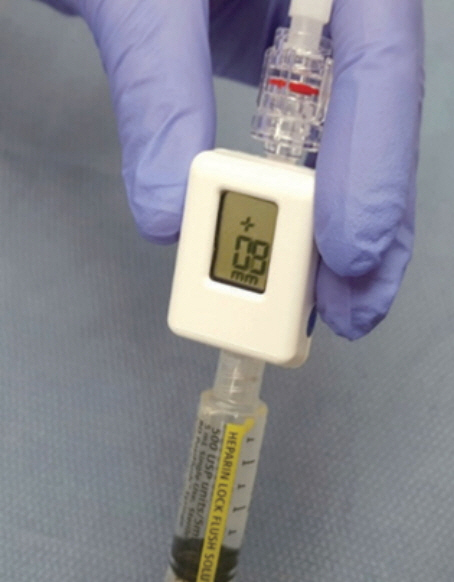
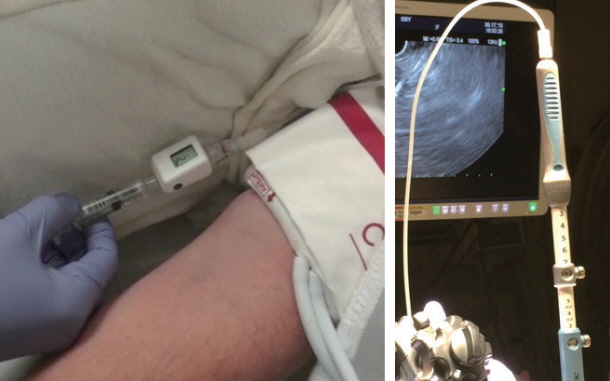
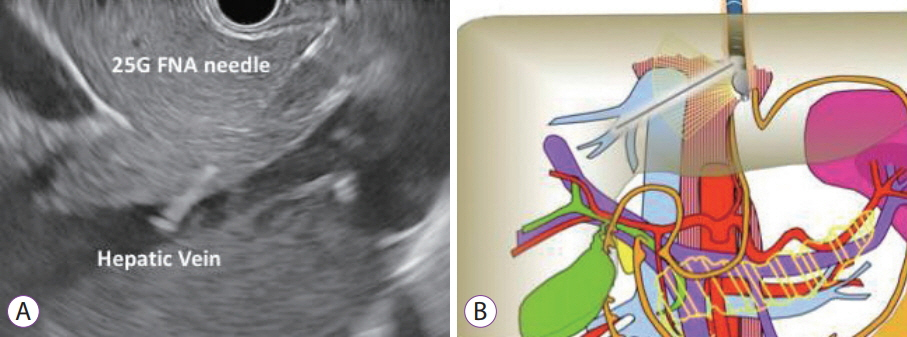
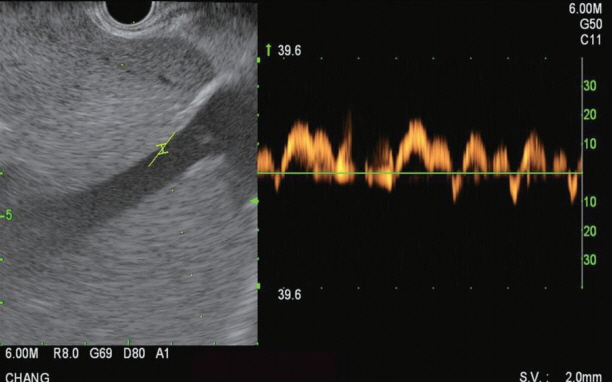
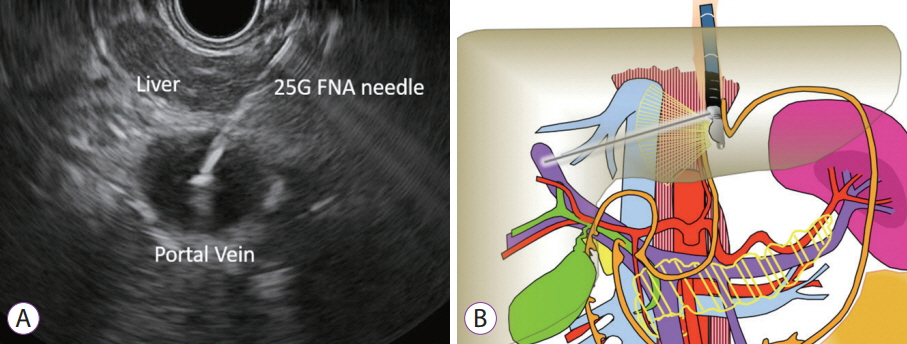
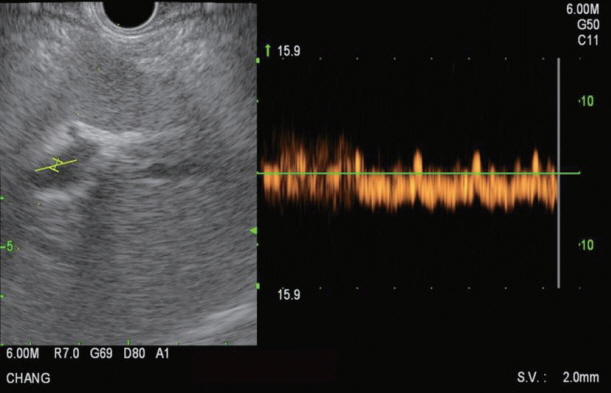
Clin Endosc.
2018 May;51(3):222-228. 10.5946/ce.2018.079.
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Portal Pressure Measurement and Interventions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, H. H. Chao Comprehensive Digestive Disease Center, University of California, Irvine Medical Center, Orange, CA, USA. jsamaras@uci.edu
- KMID: 2414862
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.079
Abstract
- A growing number of studies have explored endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided vascular catheterization. Potential clinical applications of EUS-guided portal venous access include angiography, measurement of the portosystemic pressure gradient, EUS-guided transhepatic intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation and portal vein sampling for the evaluation in gastrointestinal cancer. The following article reviews the different devices and techniques employed in these applications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lai L, Poneros J, Santilli J, Brugge W. EUS-guided portal vein catheterization and pressure measurement in an animal model: a pilot study of feasibility. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:280–283.
Article2. Magno P, Ko CW, Buscaglia JM, et al. EUS-guided angiography: a novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the vascular system. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:587–591.
Article3. Giday SA, Ko CW, Clarke JO, et al. EUS-guided portal vein carbon dioxide angiography: a pilot study in a porcine model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:814–819.
Article4. Giday SA, Clarke JO, Buscaglia JM, et al. EUS-guided portal vein catheterization: a promising novel approach for portal angiography and portal vein pressure measurements. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:338–342.
Article5. Brugge WR. EUS is an important new tool for accessing the portal vein. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:343–344.
Article6. Hawkins IF, Caridi JG. Carbon dioxide (CO2) digital subtraction angiography: 26-year experience at the University of Florida. Eur Radiol. 1998; 8:391–402.7. Liss P, Eklöf H, Hellberg O, et al. Renal effects of CO2 and iodinated contrast media in patients undergoing renovascular intervention: a prospective, randomized study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:57–65.8. Bosch J, Garcia-Pagán JC, Berzigotti A, Abraldes JG. Measurement of portal pressure and its role in the management of chronic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2006; 26:348–362.
Article9. Groszmann RJ, Bosch J, Grace ND, et al. Hemodynamic events in a prospective randomized trial of propranolol versus placebo in the prevention of a first variceal hemorrhage. Gastroenterology. 1990; 99:1401–1407.
Article10. Albillos A, Bañares R, González M, et al. Value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient to monitor drug therapy for portal hypertension: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1116–1126.
Article11. D’Amico G, Garcia-Pagan JC, Luca A, Bosch J. Hepatic vein pressure gradient reduction and prevention of variceal bleeding in cirrhosis: a systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:1611–1624.
Article12. Perelló A, Escorsell A, Bru C, et al. Wedged hepatic venous pressure adequately reflects portal pressure in hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1999; 30:1393–1397.
Article13. Tsushima Y, Koizumi J, Yokoyama H, Takeda A, Kusano S. Evaluation of portal pressure by splenic perfusion measurement using dynamic CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 170:153–155.
Article14. Suk KT. Hepatic venous pressure gradient: clinical use in chronic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2014; 20:6–14.
Article15. Thalheimer U, Bellis L, Puoti C, Burroughs AK. Should we routinely measure portal pressure in patients with cirrhosis, using hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) as a guide for prophylaxis and therapy of bleeding and rebleeding? No. Eur J Intern Med. 2011; 22:5–7.
Article16. Sarin SK, Khanna R. Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Clin Liver Dis. 2014; 18:451–476.
Article17. Pomier-Layrargues G, Kusielewicz D, Willems B, et al. Presinusoidal portal hypertension in non-alcoholic cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1985; 5:415–418.
Article18. Buscaglia JM, Shin EJ, Clarke JO, et al. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, but not esophagogastroduodenoscopy or colonoscopy, significantly increases portal venous pressure: direct portal pressure measurements through endoscopic ultrasound-guided cannulation. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:670–674.
Article19. Schulman AR, Thompson CC, Ryou M. EUS-guided portal pressure measurement using a digital pressure wire with real-time remote display: a novel, minimally invasive technique for direct measurement in an animal model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:817–820.20. Schulman AR, Thompson CC, Ryou M. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided direct portal pressure measurement using a digital pressure wire with real-time remote display: a survival study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2017; 27:1051–1054.
Article21. Huang JY, Samarasena JB, Tsujino T, Chang KJ. EUS-guided portal pressure gradient measurement with a novel 25-gauge needle device versus standard transjugular approach: a comparison animal study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 84:358–362.22. Fujii-Lau LL, Leise MD, Kamath PS, Gleeson FC, Levy MJ. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided portal-systemic pressure gradient measurement. Endoscopy. 2014; 46 Suppl 1 UCTN:E654–E656.
Article23. Huang JY, Samarasena JB, Tsujino T, et al. EUS-guided portal pressure gradient measurement with a simple novel device: a human pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:996–1001.
Article24. Buscaglia JM, Dray X, Shin EJ, et al. A new alternative for a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: EUS-guided creation of an intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:941–947.
Article25. Binmoeller KF, Shah JN. EUS-guided transgastric intrahepatic portosystemic shunt using the Axios stent. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73(Suppl 4):AB167.26. Schulman AR, Ryou M, Aihara H, et al. EUS-guided intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with direct portal pressure measurements: a novel alternative to transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:243–247.
Article27. Esmaeilsabzali H, Beischlag TV, Cox ME, Parameswaran AM, Park EJ. Detection and isolation of circulating tumor cells: principles and methods. Biotechnol Adv. 2013; 31:1063–1084.
Article28. Mizuno N, Kato Y, Izumi Y, Irimura T, Sugiyama Y. Importance of hepatic first-pass removal in metastasis of colon carcinoma cells. J Hepatol. 1998; 28:865–877.
Article29. Massague J, Obenauf AC. Metastatic colonization by circulating tumour cells. Nature. 2016; 529:298–306.
Article30. Zhou Z, Qutaish M, Han Z, et al. MRI detection of breast cancer micrometastases with a fibronectin-targeting contrast agent. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:7984.
Article31. Funaki B. Islet cell transplantation. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2006; 23:295–297.
Article32. Catenacci DV, Chapman CG, Xu P, et al. Acquisition of portal venous circulating tumor cells from patients with pancreaticobiliary cancers by endoscopic ultrasound. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149:1794–1803. e4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided vascular intervention for portal hypertension
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided vascular interventions: An overview of current and emerging techniques
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Procedures: A Review
- Recent development of endoscopic ultrasound-guided biliary drainage
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Therapy: The Present and the Future