J Korean Soc Radiol.
2018 May;78(5):358-362. 10.3348/jksr.2018.78.5.358.
A Rare Case of Zinner's Syndrome with Ectopic Prostate and Triorchidism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chung-Ang University Hosptal, Seoul, Korea. seraph377@cau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, College of Medicine and Graduate School of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2410727
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.78.5.358
Abstract
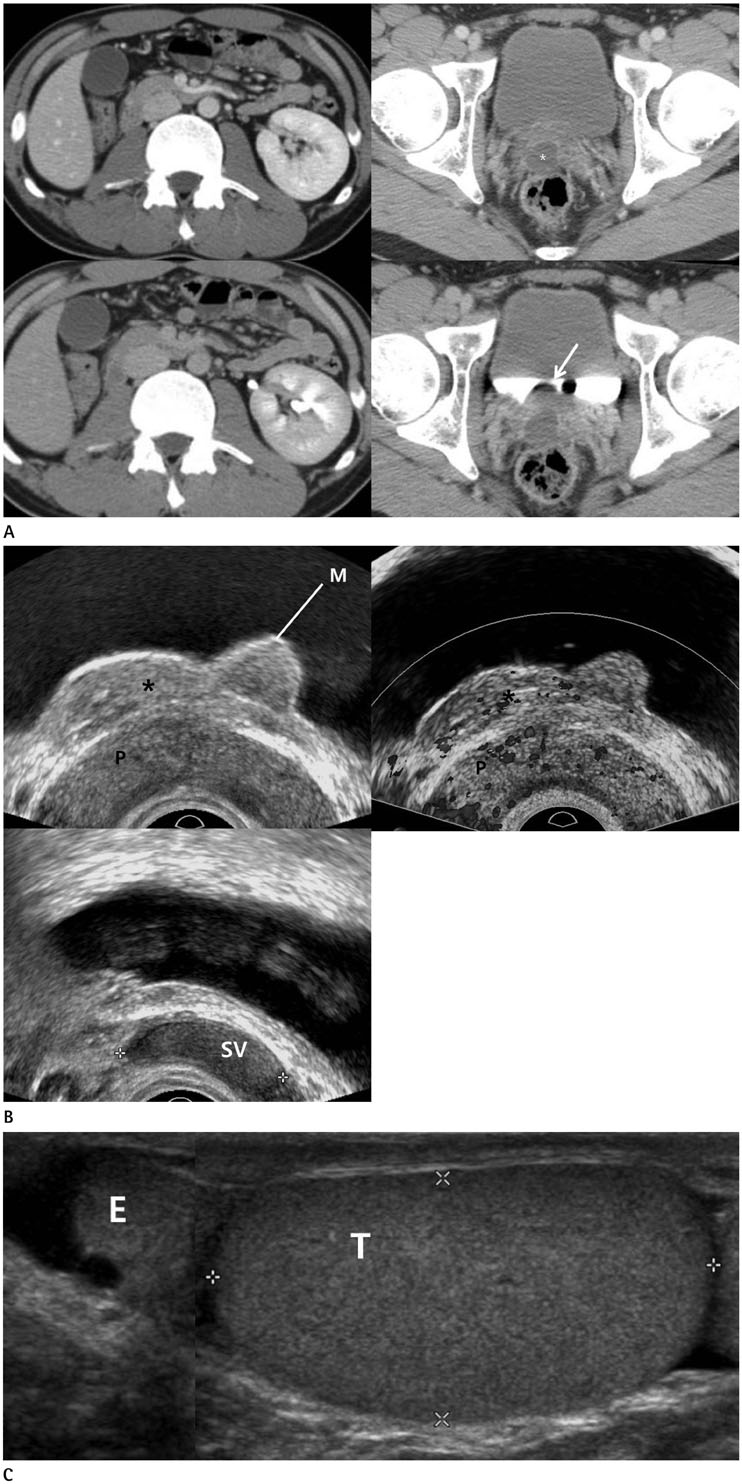
- Zinner's syndrome is a rare congenital abnormality of the mesonephric duct. Unilateral renal agenesis, ipsilateral seminal vesicle cyst, and ipsilateral ejaculatory duct obstruction are the triad of maldevelopment of the mesonephric duct which comprises Zinner's syndrome. It is an extremely rare case, in that approximately 100 cases only have been reported worldwide. We discovered a rare developmental anomaly with other mesonephric duct-associated abnormalities, Zinner's syndrome with a presumed ectopic prostate and triorchidism and do report here.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Barakat AJ. Association of unilateral renal agenesis and genital anomalies. Case Rep Clin Pract Rev. 2002; 3:57–60.2. Fisch H, Kang YM, Johnson CW, Goluboff ET. Ejaculatory duct obstruction. Curr Opin Urol. 2002; 12:509–515.
Article3. Ghonge NP, Aggarwal B, Sahu AK. Zinner syndrome: a unique triad of mesonephric duct abnormalities as an unusual cause of urinary symptoms in late adolescence. Indian J Urol. 2010; 26:444–447.
Article4. Mehra S, Ranjan R, Garga UC. Zinner syndrome-a rare developmental anomaly of the mesonephric duct diagnosed on magnetic resonance imaging. Radiol Case Rep. 2016; 11:313–317.
Article5. Kim JH, Jeen YM, Song YS. Ectopic prostate tissue at the bladder dome presenting as a bladder tumor. World J Mens Health. 2013; 31:176–178.
Article6. Seol MJ, Noh KH, Jeon DS, Lee KM. Ectopic prostatic tissue in the rectum: a case report. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2017; 76:91–95.
Article7. Musayev JS, Bagirov AM, Hasanov AB, Mammadov E. An asymptomatic intramural leiomyoma of bladder in male patient. Austin J Urol. 2014; 1:3.8. Artul S, Habib G. Polyorchidism: two case reports and a review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2014; 8:464.
Article9. Kharrazi SM, Rahmani MR, Sakipour M, Khoob S. Polyorchidism: a case report and review of literature. Urol J. 2006; 3:180–183.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Seminal Vesicle Infection of Zinner Syndrome Misdiagnosed for Neoplasm
- A Case of Ectopic ACTH Syndrome Associated with Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Retroperitoneal Ectopic Pregnancy Detected by CT: A Case Report
- Ectopic Prostate Tissue in the Posterior Wall of the Bladder
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome due to Postburn Ectopic Ossification: A Case Report