J Vet Sci.
2017 Mar;18(1):73-79. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.1.73.
Pulsed-wave Doppler ultrasonographic evaluation of hepatic vein in dogs with tricuspid regurgitation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 05029, Korea. eomkd@konkuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2412590
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.1.73
Abstract
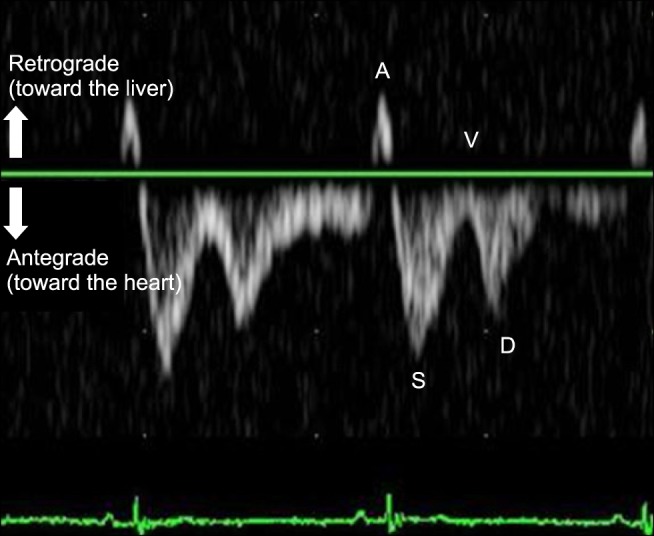
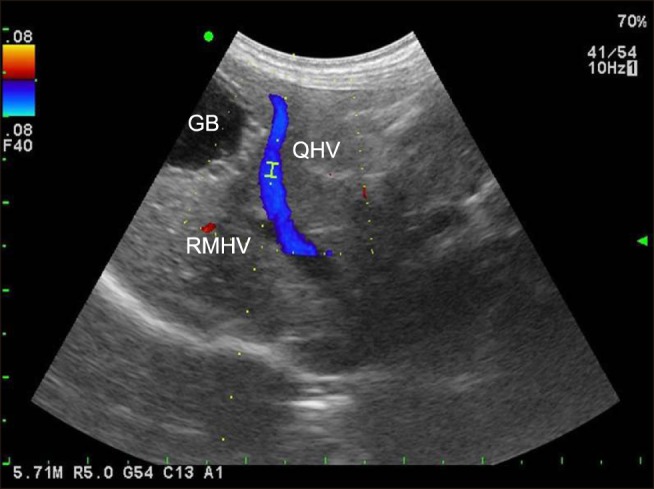
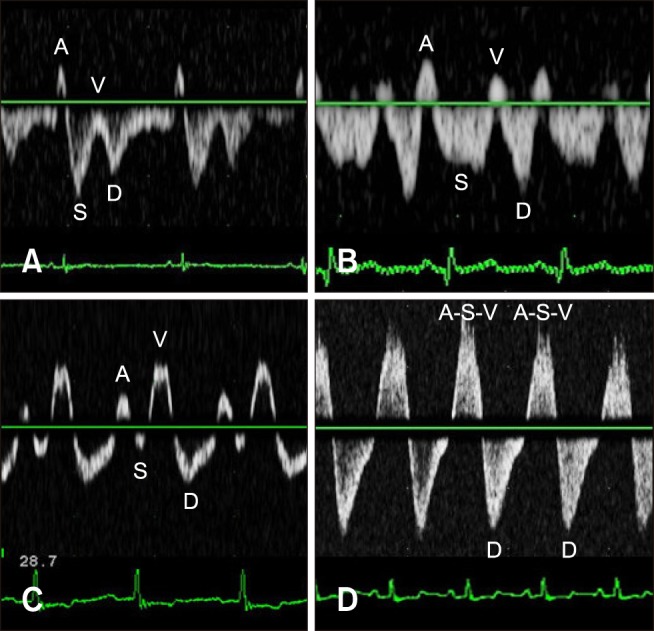
- This study was performed to identify the relationships between hepatic vein (HV) measurements, including flow velocity and waveform, using pulsed-wave (PW) Doppler ultrasonography, and the severity of tricuspid regurgitation (TR) in dogs. The study included 22 dogs with TR and 7 healthy dogs. The TR group was subdivided into 3 groups according to TR jet profile obtained by echocardiography. The hepatic venous waveform was obtained and classified into 3 types. A variety of HV measurements, including the maximal velocities of the atrial systolic, systolic (S), end ventricular systolic, and diastolic (D) waves and the ratio of the S- and D- wave velocities (S/D ratio), were acquired. TR severity was significantly correlated with the S- (r = −0.380, p = 0.042) and D- (r = 0.468, p = 0.011) wave velocities and the S/D ratio (r = −0.747, p < 0.001). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis revealed the highest sensitivity and specificity for the S/D ratio (89% and 75%, respectively) at a threshold of 0.97 with excellent accuracy (AUC = 0.911, p < 0.001). In conclusion, PW Doppler ultrasonography of the HV can be used to identify the presence of significant TR and to classify TR severity in dogs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abu-Yousef MM. Duplex Doppler sonography of the hepatic vein in tricuspid regurgitation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991; 156:79–83. PMID: 1898574.
Article2. Boon JA. Acquired valvular disease. In: Veterinary Echocardiography. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell;2011. p. 267–334.3. Coulden RA, Lomas DJ, Farman P, Britton PD. Doppler ultrasound of the hepatic veins: normal appearances. Clin Radiol. 1992; 45:223–227. PMID: 1395374.
Article4. Colli A, Cocciolo M, Riva C, Martinez E, Prisco A, Pirola M, Bratina G. Abnormalities of Doppler waveform of the hepatic veins in patients with chronic liver disease: correlation with histologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 162:833–837. PMID: 8141001.
Article5. Finn-Bodner ST, Hudson JA. Abdominal vascular sonography. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1998; 28:887–942. PMID: 9698620.
Article6. Gonzalez-Vilchez F, Zarauza J, Vazquez de Prada JA, Martín Durán R, Ruano J, Delgado C, Figueroa A. Assessment of tricuspid regurgitation by Doppler color flow imaging: angiographic correlation. Int J Cardiol. 1994; 44:275–283. PMID: 8077074.
Article7. Greiner M, Pfeiffer D, Smith RD. Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med. 2000; 45:23–41. PMID: 10802332.
Article8. Ginghină C, Muraru D, Vlădaia A, Jurcuţ R, Popescu BA, Călin A, Giuşcă S. Doppler flow patterns in the evaluation of pulmonary hypertension. Rom J Intern Med. 2009; 47:109–121. PMID: 20067161.9. Hamato N, Moriyasu F, Someda H, Nishikawa K, Chiba T, Okuma M. Clinical application of hepatic venous hemodynamics by Doppler ultrasonography in chronic liver disease. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1997; 23:829–835. PMID: 9300986.
Article10. Koslin DB, Berland LL. Duplex Doppler examination of the liver and portal venous system. J Clin Ultrasound. 1987; 15:675–686. PMID: 3119672.
Article11. Killi RM. Doppler sonography of the native liver. Eur J Radiol. 1999; 32:21–35. PMID: 10580320.
Article12. Kok T, van der Jagt EJ, Haagsma EB, Bijleveld CM, Jansen PL, Boeve WJ. The value of Doppler ultrasound in cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1999; 230:82–88. PMID: 10499467.13. Lancellotti P, Moura L, Pierard LA, Agricola E, Popescu BA, Tribouilloy C, Hagendorff A, Monin JL, Badano L, Zamorano JL. European Association of Echocardiography. European Association of Echocardiography recommendations for the assessment of valvular regurgitation. Part 2: mitral and tricuspid regurgitation (native valve disease). Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010; 11:307–332. PMID: 20435783.
Article14. Martínez-Noguera A, Montserrat E, Torrubia S, Villalba J. Doppler in hepatic cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2002; 23:19–36. PMID: 11866220.
Article15. Murat A, Akarsu S, Cihangiroğlu M, Yildirim H, Serhatlioğlu S, Kalender O. Assessment of Doppler waveform patterns and flow velocities of hepatic veins in children with acute viral hepatitis. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2006; 12:85–89. PMID: 16752355.16. Nyland TG, Mattoon JS. Liver. Small Animal Diagnostic Ultrasound. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2002. p. 93–127.17. Oguzkurt L, Yildirim T, Torun D, Tercan F, Kizilkilic O, Niron EA. Hepatic vein Doppler waveform in patients with diffuse fatty infiltration of the liver. Eur J Radiol. 2005; 54:253–257. PMID: 15837406.
Article18. Oh JK, Seward JB, Tajik AJ. Valvular heart disease. The Echo Manual. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2006. p. 189–225.19. Sakai K, Nakamura K, Satomi G, Kondo M, Hirosawa K. Evaluation of tricuspid regurgitation by blood flow pattern in the hepatic vein using pulsed Doppler technique. Am Heart J. 1984; 108:516–523. PMID: 6475714.
Article20. Szatmári V, Sótonyi P, Vörös K. Normal duplex Doppler waveforms of major abdominal blood vessels in dogs: a review. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2001; 42:93–107. PMID: 11327368.21. Smithenson BT, Mattoon JS, Bonagura JD, Abrahamsen EJ, Drost WT. Pulsed-wave Doppler ultrasonographic evaluation of hepatic veins during variable hemodynamic states in healthy anesthetized dogs. Am J Vet Res. 2004; 65:734–740. PMID: 15198211.
Article22. Scheinfeld MH, Bilali A, Koenigsberg M. Understanding the spectral Doppler waveform of the hepatic veins in health and disease. Radiographics. 2009; 29:2081–2098. PMID: 19926763.
Article23. Von Bibra H, Schober K, Jenni R, Busch R, Sebening H, Blömer H. Diagnosis of constrictive pericarditis by pulsed Doppler echocardiography of the hepatic vein. Am J Cardiol. 1989; 63:483–488. PMID: 2644801.
Article24. von Herbay A, Frieling T, Häussinger D. Association between duplex Doppler sonographic flow pattern in right hepatic vein and various liver diseases. J Clin Ultrasound. 2001; 29:25–30. PMID: 11180181.
Article25. Zhang-An , Himura Y, Kumada T, Hayashida W, Ishikawa N, Noda M, Kohno F, Kambayashi M, Kawai C. The characteristics of hepatic venous flow velocity pattern in patients with pulmonary hypertension by pulsed Doppler echocardiography. Jpn Circ J. 1992; 56:317–324. PMID: 1578603.
Article26. Zoghbi WA, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Kraft CD, Levine RA, Nihoyannopoulos P, Otto CM, Quinones MA, Rakowski H, Stewart WJ, Waggoner A, Weissman NJ. American Society of Echocardiography. Recommendations for evaluation of the severity of native valvular regurgitation with two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003; 16:777–802. PMID: 12835667.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tricuspid Regurgitation in Heart Diseases in Infants and Children
- Tricuspid Regurgitation in Patients with Atrial Septal Defect
- Comparison of Cine Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Doppler Echocardiography for the Quantative Evaluation of Tricuspid Regurgitation in Newborn
- Comparative analysis of pulsed doppler ultrasonography of portal vein vs indirect portography
- Value of Pulsed Doppler Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Aortic Regurgitation