J Vet Sci.
2016 Jun;17(2):189-197. 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.2.189.
Effects of induced endometritis on uterine blood flow in cows as evaluated by transrectal Doppler sonography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Clinic for Cattle, University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover, 30173 Hannover, Germany.
- 2Department of Veterinary Medical Sciences, University of Bologna, 40064 Ozzano Emilia, Italy. barbara.merlo@unibo.it
- 3Clinic of Reproductive Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Zurich, CH-8057 Zürich, Switzerland.
- 4Institute of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Leipzig, 04103 Leipzig, Germany.
- KMID: 2413168
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2016.17.2.189
Abstract
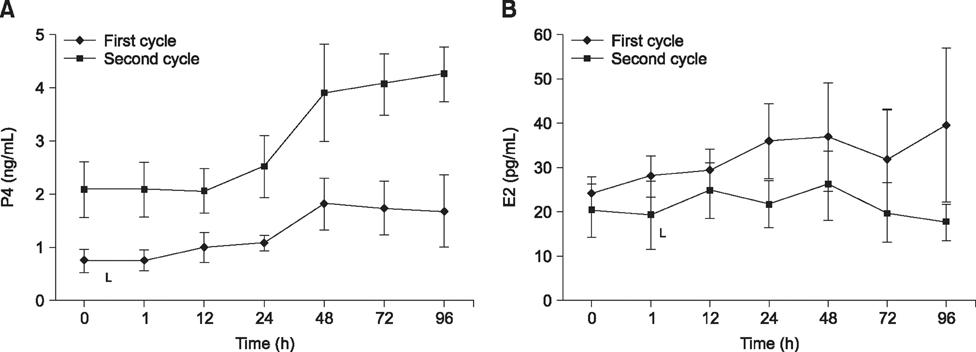
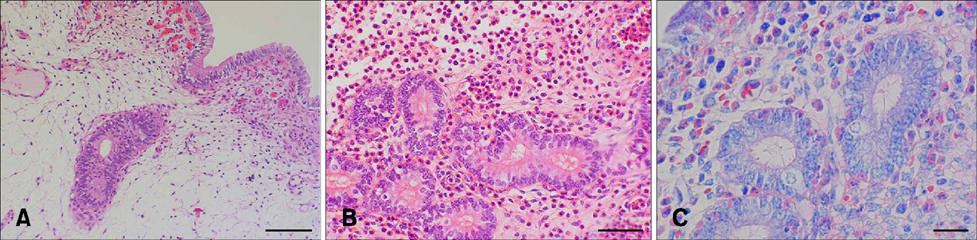
- This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of induced endometritis on uterine blood flow in cows. Transrectal Doppler sonography was performed on uterine arteries of six cyclic cows before and for 4 days after inducing acute endometritis by intrauterine infusion of 720 mg of policresulen, and for 4 days of the following estrous cycle. Time-averaged maximum velocity (TAMV) increased (p < 0.001) and pulsatility index (PI) decreased (p < 0.0001) within 1 h of policresulen administration, and did not change (p > 0.05) in the next 4 days of the same cycle. TAMV and PI values in the subsequent cycle did not differ (p > 0.05) from the values measured before infusion and showed no changes (p > 0.05) within the cycle. Blood flow parameters were not related (p > 0.05) to plasma concentrations of progesterone and estrogen. All cows showed an acute endometritis determined by histopathological findings of biopsy samples taken 1 day after infusion and fibrotic endometrial alterations detected in the subsequent cycle. No relationships were observed between fibrotic changes of the endometrium and uterine blood flow during either cycle. In conclusion, acute inflammation is accompanied by a rise in uterine blood flow, but fibrotic alterations do not seem to be related to Doppler sonographic findings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alataş C, Aksoy E, Akarsu C, Yakin K, Bahçeci M. Hemodynamic assessment in pelvic inflammatory disease by transvaginal color Doppler ultrasonography. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1996; 70:75–78.
Article2. Andresen P, Pohlenz J. Experimental studies on the treatment of bovine sterility with the acid derivative Lotagen. Tierarztl Umsch. 1971; 26:479–480.3. Bollwein H, Baumgartner U, Stolla R. Transrectal Doppler sonography of uterine blood flow in cows during pregnancy. Theriogenology. 2002; 57:2053–2061.
Article4. Bollwein H, Maierl J, Mayer R, Stolla R. Transrectal color Doppler sonography of the A. uterina in cyclic mares. Theriogenology. 1998; 49:1483–1488.
Article5. Bollwein H, Meyer HHD, Maierl J, Weber F, Baumgartner U, Stolla R. Transrectal Doppler sonography of uterine blood flow in cows during the estrous cycle. Theriogenology. 2000; 53:1541–1552.
Article6. Bollwein H, Sowade C, Stolla R. The effect of semen extender, seminal plasma and raw semen on uterine and ovarian blood flow in mares. Theriogenology. 2003; 60:607–616.
Article7. Brander GC, Pugh DM, Bywater RJ, Jenkins WL. Veterinary Applied Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. London: Bailliere Tindall;1991.8. Ford SP. Control of uterine and ovarian blood flow throughout the estrous cycle and pregnancy in ewes, sows, and cows. J Anim Sci. 1982; 55:Suppl 2. 32–42.9. Ford SP. Factors controlling uterine blood flow during estrus and early pregnancy. In : Rosenfield CR, editor. The Uterine Circulation. Ithaca: Perinatology Press;1989.10. Ford SP, Chenault JR, Echternkamp SE. Uterine blood flow of cows during the oestrous cycle and early pregnancy: effect of the conceptus on the uterine blood supply. J Reprod Fertil. 1979; 56:53–62.
Article11. Foster RA. Female reproductive system. In : McGavin MD, Zachary JF, editors. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease. 4th ed. Mosby Elsevier;2007. p. 1263–1316.12. Frei A. Experience with Lotagen in the veterinary practice. Tierarztl Umsch. 1954; 9:343–346.13. Frei A. The endometritis treatment of cattle with Lotagen. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1951; 93:553–564.14. Gilbert RO, Schwark WS. Pharmacologic considerations in the management of peripartum conditions in the cow. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1992; 8:29–56.
Article15. Heppelmann M, Brömmling A, Ulbrich SE, Weinert M, Piechotta M, Wrenzycki C, Merbach S, Schoon HA, Hoedemaker M, Bollwein H. Effect of suppression of postpartum ovulation on endometrial inflammation in dairy cows. Theriogenology. 2015; 84:155–162.
Article16. Heppelmann M, Krüger L, Leidl S, Bollwein H. Transrectal Doppler sonography of uterine blood flow during the first two weeks after parturition in Simmenthal heifers. J Vet Sci. 2013; 14:323–327.
Article17. Heppelmann M, Weinert M, Brömmling A, Piechotta M, Hoedemaker M, Bollwein H. The effect of puerperal uterine disease on uterine involution in cows assessed by Doppler sonography of the uterine arteries. Anim Reprod Sci. 2013; 143:1–7.
Article18. Herzog K, Bollwein H. Application of Doppler ultrasonography in cattle reproduction. Reprod Domest Anim. 2007; 42:Suppl 2. 51–58.
Article19. Honnens A, Niemann H, Paul V, Meyer HHD, Bollwein H. Doppler sonography of the uterine arteries during a superovulatory regime in cattle uterine blood flow in superovulated cattle. Theriogenology. 2008; 70:859–867.
Article20. Honnens A, Voss C, Herzog K, Niemann H, Rath D, Bollwein H. Uterine blood flow during the first 3 weeks of pregnancy in dairy cows. Theriogenology. 2008; 70:1048–1056.
Article21. Hussain AM, Daniel RCW. Bovine endometritis: current and future alternative therapy. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1991; 38:641–651.
Article22. Katkiewicz M, Wierzchon M, Boryczko Z. Endometritis accompanying endometriosis in cows. Zycie Weterynaryjne. 2011; 86:614–617.23. Kenney RM. Cyclic and pathologic changes of the mare endometrium as detected by biopsy, with a note on early embryonic death. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978; 172:241–262.24. Krueger L, Koerte J, Tsousis G, Herzog K, Flachowsky G, Bollwein H. Transrectal Doppler sonography of uterine blood flow during the first 12 weeks after parturition in healthy dairy cows. Anim Reprod Sci. 2009; 114:23–31.
Article25. Kupesic S, Kurjak A, Pasalic L, Benic S, Ilijas M. The value of transvaginal color Doppler in the assessment of pelvic inflammatory disease. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1995; 21:733–738.
Article26. Meyer HH, Sauerwein H, Mutayoba BM. Immunoaffinity chromatography and biotin-streptavidin amplified enzymeimmunoassay for sensitive and specific estimation of estradiol-17 beta. J Steroid Biochem. 1990; 35:263–269.
Article27. Miyamoto A, Shirasuna K, Wijayagunawardane MPB, Watanabe S, Hayashi M, Yamamoto D, Matsui M, Acosta TJ. Blood flow: a key regulatory component of corpus luteum function in the cow. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2005; 29:329–339.
Article28. Özbay K, Deveci S. Relationships between transvaginal colour Doppler findings, infectious parameters and visual analogue scale scores in patients with mild acute pelvic inflammatory disease. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011; 156:105–108.
Article29. Panarace M, Garnil C, Marfil M, Jauregui G, Lagioia J, Luther E, Medina M. Transrectal Doppler sonography for evaluation of uterine blood flow throughout pregnancy in 13 cows. Theriogenology. 2006; 66:2113–2119.
Article30. Prakash BS, Meyer HH, Schallenberger E, van de Wiel DF. Development of a sensitive enzymeimmunoassay (EIA) for progesterone determination in unextracted bovine plasma using the second antibody technique. J Steroid Biochem. 1987; 28:623–627.
Article31. Rosselli M, Keller PJ, Dubey RK. The role of nitric oxide in the biology, physiology and pathophysiology of reproduction. Hum Reprod Update. 1998; 4:3–24.
Article32. Schnyder D, Küpfer U, Zwahlen R. Endometrial histology after infusion of various drugs into the uterus of cows. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1990; 132:353–364.33. Sheldon IM, Cronin J, Goetze L, Donofrio G, Schuberth HJ. Defining postpartum uterine disease and the mechanisms of infection and immunity in the female reproductive tract in cattle. Biol Reprod. 2009; 81:1025–1032.
Article34. Still JG, Greiss FC Jr. The effect of prostaglandins and other vasoactive substances on uterine blood flow and myometrial activity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1978; 130:1–8.
Article35. Stolla R, Bollwein H. Color Doppler sonography of the uterine artery in subfertile mares. Pferdeheilkunde. 1997; 13:547.36. Strube K, Hühn R, Busch W, Werner E. A phagocytosis test for the evaluation of the local immunity status during endometritis therapy with special regard to the use of uterofertil in cattle. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1991; 98:230–234.37. Tepper R, Aviram R, Cohen N, Cohen I, Holtzinger M, Beyth Y. Doppler flow characteristics in patients with pelvic inflammatory disease: responders versus nonresponders to therapy. J Clin Ultrasound. 1998; 26:247–249.
Article38. Tinkanen H, Kunjansuu E. Doppler ultrasound studies in pelvic inflammatory disease. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1992; 34:240–242.
Article39. Vandeplassche M. Stimulation and inhibition of phagocytosis in domestic animals. In : Proceedings of the 10th International Congress on Animal Reproduction and Artificial Insemination, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign; 10-14 June 1984; Champaign, USA.40. Waite LR, Ford SP, Young DF, Conley AJ. Use of ultrasonic Doppler waveforms to estimate changes in uterine artery blood flow and vessel compliance. J Anim Sci. 1990; 68:2450–2458.
Article41. Williams EJ, Fischer DP, Noakes DE, England GCW, Rycroft A, Dobson H, Sheldon IM. The relationship between uterine pathogen growth density and ovarian function in the postpartum dairy cow. Theriogenology. 2007; 68:549–559.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transrectal Doppler sonography of uterine blood flow during the first two weeks after parturition in Simmenthal heifers
- Risk factors for repeat breeder dairy cows and their impacts on reproductive performance
- Cystic endometrial hyperplasia and endometritis in a dog following prolonged treatment of medroxyprogesterone acetate
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Due to Vascular Abnormality Caused by D&E : Doppler Sonography for Diagnosis and Transcatheter Arterial Embolization for Treatment
- Availability of Transvaginal Color Doppler Sonography to Discriminate Between Benign and, Mlignant Ovarian Tumor According to Tumor Morphology and Blood Flow Characteristics