Clin Endosc.
2018 Mar;51(2):150-155. 10.5946/ce.2017.125.
Current Status of Endoscopic Gallbladder Drainage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, Shatin, Hong Kong SAR China. anthonyteoh@surgery.cuhk.edu.hk
- KMID: 2410981
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.125
Abstract
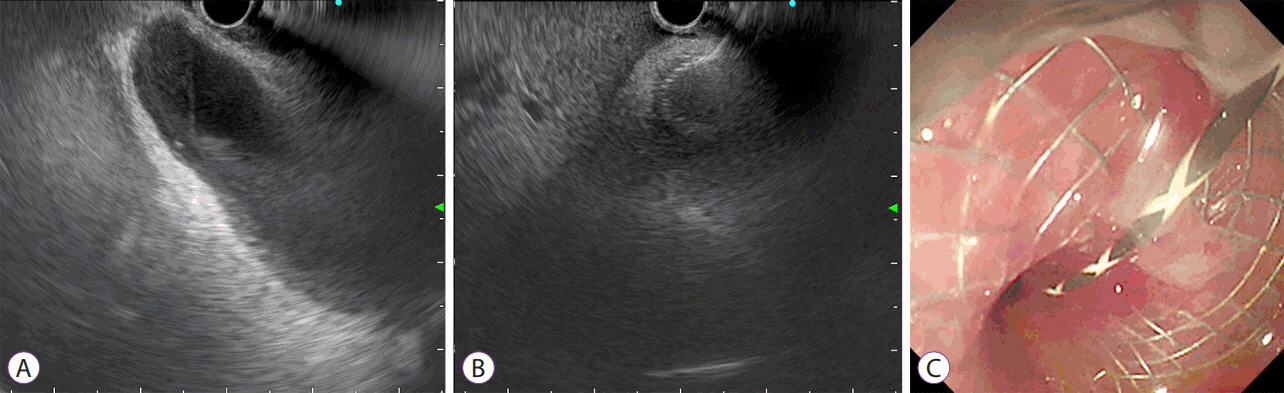
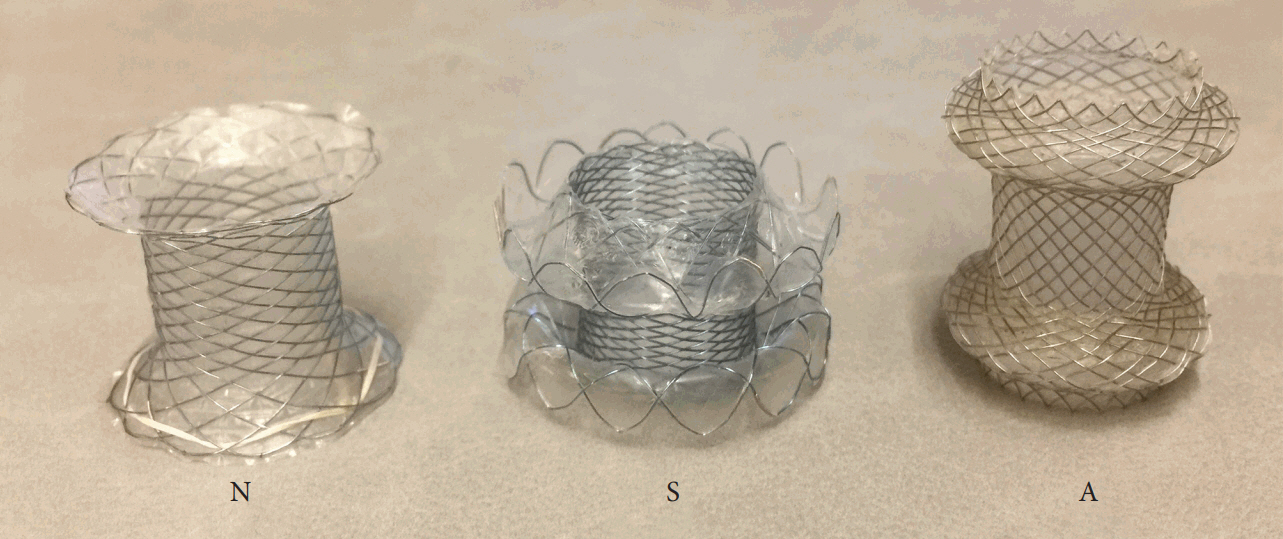
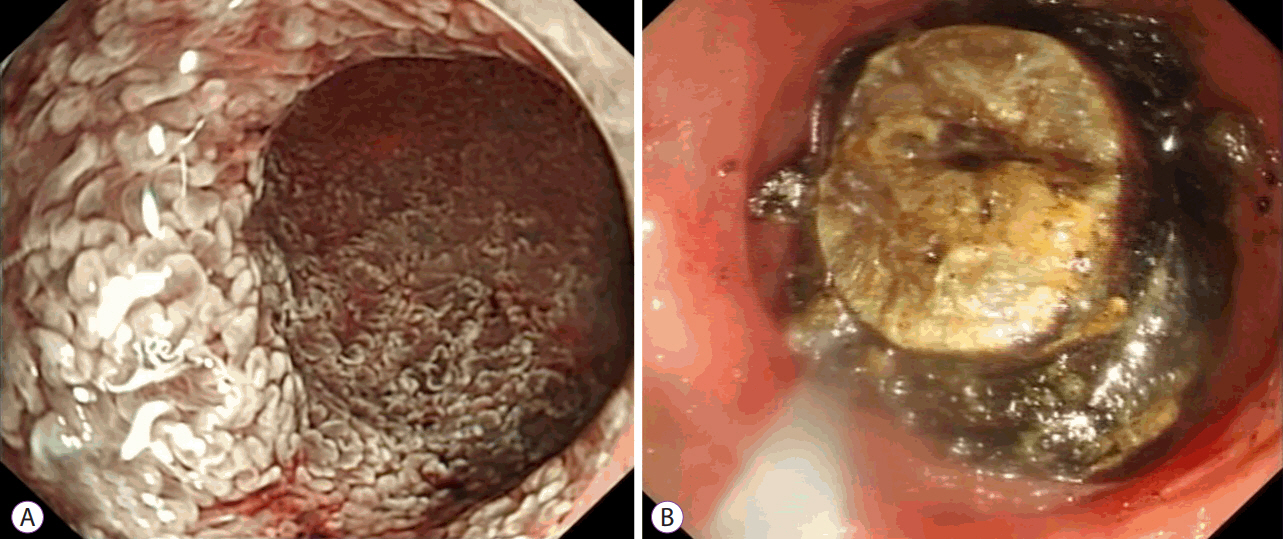
- The gold standard for treatment of acute cholecystitis is laparoscopic cholecystectomy. However, cholecystectomy is often not suitable for surgically unfit patients who are too frail due to various co-morbidities. As such, several less invasive endoscopic treatment modalities have been developed to control sepsis, either as a definitive treatment or as a temporizing modality until the patient is stable enough to undergo cholecystectomy at a later stage. Recent developments in endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage (EUS-GBD) with endoscopic ultrasound EUS-specific stents having lumen-apposing properties have demonstrated potential as a definitive treatment modality. Furthermore, advanced gallbladder procedures can be performed using the stents as a portal. With similar effectiveness as percutaneous transhepatic cholecystostomy and lower rates of adverse events reported in some studies, EUS-GBD has opened exciting possibilities in becoming the next best alternative in treating acute cholecystitis in surgically unfit patients. The aim of this review article is to provide a summary of the various methods of gallbladder drainage GBD with particular focus on EUS-GBD and the many new prospects it allows.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Guidewire May Save the Day
Rajat Garg, Mohammed Barawi
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018;72(2):83-85. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2018.72.2.83.A Rare Fatal Bile Peritonitis after Malposition of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided 5-Fr Naso-Gallbladder Drainage
Tae Hyung Kim, Hyun Jin Bae, Seung Goun Hong
Clin Endosc. 2020;53(1):97-100. doi: 10.5946/ce.2019.032.
Reference
-
1. Teoh AY, Chong CN, Wong J, et al. Routine early laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis after conclusion of a randomized controlled trial. Br J Surg. 2007; 94:1128–1132.
Article2. Yeung B, Teoh AY. Endoscopic management of gallbladder stones: can we eliminate cholecystectomy? Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2016; 18:42.
Article3. Kortram K, de Vries Reilingh TS, Wiezer MJ, van Ramshorst B, Boerma D. Percutaneous drainage for acute calculous cholecystitis. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:3642–3646.
Article4. Winbladh A, Gullstrand P, Svanvik J, Sandström P. Systematic review of cholecystostomy as a treatment option in acute cholecystitis. HPB (Oxford). 2009; 11:183–193.
Article5. Itoi T, Coelho-Prabhu N, Baron TH. Endoscopic gallbladder drainage for management of acute cholecystitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:1038–1045.
Article6. McGahan JP, Lindfors KK. Percutaneous cholecystostomy: an alternative to surgical cholecystostomy for acute cholecystitis? Radiology. 1989; 173:481–485.
Article7. Sugiyama M, Tokuhara M, Atomi Y. Is percutaneous cholecystostomy the optimal treatment for acute cholecystitis in the very elderly? World J Surg. 1998; 22:459–463.
Article8. Feretis CB, Manouras AJ, Apostolidis NS, Golematis BC. Endoscopic transpapillary drainage of gallbladder empyema. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990; 36:523–525.
Article9. Itoi T, Sofuni A, Itokawa F, et al. Endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage in patients with acute cholecystitis in whom percutaneous transhepatic approach is contraindicated or anatomically impossible (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:455–460.
Article10. Nakatsu T, Okada H, Saito K, et al. Endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage (ETGBD) for the treatment of acute cholecystitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 1997; 4:31–35.
Article11. Kjaer DW, Kruse A, Funch-Jensen P. Endoscopic gallbladder drainage of patients with acute cholecystitis. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:304–308.
Article12. Khan MA, Atiq O, Kubiliun N, et al. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic gallbladder drainage in acute cholecystitis: is it better than percutaneous gallbladder drainage? Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:76–87. e3.
Article13. Itoi T, Takada T, Hwang TL, et al. Percutaneous and endoscopic gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis: international multicenter comparative study using propensity score-matched analysis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2017; 24:362–368.
Article14. Mutignani M, Iacopini F, Perri V, et al. Endoscopic gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis: technical and clinical results. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:539–546.
Article15. Lee TH, Park DH, Lee SS, et al. Outcomes of endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder stenting for symptomatic gallbladder diseases: a multicenter prospective follow-up study. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:702–708.
Article16. Teoh AY, Binmoeller KF, Lau JY. Single-step EUS-guided puncture and delivery of a lumen-apposing stent for gallbladder drainage using a novel cautery-tipped stent delivery system. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:1171.
Article17. Swain CP, Mills TN. Anastomosis at flexible endoscopy: an experimental study of compression button gastrojejunostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37:628–631.
Article18. Teoh AY, Ng EK, Chan SM, et al. Ex vivo comparison of the lumen-apposing properties of EUS-specific stents (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 84:62–68.19. de la Serna-Higuera C, Pérez-Miranda M, Gil-Simón P, et al. EUS-guided transenteric gallbladder drainage with a new fistula-forming, lumen- apposing metal stent. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:303–308.20. Walter D, Teoh AY, Itoi T, et al. EUS-guided gall bladder drainage with a lumen-apposing metal stent: a prospective long-term evaluation. Gut. 2016; 65:6–8.
Article21. Dollhopf M, Larghi A, Will U, et al. EUS-guided gallbladder drainage in patients with acute cholecystitis and high surgical risk using an electrocautery-enhanced lumen-apposing metal stent device. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86:636–643.22. Choi JH, Lee SS, Choi JH, et al. Long-term outcomes after endoscopic ultrasonography-guided gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis. Endoscopy. 2014; 46:656–661.
Article23. Jang JW, Lee SS, Park DH, Seo DW, Lee SK, Kim MH. Feasibility and safety of EUS-guided transgastric/transduodenal gallbladder drainage with single-step placement of a modified covered self-expandable metal stent in patients unsuitable for cholecystectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:176–181.
Article24. Irani S, Ngamruengphong S, Teoh A, et al. Similar efficacies of endoscopic ultrasound gallbladder drainage with a lumen-apposing metal stent versus percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 15:738–745.25. Tyberg A, Saumoy M, Sequeiros EV, et al. EUS-guided versus percutaneous gallbladder drainage: isn’t it time to convert? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2018; 52:79–84.26. Teoh AYB, Serna C, Penas I, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage reduces adverse events compared with percutaneous cholecystostomy in patients who are unfit for cholecystectomy. Endoscopy. 2017; 49:130–138.
Article27. Chan SM, Teoh AYB, Yip HC, Wong VWY, Chiu PWY, Ng EKW. Feasibility of per-oral cholecystoscopy and advanced gallbladder interventions after EUS-guided gallbladder stenting (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:1225–1232.28. Teoh AY, Chan AW, Chiu PW, Lau JY. In vivo appearances of gallbladder carcinoma under magnifying endoscopy and probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy after endosonographic gallbladder drainage. Endoscopy. 2014; 46 Suppl 1 UCTN:E13–E14.
Article29. Nakai Y, Isayama H, Shinoura S, et al. Confocal laser endomicroscopy in gastrointestinal and pancreatobiliary diseases. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26 Suppl 1:86–94.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Transpapillary Gallbladder Stenting for Acute Cholecystitis in a Patient with Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer
- The Successful Treatment of Percutaneous Transhepatic Gallbladder Drainage Related Pleurobiliary Fistula via Endoscopic Transpapillary Gallbladder Drainage
- Current Status in the Treatment of Acute Cholecystitis Patients Receiving Antithrombotic Therapy: Is Endoscopic Drainage Feasible?- A Systematic Review
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Drainage in Pancreatobiliary Diseases
- Stent occlusion in endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage from bleeding mitigated by double pigtail plastic stent deployment within lumen apposing metal stent