J Korean Soc Echocardiogr.
1995 Jul;3(1):27-31. 10.4250/jkse.1995.3.1.27.
Safety of Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation in Patients with Supraventricular Tachycardia Confirmed by Means of Echocardiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Taegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2410429
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jkse.1995.3.1.27
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
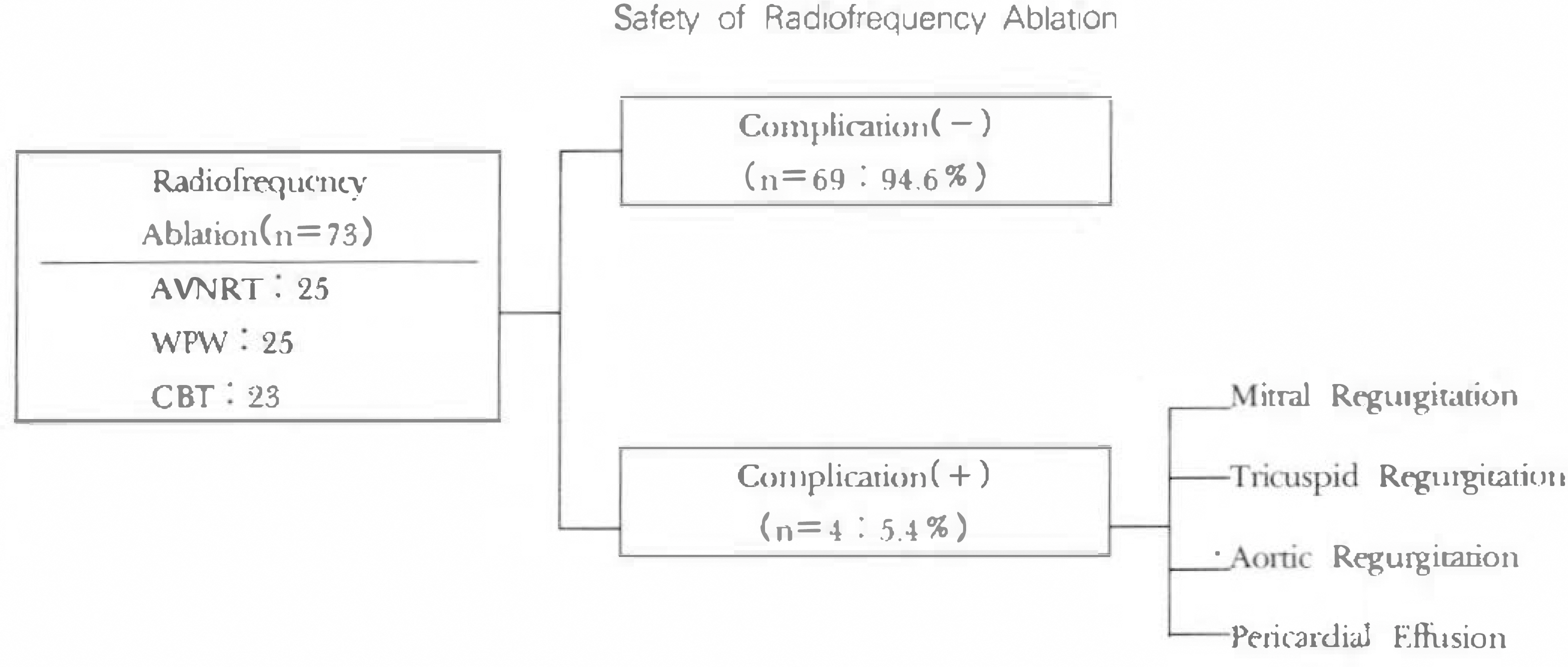
Radiofrequecy(RF) catheter ablation is the choice of treatment of refractory supraventricular tachycardia. Althogh catheter ablation is invasive, it is well-known that this procedure is safe. However RF catheter ablation may provoke some adverse conditions. The purpose of this study was to assess functional and morphologic changes shortly after radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with supraventricular tachycardia by means of two-dimensional echocardiography. METHOD: Echocardiogram underwent 1 day before and within 3 days after RF catheter ablation. Cardiac chamber size, wall thickness, and valve motion in the M-mode were Measured. Left ventricular volume, area, dimension, pericardial effusion and segmental wall motion were measured by means of two-dimensional echocardiography and valve incompetence were also measured with color Doppler echocardiography.
RESULTS
New echocardiographic abnormalities were observed in 4(5.4%) among 73 patients. One mild aortic regurgitation,one increase in severity of tricuspid imcompetence, one increase in severity of mitral regurgitation and one mild pericardial effusion were found.
CONCLUSION
We concluded that echocardiographic changes after radiofrequency ablation are rate and of minor significance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Scheinmann MM, Morady F, Hess DS, Gonzalez R. Catheter-induced ablation of the atrioventricular junction to control refractory supraventricular arrhythmias. JAMA. 248:851–855. 1982.
Article2). Gallagher JJ, Svenson RH, Kasell JH, German LD, Bardy GH, Broughton A, Critelli G. Catheter technique for closed chest ablation of the atrioventricular conduction system. N Engl J Med. 306:194–200. 1982.3). Ward DE, Davies M. Transvenous high energy shock for ablation atrioventricular conduction in man. Observations on the hisological effects. Br Heart J. 51:175. 1984.4). Jackmann WM, Wang X, Friday KJ, Roman CA, Moulton KP, Meckman KJ, McClelland JH, Twidale N, Hazlitt AH, Prior MI, Margolos PD, Calame JD, Overholt ED, Lazzara R. Catheter ablation of accessory pathways(Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome) by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med. 324:1605–1611. 1991.5). Calkins H, Sousa J, El-Atassi R, Rosenheck S, de Buitleir M, Kou WH, Kadish AH, Langberg JJ, Morady F. Diagnosis and cure of the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia during a single electrophysiologic test. N Engl J Med. 324:1612–1618. 1991.6). Bharati S, Lev M. Histopathologic changes in the heart including the conduction system after catheter ablation. PACE. 12:159–169. 1989.
Article7). Chin MC, Schuenmeyer T, Finkelbeiner WE, Stern RA, Scheinman MM, Langberg JJ. Histopathology of monopolar transcatheter radiofrequency ablation at the mitral valve annulus. PACE. 14:1956–1960. 1991.
Article8). Stickberger SA, Okishige K, Meyerovitz , Shea J, Friedman PL. Evaluation of possible long term adverse consequences of radiofrequency Itionaba of accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. 71:473–475. 1993.9). Huang SK, Bharati S, Graham AR, et al. Closed chest catheter desiccation of the atrioventricular junction using radiofrequency energy- A new Method of catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 9:349. 1987.10). Conti JB, Geiser E, Curtis AB. Catheter entrapment in the mitral valve apparatus during radiofrequency ablation. PACE. 17:1681–1685. 1994.
Article11). Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, DeMaria A, Devereux R, Feigenbaum NH, Tajik AJ. Recommandations for quantification of the left ventricle by two-dimensional echocardiography. American Society of Echocardiography. Committee on standards. Subcommittee on quantification of two-dimensional echocardiograms. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2:358–367. 1989.12). 김융년 • 박경아 · 허숭호 • 한성욱 • 심경목 • 김기 식 • 김권배. 고주파 에너지에 의한 조직손상정도에 관한 연구 순환기 1995 제 25 권 제 4 호 (in press).13). Metzger JT, Cheriex EC, Smeets JL, Vanagt E, Rodriquez LM, Pieters FA, Weide A, Wellens HJ. Safety of radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways. Am Heart J. 127:1533–1538. 1994.
Article14). Chu E, Kalman JM, Kwasman MA, Jue JC, Fitzgerald PJ, Epstein LM, Schiller NB, Yock PG. Intracardiac echocardiography during radiofrequency catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmia in human. J Am Coll Cardiol. 24:1351–1357. 1994.15). Stellbrink C, Siebels J, Hebe J, Koschyk D, Halten G, Ziegler K, Hanrath P, Kuck KH. Potential of intracardiac ultrasonography as an adjunct for mapping and ablation. Am Heart J. 127:1095–1101. 1994.
Article16). Tardif JC, Vannan MA, Miller DS, Schwarz SL, Pandian NG. Potential applications of intracardiac echocardiography in interventional electrophysiology. Am Heart J. 127:1090–1094. 1994.
Article17). Chu E, Fitzpatrick AP, Chin MC, Sudhir K, Yock PG, Lesh MD. Radiofrequency catheter ablation guided by intracardiac echocardiography. Circulation. 89:1301–1305. 1994.
Article18). Saxon LA, Stevenson WG, Fonarow GC, Middlekauff HR, Yeatman LA, Sherman CT, Child JS. Transesophageal echocardiography during radiofrequency catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia. Am J Cardiol. 72:658–661. 1993.
Article19). Minich LL, Snider RA, Dick II MD. Doppler detection of valvular regurgitation after radiofrequency ablation of accessory connections. Am J Cardiol. 70:116–117. 1992.
Article20). Seifert MI, Morady F, Calkins HG, Langberg JJ. Aortic leaflet perforation during radiofrequency ablation. PACE. 14:1582–1585. 1991.
Article21). Gerlis LM, Davies MJ, Boyle R, Williams G, Scott H. Pre-excitation due to accessory sinoventricular connections associated with coronary sinus aneurysms. A report of two cases. Br Heart J. 53:314–322. 1985.22). Guiraudon GM, Giuraudon CM, Klein GJ, Sharma AD, Yee R. The coronary sinus diverticulum: A pathologic entity associated with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 62:733–735. 1988.
Article23). Lesh MD, Van Hare G, Kao AK, Scheinman MM. Radiofrequency catheter ablation for the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome associated with a coronary sinus diverticulum. PACE. 14:1479–1484. 1991.24). Wood MA, DiMarco JP, Haines DE. Electrocardiographic abnormalities after rediofrequency catheter ablation of accessory bypass tracts in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. AM J Cardiol. 70:200–204. 1992.25). Kalbfleisch SJ, Sousa J, El-Atassi R, Calkins H, Langberg J, Morady F. Repolarization abnomalities after catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections with radiofrequency current. J Am Coll Cardiol. 18:1761–1766. 1991.26). Katz AM. T wave “memory”: Possible causal relationship to stress-induced changes in cardiac ion channels ?; Cardivasc Electrophysiol. 3:150–159. 1992.27). Shyu KG, Lin JL, Chen JJ, Ko YL, Hwang JJ, Tseng YZ, Lien WP. Change in left ventricular diastolic filling patterns in patients with supraventricular tachycardia treated by radiofrequency ablation; a Doppler echocardiographic study. Cardiology. 85:193–200. 1994.
Article28). Voci P, Yang Y, Greco C, Nigri A, Critell G. Coronary air embolism complication accessory pathway catheter ablation: detection by echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 73:312–314. 1994.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Ablation of Resistant Left Lateral Accessory Pathway and Coexisting Atypical Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia
- Catheter ablation for treatment of tachyarrhythmia
- Evaluation of Myocardial Injury after Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation for Supraventricular Tachycardia by Means of Measurement of Myocardial Enzyme
- Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
- Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia by Catheter Ablation Using Radiofrequency Currents in Children and Adolescents