Investig Clin Urol.
2017 Nov;58(6):447-452. 10.4111/icu.2017.58.6.447.
Thermo-expandable prostatic stents for bladder outlet obstruction in the frail and elderly population: An underutilized procedure?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Ballarat Health Services, Ballarat, Australia. drkapilsethi@gmail.com
- 2St. John of God Hospital Ballarat, Ballarat, Australia.
- KMID: 2414773
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2017.58.6.447
Abstract
- PURPOSE
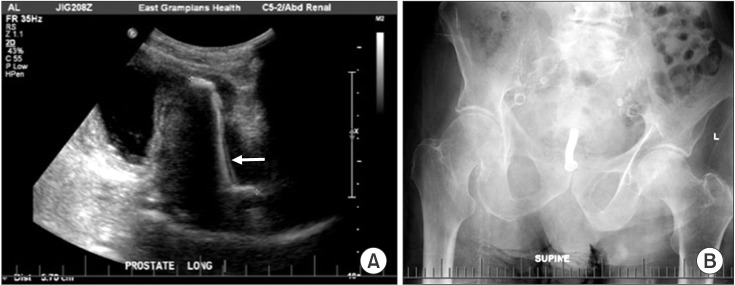
To report our outcomes with the use of a thermo-expandable metallic intraprostatic stent (Memokath) for patients with bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) secondary to prostatic obstruction, and to assess it is a feasible option for many frail and elderly men unsuitable for surgery.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed patients who underwent insertion of a Memokath stent for BOO over 17 years (January 1999 to December 2015) at one regional center over a long follow-up period (median, 7 years). Patients were selected if they had obstructive urinary symptoms or urinary retention with an indwelling catheter in situ, and were ineligible for transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) under general or spinal anesthesia. Primary outcomes assessed were the improvement in urinary symptoms and voiding parameters, as well as the ability to void spontaneously if catheterized, along with complications.
RESULTS
One hundred forty-four patients who presented with BOO or urinary retention had a Memokath stent inserted. Ninety patients (62.5%) had a successful stent insertion with a significant difference between the median preoperative (550 mL) and postoperative residual volume (80 mL, p<0.0001). Nearly two-thirds of men (64%) returned to unassisted voiding with no increased risk of complications over time. Fifty-four patients (37.5%) experienced stent failure. Main complications requiring stent removal or repositioning were migration, occlusion, refractory urinary retention and irritative voiding symptoms.
CONCLUSIONS
In elderly and frail men with BOO deemed unsuitable to undergo TURP, prostatic stent is a safe and practical alternative to long-term catheterization.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984; 132:474–479. PMID: 6206240.
Article2. Choi SY, Kim TH, Myung SC, Moon YT, Kim KD, Kim YS, et al. Impact of changing trends in medical therapy on surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia over two decades. Korean J Urol. 2012; 53:23–28. PMID: 22323970.
Article3. Vela-Navarrete R, Gonzalez-Enguita C, Garcia-Cardoso JV, Manzarbeitia F, Sarasa-Corral JL, Granizo JJ. The impact of medical therapy on surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a study comparing changes in a decade (1992-2002). BJU Int. 2005; 96:1045–1048. PMID: 16225526.
Article4. Glynn RJ, Campion EW, Bouchard GR, Silbert JE. The development of benign prostatic hyperplasia among volunteers in the Normative Aging Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1985; 121:78–90. PMID: 3964994.5. Lee TH, Marcantonio ER, Mangione CM, Thomas EJ, Polanczyk CA, Cook EF, et al. Derivation and prospective validation of a simple index for prediction of cardiac risk of major noncardiac surgery. Circulation. 1999; 100:1043–1049. PMID: 10477528.
Article6. Brierly RD, Mostafid AH, Kontothanassis D, Thomas PJ, Fletcher MS, Harrison NW. Is transurethral resection of the prostate safe and effective in the over 80-year-old? Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2001; 83:50–53. PMID: 11212452.7. Kohler-Ockmore J, Feneley RC. Long-term catheterization of the bladder: prevalence and morbidity. Br J Urol. 1996; 77:347–351. PMID: 8814836.8. National Clinical Guideline Centre (UK). Chapter 10, Long term urinary catheters. Infection: prevention and control of healthcare-associated infections in primary and community care: partial update of NICE clinical guideline 2. NICE Clinical Guidelines, No. 139. London: Royal College of Physicians (UK);2012.9. Armitage JN, Rashidian A, Cathcart PJ, Emberton M, van der Meulen JH. The thermo-expandable metallic stent for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review. BJU Int. 2006; 98:806–810. PMID: 16879446.
Article10. Papatsoris AG, Junaid I, Zachou A, Kachrilas S, Zaman F, Masood J, et al. New developments in the use of prostatic stents. Open Access J Urol. 2011; 3:63–68. PMID: 24198637.
Article11. Poulsen AL, Schou J, Ovesen H, Nordling J. Memokath: a second generation of intraprostatic spirals. Br J Urol. 1993; 72:331–334. PMID: 7693295.12. Minagawa T, Murata Y, Seki S. Placement of a shape-memory alloy intraurethral catheter (Memokath) using transrectal ultrasonography and fluoroscopy. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 2009; 100:508–512. PMID: 19348192.
Article13. Kimata R, Nemoto K, Tomita Y, Takahashi R, Hamasaki T, Kondo Y. Efficacy of a thermoexpandable metallic prostate stent (Memokath) in elderly patients with urethral obstruction requiring long-term management with urethral Foley catheters. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015; 15:553–558. PMID: 24852087.
Article14. Perry MJ, Roodhouse AJ, Gidlow AB, Spicer TG, Ellis BW. Thermo-expandable intraprostatic stents in bladder outlet obstruction: an 8-year study. BJU Int. 2002; 90:216–223. PMID: 12133055.
Article15. Lee G, Marathe S, Sabbagh S, Crisp J. Thermo-expandable intra-prostatic stent in the treatment of acute urinary retention in elderly patients with significant co-morbidities. Int Urol Nephrol. 2005; 37:501–504. PMID: 16307329.
Article16. Na HK, Song HY, Kim JH, Nam DH, Park JH, Jeong IG, et al. Evaluation of the anti-migration effect of barbed prostatic stents: in vitro study in urethra-mimicking bovine pericardium phantoms. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013; 36:229–236. PMID: 22829302.
Article17. Woo CW, Song HY, Yoon CJ, Kim TH, Kim EY, Kim JH, et al. Is a flared stent effective for decreasing stent migration in canine prostatic urethra? Acta Radiol. 2008; 49:285–290. PMID: 18365816.
Article18. Gould CV, Umscheid CA, Agarwal RK, Kuntz G, Pegues DA, Brennan J, et al. Guideline for prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Atlanta (GA): Centres for Disease Control and Prevention;2009.19. Booth CM, Chaudry AA, Lyth DR. Alternative prostate treatments: stent or catheter for the frail. J Manag Care. 1997; 1:24–26.
Article20. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2012. Health expenditure Australia 2010-11. Health and welfare expenditure series No. 47. Cat. No. HWE 56. Canberra (Australia): Australian Institute of Health and Welfare;2012.21. Rashid P, Gianduzzo TR. Urology technical and non-technical skills development: the emerging role of simulation. BJU Int. 2016; 117(Suppl 4):9–16.
Article22. Jumper C, Snyder P, Yap RL. Rapid ambulatory pathway laser prostatectomy is safe: results within the global period. BJU Int. 2012; 110:1190–1193. PMID: 22372831.
Article23. Roehrborn CG, Gange SN, Shore ND, Giddens JL, Bolton DM, Cowan BE, et al. The prostatic urethral lift for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with prostate enlargement due to benign prostatic hyperplasia: the L.I.F.T. Study. J Urol. 2013; 190:2161–2167. PMID: 23764081.24. Rukstalis D, Rashid P, Bogache WK, Tutrone RF, Barkin J, Chin PT, et al. 24-month durability after crossover to the prostatic urethral lift from randomised, blinded sham. BJU Int. 2016; 118(Suppl 3):14–22.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Self-Expandable Metallic Stent Placement in the Palliative Treatment of Malignant Obstruction of Gastric Outlet and Duodenum
- Removal of Migrated Thermo-Expandable Ureteral Stent (Memokath): Open Procedure 1 Case
- Effect of Bladder Outlet Obstruction on Blood Flow and Tissue Collagen in Rat Bladder
- Malignant Gastric Outlet Obstructions: Treatment with Self-Expandable Metallic Stents
- Unusual Bladder Stones -Report of Three Cases-