Korean J Radiol.
2018 Jun;19(3):381-388. 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.3.381.
Magnetic Resonance Venography Findings of Obstructed Hepatic Veins and the Inferior Vena Cava in Patients with Budd-Chiari Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ultrasound, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Ji'nan 250021, China. yhgaiusdoc@163.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Ji'nan 250021, China.
- 3Department of Ultrasound, Fifth Hospital of Jinan, Ji'nan 250000, China.
- 4Department of Gastroenterology, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Ji'nan 250021, China.
- KMID: 2410808
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.3.381
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
This study aimed to illustrate the magnetic resonance venography (MRV) manifestations of obstructed hepatic veins (HVs), the inferior vena cava (IVC), and accessory hepatic veins (AHVs) in patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) and to evaluate the visualization capacity of MRV in the diagnosis of BCS.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifty-two patients with chronic BCS were included in this study. All patients were examined via MRV performed with a 3T system following injections of gadolinium-diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA) or Gd-ethoxibenzyl-DTPA. HV and IVC lesions were classified, and their characteristics were described. HV cord-like occlusions detected via MRV were compared using ultrasonography (US). Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) was performed as a contrast in the MRV detection of IVC lesions. The HVs draining collaterals, mainly AHVs, were carefully observed. HV lesions were classified as segmental stenosis, segmental occlusion, membranous stenosis, membranous occlusion, cord-like occlusion, or non-visualized. Except for patent IVCs, IVC lesions were classified as segmental occlusion, segmental stenosis, membranous occlusion, membranous stenosis, and hepatomegaly-induced stenosis.
RESULTS
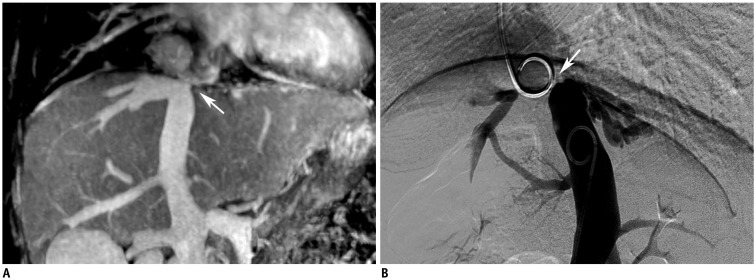
All patients (52/52, 100%) showed HV lesions of different degrees. MRV was inferior to US in detecting cord-like occlusions (6 vs. 19, χ2 = 11.077, p < 0.001). Dilated AHVs, including 50 (50/52, 96.2%) caudate lobe veins and 37 (37/52, 71.2%) inferior HV and AHV lesions, were well-detected. There were no significant differences in detecting segmental lesions and thrombosis between MRV and DSA (χ2 = 0.000, p1 = 1.000, p2 = 1.000). The capacity of MRV to detect membranous lesions was inferior to that of DSA (7 vs. 15, χ2 = 6.125, p = 0.013).
CONCLUSION
In patients with BCS, MRV can clearly display the lesions in HVs and the IVC, as well as in AHVs, and it has diagnostic and therapeutic value.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
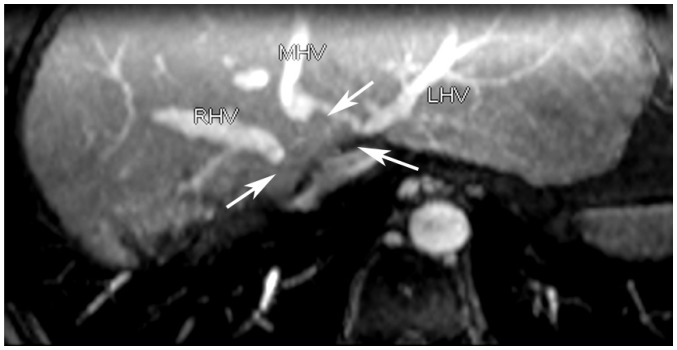
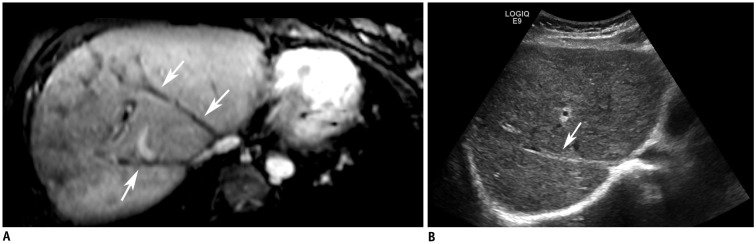
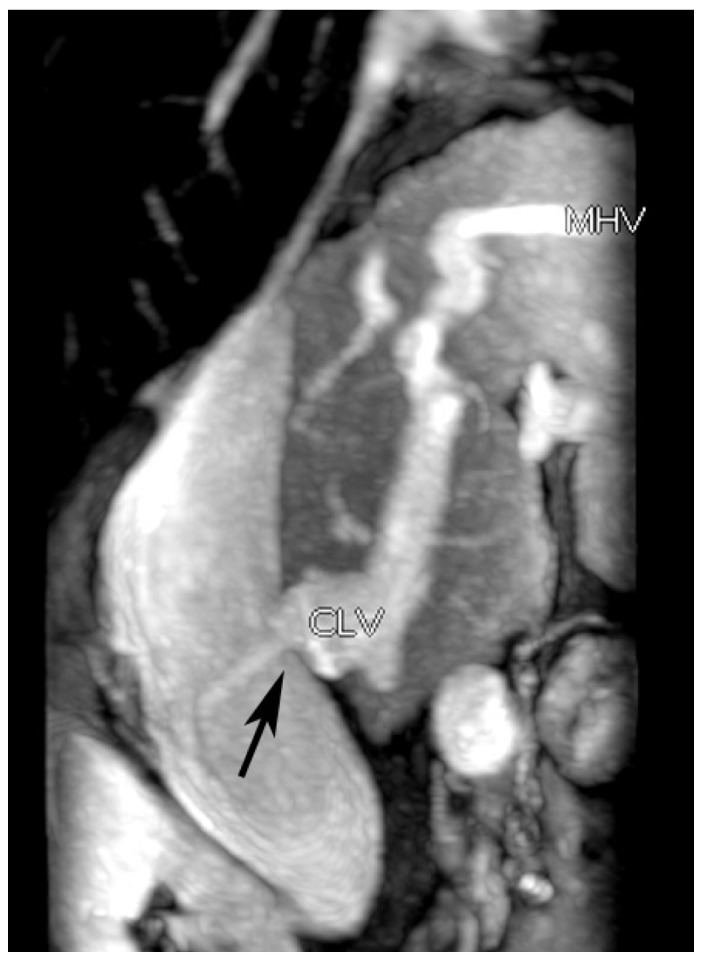
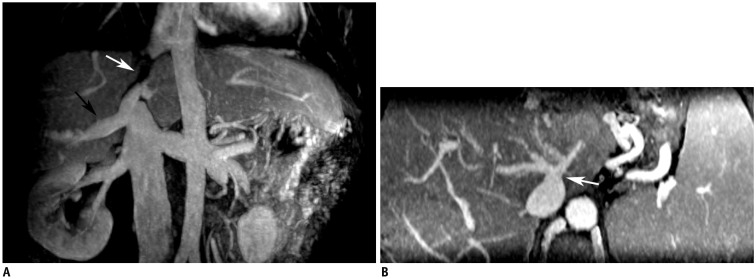
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hefaiedh R, Cheikh M, Marsaoui L, Ennaifer R, Romdhane H, Ben Nejma H, et al. The Budd-Chiari syndrome. Tunis Med. 2013; 91:376–281. PMID: 23868034.2. Hidaka M, Eguchi S. Budd-Chiari syndrome: focus on surgical treatment. Hepatol Res. 2017; 47:142–148. PMID: 27249222.
Article3. Klein AS. Management of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Liver Transpl. 2006; 12:S23–S28. PMID: 17051553.
Article5. Gai YH. [Sonographic classification of blood-drainage in Budd-Chiari syndrome with hepatic vein obstruction]. Chin J UItrasonogr. 2008; 6:517–520.6. Gai YH, Ma S, Guo WB, Liang B, JIA T, Zhang SZ, et al. [Further study of sonographic examination skills and classifications of the inferior vena cava lesions in patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome]. Chin J UItrasonogr. 2012; 11:965–968.7. Gai YH, Cai SF, Guo WB, Zhang CQ, Liang B, Jia T, et al. Sonographic classification of draining pathways of obstructed hepatic veins in Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Clin Ultrasound. 2014; 42:134–142. PMID: 24166054.
Article8. Bargalló X, Gilabert R, Nicolau C, García-Pagán JC, Bosch J, Brú C. Sonography of the caudate vein: value in diagnosing Budd-Chiari syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:1641–1645. PMID: 14627589.9. Kanamura T, Murakami G, Hirai I, Hata F, Sato TJ, Kumon M, et al. High dorsal drainage routes of Spiegel's lobe. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2001; 8:549–556. PMID: 11956907.10. Xing X, Li H, Liu WG. Clinical studies on inferior right hepatic veins. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007; 6:579–584. PMID: 18086621.11. Lu X, Yang C, Xu K, Rong YT, Li SD, Li JS, et al. Magnetic resonance venography in the diagnosis of inferior vena cava obstruction in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015; 19:256–264. PMID: 25683939.12. Faraoun SA, Boudjella Mel A, Debzi N, Afredj N, Guerrache Y, Benidir N, et al. Budd-Chiari syndrome: a prospective analysis of hepatic vein obstruction on ultrasonography, multidetectorrow computed tomography and MR imaging. Abdom Imaging. 2015; 40:1500–1509. PMID: 25687630.
Article13. Standring S. Gray's anatomy. 40th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone;2008. p. 2108.14. Ueda K, Matsui O, Kadoya M, Yoshikawa J, Gabata T, Kawamori Y, et al. CTAP in budd-chiari syndrome: evaluation of intrahepatic portal flow. Abdom Imaging. 1998; 23:304–308. PMID: 9569303.
Article15. Cai SF, Gai YH, Ma S, Liang B, Wang GC, Liu QW. Ultrasonographic visualization of accessory hepatic veins and their lesions in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015; 41:2091–2098. PMID: 25952161.
Article16. Plessier A, Rautou PE, Valla DC. Management of hepatic vascular diseases. J Hepatol. 2012; 56(Suppl 1):S25–S38. PMID: 22300463.
Article17. Xue H, Li YC, Shakya P, Palikhe M, Jha RK. The role of intravascular intervention in the management of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:2659–2663. PMID: 20035404.
Article18. Cura M, Haskal Z, Lopera J. Diagnostic and interventional radiology for Budd-Chiari syndrome. Radiographics. 2009; 29:669–681. PMID: 19448109.
Article19. Xu PQ, Dang XW. reatment of membranous Budd-Chiari syndrome: analysis of 480 cases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2004; 3:73–76. PMID: 14969842.20. Wang ZG. Experience on management of Budd-Chiari syndrome in 143 cases. Angio Arch. 1989; 17:147–152.21. Yang C, Li C, Zeng M, Lu X, Li J, Wang J, et al. Non-contrastenhanced MR angiography in the diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS) compared with digital subtraction angiography (DSA): preliminary results. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017; 36:7–11. PMID: 27742430.
Article22. Shimada K, Isoda H, Okada T, Kamae T, Arizono S, Hirokawa Y, et al. Non-contrast-enhanced hepatic MR angiography: do two-dimensional parallel imaging and short tau inversion recovery methods shorten acquisition time without image quality deterioration? Eur J Radiol. 2011; 77:137–142. PMID: 19556088.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Budd Chiari Syndrome Caused by Membraneous Obstruction of Suprahepatic Inferior Vena Cava
- Balloon Angioplasty for Budd-Chiari Syndrome Resulting from Primary Repair of an Inferior Vena Cava Injury
- Budd-Chiari syndrome caused by membranous obstruction of inferior vena cava
- Hepatoblastoma with budd-chiari syndrome in child: a case report
- Mesoatrial Shunt Operation for Treatment of Budd-Chiari Syndrome: A case report