Blood Res.
2018 Mar;53(1):74-78. 10.5045/br.2018.53.1.74.
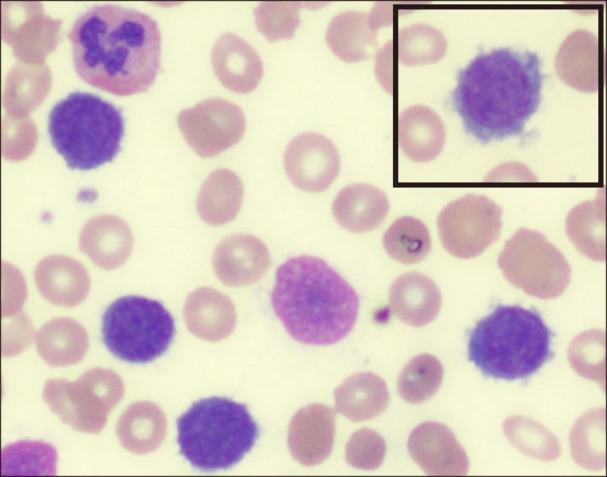
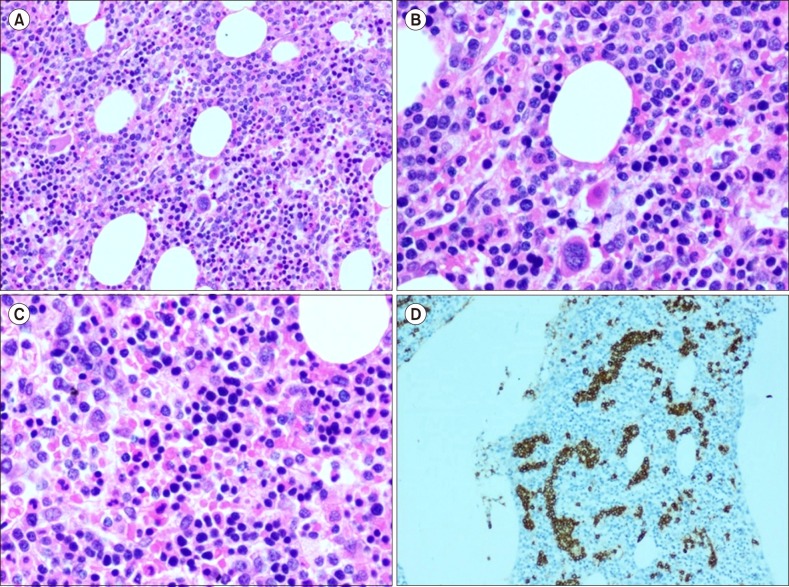
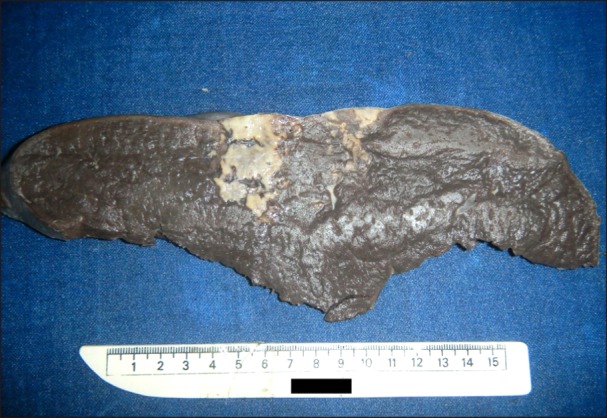
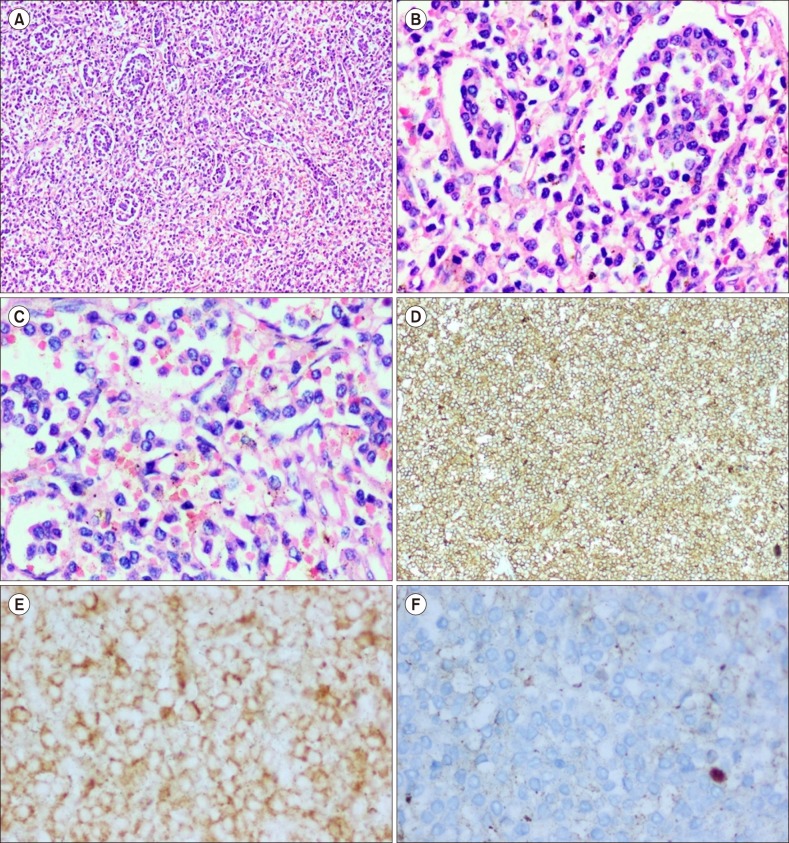
A rare case of splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma (SDRPL): a review of the literature on primary splenic lymphoma with hairy cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore, India. medicovig@gmail.com
- 2Department of Clinical Hematology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore, India.
- KMID: 2414368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2018.53.1.74
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Piris MA, Foucar KM, Mollejo M, Campo E, Falini B. Splenic lymphoma/leukemia, unclassifiable. In : Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, editors. WHO classification of tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press;2008. p. 191–193.2. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016; 127:2375–2390. PMID: 26980727.
Article3. Ponzoni M, Kanellis G, Pouliou E, et al. Bone marrow histopathology in the diagnostic evaluation of splenic marginal-zone and splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma: a reliable substitute for spleen histopathology? Am J Surg Pathol. 2012; 36:1609–1618. PMID: 23073320.4. Behdad A, Bailey NG. Diagnosis of splenic B-cell lymphomas in the bone marrow: a review of histopathologic, immunophenotypic, and genetic findings. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014; 138:1295–1301. PMID: 25268192.
Article5. Cessna MH, Hartung L, Tripp S, Perkins SL, Bahler DW. Hairy cell leukemia variant: fact or fiction. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005; 123:132–138. PMID: 15762289.6. Dong HY, Weisberger J, Liu Z, Tugulea S. Immunophenotypic analysis of CD103+ B-lymphoproliferative disorders: hairy cell leukemia and its mimics. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009; 131:586–595. PMID: 19289595.7. Traverse-Glehen A, Baseggio L, Bauchu EC, et al. Splenic red pulp lymphoma with numerous basophilic villous lymphocytes: a distinct clinicopathologic and molecular entity? Blood. 2008; 111:2253–2260. PMID: 18042795.
Article8. Kanellis G, Mollejo M, Montes-Moreno S, et al. Splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma: revision of a series of cases reveals characteristic clinico-pathological features. Haematologica. 2010; 95:1122–1129. PMID: 20220064.
Article9. Gujral S, Lad P, Subramanian PG, et al. Histopathological audit of splenectomies received at a cancer hospital. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2011; 54:487–496. PMID: 21934208.
Article10. Traverse-Glehen A, Baseggio L, Salles G, Coiffier B, Felman P, Berger F. Splenic diffuse red pulp small-B cell lymphoma: toward the emergence of a new lymphoma entity. Discov Med. 2012; 13:253–265. PMID: 22541613.11. Tiacci E, Trifonov V, Schiavoni G, et al. BRAF mutations in hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:2305–2315. PMID: 21663470.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Splenic Lymphoma with Splenic Hilar Lymphadenopathy
- Efficacy of Annexin A1 Immunostaining in Bone Marrow for the Diagnosis of Hairy Cell Leukemia
- Three Cases of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Presenting as Primary Splenic Lymphoma
- A case of primary splenic lymphoma presenting as a splenic abscess
- Primary Lymphoma of the Spleen: A case report