J Korean Soc Echocardiogr.
1994 Dec;2(2):209-214. 10.4250/jkse.1994.2.2.209.
Efficacy of Interavascular Ultrasound in the Palmaz-Schatz Stent Implantation: Clinical Experience of 3 Coronary Artery Disease Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University and Saedongrae Hospital, Pusan, Korea.
- KMID: 2410450
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jkse.1994.2.2.209
Abstract
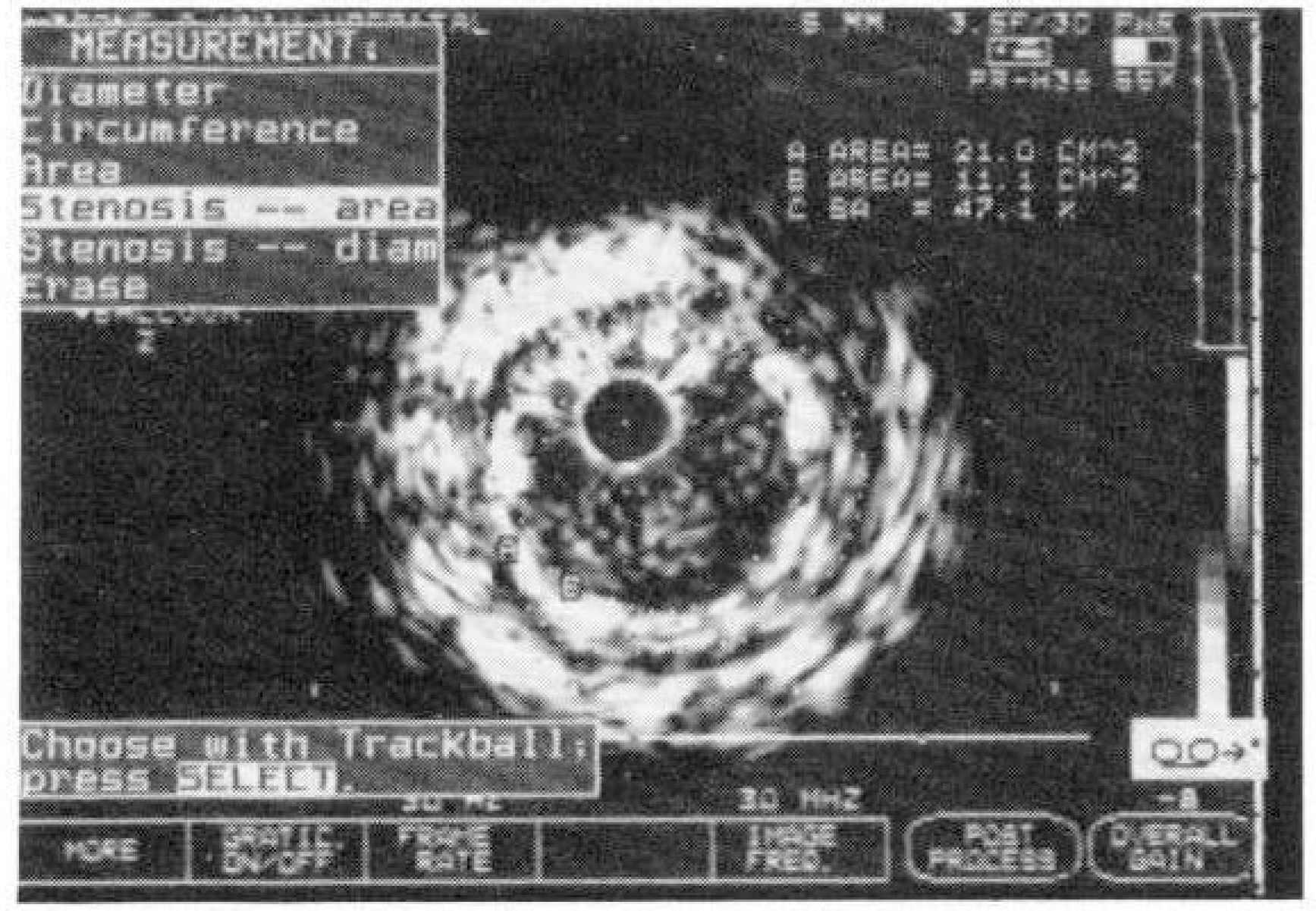
- Intravascular ultrasound is a usful too to assess the adequate stent strut expansion after stent implantation and nowadays it can bo also used as a dicision making method about omitting anticoagulant therapy. We used intravascular ultrasound before and after Palmz-schatz stent implantation in 3 patients with coronary artery narrowings and analysed serial post porcedure lumen diameter, cross sectional area. We think it is a useful tool to assess the effect of stent implantation and post stent balloon dilatation.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Carrozza JP Jr, Kuntz RE, Levine HJ, et al. Angiographic and clinical outcome of intracoronary stenting: immediate and long-term results from a large single-center experience. J Am Coll Cardiol. 20:328–337. 1992.
Article2). Kimura T, Tamura T, Yokoi H, Nobuyoshi M. Long-term clinical and angiographic follow-up after placement of Palmaz-Schatz cornonary stent: A single center experience. J Interven Cardiol. 7:129–139. 1994.3). Hall P, Colombo A, Almagor Y, Maiello L, Nakamura S, Martini G, Tobis JM. Preliminary experience with intravascular ultrasound guided Palmaz-Schatz coronary stenting: The acute and short-term results on a consecutive series of patients. J Interven Cardiol. 7:141–159. 1994.
Article4). Hodgson JM, Reddy KG, Suneja R, Nair RN, Lesnefsky EJ, Seehan HM. Intracoronary ultrasound imaging: correlation of plague morphology with angiography, clinical syndrome and procedural results in patients undergoing coronary angioplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol. 21:35–44. 1993.5). Honye Junko, Mahon DJ, Jain A, White CJ, Ramee SR, Wallis JB, Al-Zarka A, Tobis JM. Morphologic effects of coronary balloon angioplasty in vivo assessed by intravascular ultrasound imaging. Circulation. 85:1012–1025. 1992.6). Ellis SG, Roubin GS, King SB III, et al. Angiographic and clinical predictors of acute closure after native vessel coronary angioplasty. Circulation. 77:372–379. 1988.
Article7). Serruys PW, Luijten HE, Beatt KJ, et al. Incidence of restenosis after successful coronary angioplasty: A time-related phenomenon. Quantitative angiographic study in 342 consecutive patients at 1, 2, 3, 4, months. Circulation. 77:361–371. 1988.8). Nobuyoshi M, Kimura T, Nosaka H, et al. Restenosis after successful percuteneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: Serial angiographic follow-up of 229 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 12:616–623. 1988.9). Keren G, Douek Pc, Bartorelli AL, Bonner RF, Leon MB. Intravascular ultrasound examination of coronary stents. Intravascular Ultrasound Imaging. Tobis JM, Yock PG, editors. 1st Ed.p. 219–230. New York: Churchill Livingstone Inc;1992.10). Kuntz RE, Safian RD, Carrozza JP, Fishman RF, Mansour M, Baim DS. The importance of acute luminal diameter in determining restenosis after coronary atherectomy or stenting. Circulation. 86:1827–1835. 1992.
Article11). Tobis JM, Malley JA, Gessert J, Griffith J, Mahon D, Bessen M, Moriuchi M, McLeay L, McRae M, Henry WL. Intravascular ultrasound cross-sectional arterial imaging before and after balloon angioplasty in vitro. Circulation. 80:873–882. 1990.
Article12). Tenaglia AN, Buller CE, Kisslo KB, Stack RS, Davidson CJ. Mechanisms of balloon angioplasty and directional coronary atherectomy as assessed by intracoronary ultrasound. J Am Coll Cardiol. 20:685–691. 1992.
Article13). Kovach JA, Mintz GS, Pichard AD, Kent KM, Popma JJ, Salter LF, Leon MB. Sequential intravascular ultrasound characterization of the mechanism of rotational athrectomy and adjunctine balloon angioplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol. 22:1024–1032. 1993.14). Mintz GS, Pichard AD, Kovach JA, Kent KM, Satler LF, Javier SP, Pompa JJ, Leon MB. Impact of preintervention intravascular ultrasound imaging on transcatheter treatment strategies in coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 73:423. 1994.
Article15). Nakamura S, Colombo A, Gaglione A, Almagor Y, Goldberg SL, Maiello L, Finci L, Tobis TM. Intracoronary ultrasound observations during stent implantation. Circulation. 89:2026–2034. 1994.
Article16). Degawa T, Akiyama T, Harada M, et al. Intravascular ultrasound evaluation of lumen enlargement after Palmaz-Schatz coronary stenting: A comparison with percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Jpn J Interv Cardiol. 9:411–418. 1994.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronic Stent Recoil of Different Design of Stents: An Intravascular Ultrasound Study
- Clinical Experience with the Palmaz-Schatz Coronary Stent: Initial Results and 7 Month Follow-up
- Comparison of Slotted Tube versus Coil Stent Implantation for Ostial Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery Stenosis: Initial and Late Clinical Outcomes
- Plamaz-Schatz Coronary Stenting Accomplished by High Pressure Balloon Dilatation without Anticoagulation
- Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty with Palmaz-Schatz Stent in the Carotid Artery Stenosis