. Manios E, Michas F, Stamatelopoulos K, et al. White-coat isolated systolic hypertension is a risk factor for carotid atherosclerosis. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016; 18:1095–1102. PMID: 27480205.26. Mancusi C, Gerdts E, Losi MA, et al. Differential effect of obesity on prevalence of cardiac and carotid target organ damage in hypertension (the Campania Salute Network). Int J Cardiol. 2017; 244:260–264. PMID: 28629621.27. Cuspidi C, Sala C, Tadic M, Rescaldani M, Grassi G, Mancia G. Is white-coat hypertension a risk factor for carotid atherosclerosis? A review and meta-analysis. Blood Press Monit. 2015; 20:57–63. PMID: 25405819.28. Mancia G, Facchetti R, Bombelli M, Grassi G, Sega R. Long-term risk of mortality associated with selective and combined elevation in office, home, and ambulatory blood pressure. Hypertension. 2006; 47:846–853. PMID: 16567588.29. Mancia G, Bombelli M, Brambilla G, et al. Long-term prognostic value of white coat hypertension: an insight from diagnostic use of both ambulatory and home blood pressure measurements. Hypertension. 2013; 62:168–174. PMID: 23716584.30. Mancia G, Facchetti R, Grassi G, Bombelli M. Adverse prognostic value of persistent office blood pressure elevation in white coat hypertension. Hypertension. 2015; 66:437–444. PMID: 26056342.31. Pierdomenico SD, Cuccurullo F. Prognostic value of white-coat and masked hypertension diagnosed by ambulatory monitoring in initially untreated subjects: an updated meta analysis. Am J Hypertens. 2011; 24:52–58. PMID: 20847724.32. Franklin SS, Thijs L, Hansen TW, et al. Significance of white-coat hypertension in older persons with isolated systolic hypertension: a meta-analysis using the International Database on Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Relation to Cardiovascular Outcomes population. Hypertension. 2012; 59:564–571. PMID: 22252396.33. Tientcheu D, Ayers C, Das SR, et al. Target organ complications and cardiovascular events associated with masked hypertension and white-coat hypertension: analysis from the Dallas Heart Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:2159–2169. PMID: 26564592.34. Briasoulis A, Androulakis E, Palla M, Papageorgiou N, Tousoulis D. White-coat hypertension and cardiovascular events: a meta-analysis. J Hypertens. 2016; 34:593–599. PMID: 26734955.35. Banegas JR, Ruilope LM, de la Sierra A, et al. Relationship between clinic and ambulatory blood-pressure measurements and mortality. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:1509–1520. PMID: 29669232.36. Høegholm A, Wiinberg N, Kristensen KS. The effect of antihypertensive treatment with dihydropyridine calcium antagonists on white-coat hypertension. Blood Press Monit. 1996; 1:375–380. PMID: 10226262.37. Bulpitt CJ, Beckett N, Peters R, et al. Does white coat hypertension require treatment over age 80?: Results of the hypertension in the very elderly trial ambulatory blood pressure side project. Hypertension. 2013; 61:89–94. PMID: 23172934.38. Fagard RH, Staessen JA, Thijs L, et al. Response to antihypertensive therapy in older patients with sustained and nonsustained systolic hypertension. Circulation. 2000; 102:1139–1144. PMID: 10973843.39. Mancia G, Facchetti R, Parati G, Zanchetti A. Effect of long-term antihypertensive treatment on white-coat hypertension. Hypertension. 2014; 64:1388–1398. PMID: 25245386.40. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (UK). Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management. Clinical guideline [Internet]. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence;2011. cited 2011 Aug. Available from: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG127.41. Leung AA, Daskalopoulou SS, Dasgupta K, et al. Hypertension Canada's 2017 guidelines for diagnosis, risk assessment, prevention, and treatment of hypertension in adults. Can J Cardiol. 2017; 33:557–576. PMID: 28449828.42. Mancia G, Verdecchia P. Clinical value of ambulatory blood pressure: evidence and limits. Circ Res. 2015; 116:1034–1045. PMID: 25767288.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of White-coat Hypertension on Heart Rate Recovery and Blood Pressure Response during Exercise Test
- The Comparison of White Coat Effect in Elderly White Coat Hypertensive Patients with Youngers
- Influences of White-Coat Hypertension and White-Coat Effect on the Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function
- Management of Hypertension in Geriatrics
- Clinical Manifestation of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Children and Adolescent with Hypertension