J Korean Soc Echocardiogr.
1995 Dec;3(2):196-203. 10.4250/jkse.1995.3.2.196.
Quantification of Large Pericardial Effusion by Two-Dimensional Echocardiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Taegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2410422
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jkse.1995.3.2.196
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
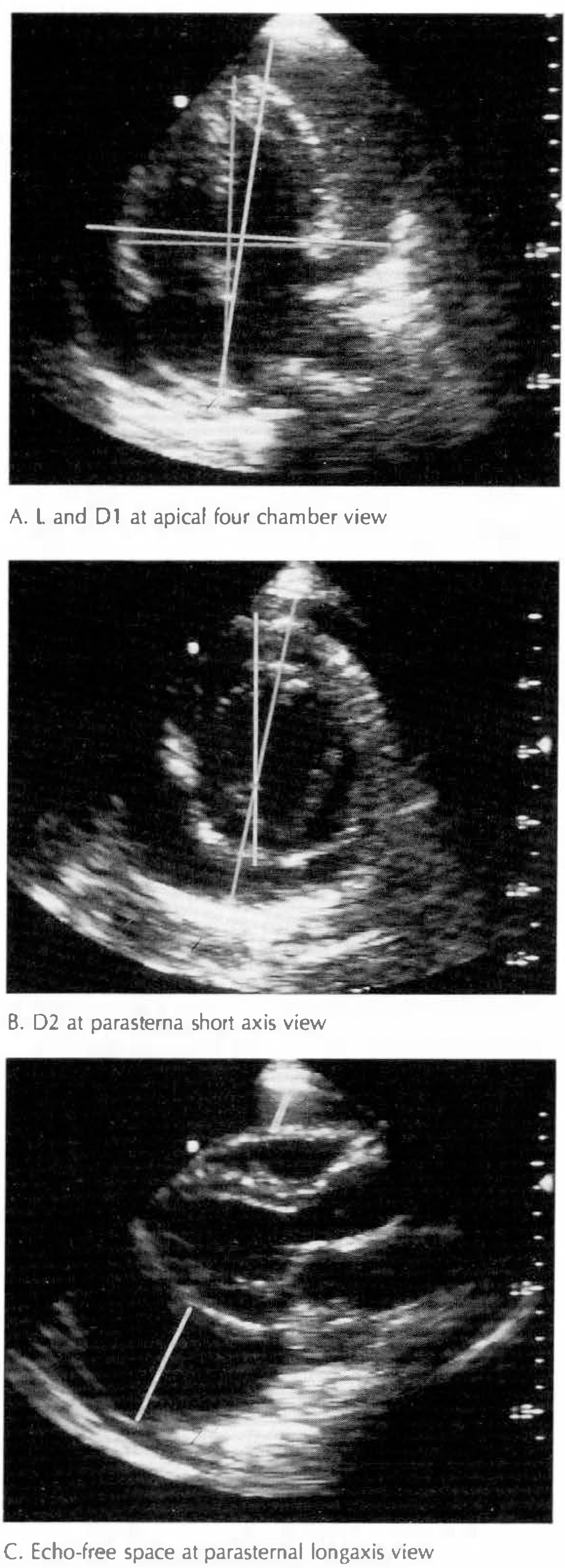
The accurate information about the volume of pericardial effusion can assist in clinical decisions and has impartant prognostic value. In addition, accurate quantification of serial change in effusion volume is necessary in assessing pericardial disease and making a decision of immediate drainage. This study was performed to evaluate the efficacy of 2-D echocardiographic quantification of pericardial effusion. METHOD: The study populations are 22 patients with large pericardial effusion whose volume of effusion is confirmed by paracentesis or surgical drainage. Through the echocardiographic reviw, the volume of pericardial sac and heart was calculated by method of D'cruz and then, the effusion volume was derived as the difference of two volumes. Each echocardiographically calculated volume of pericardial effusion was compared with the measured volume drained percutaneously or surgically.
RESULTS
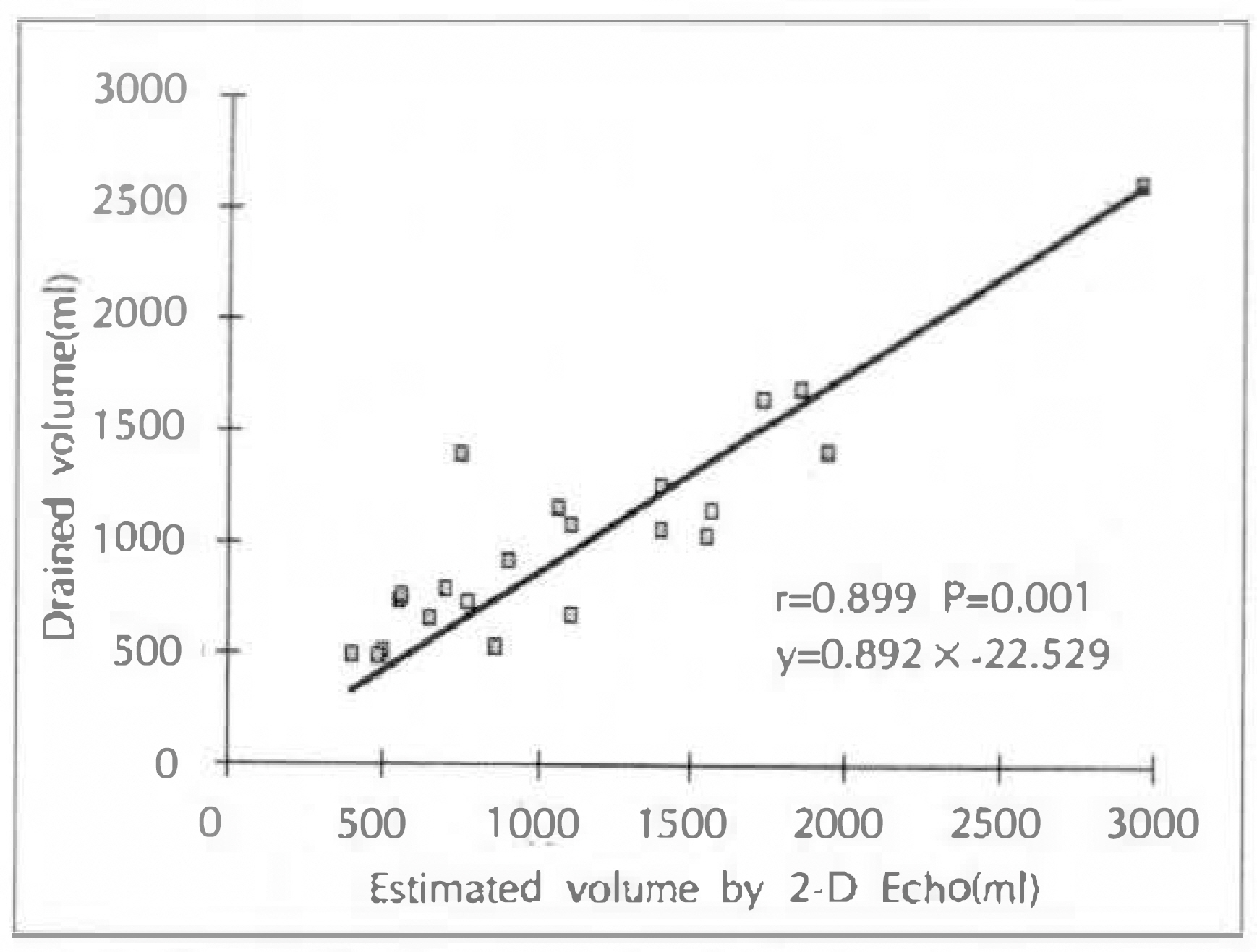
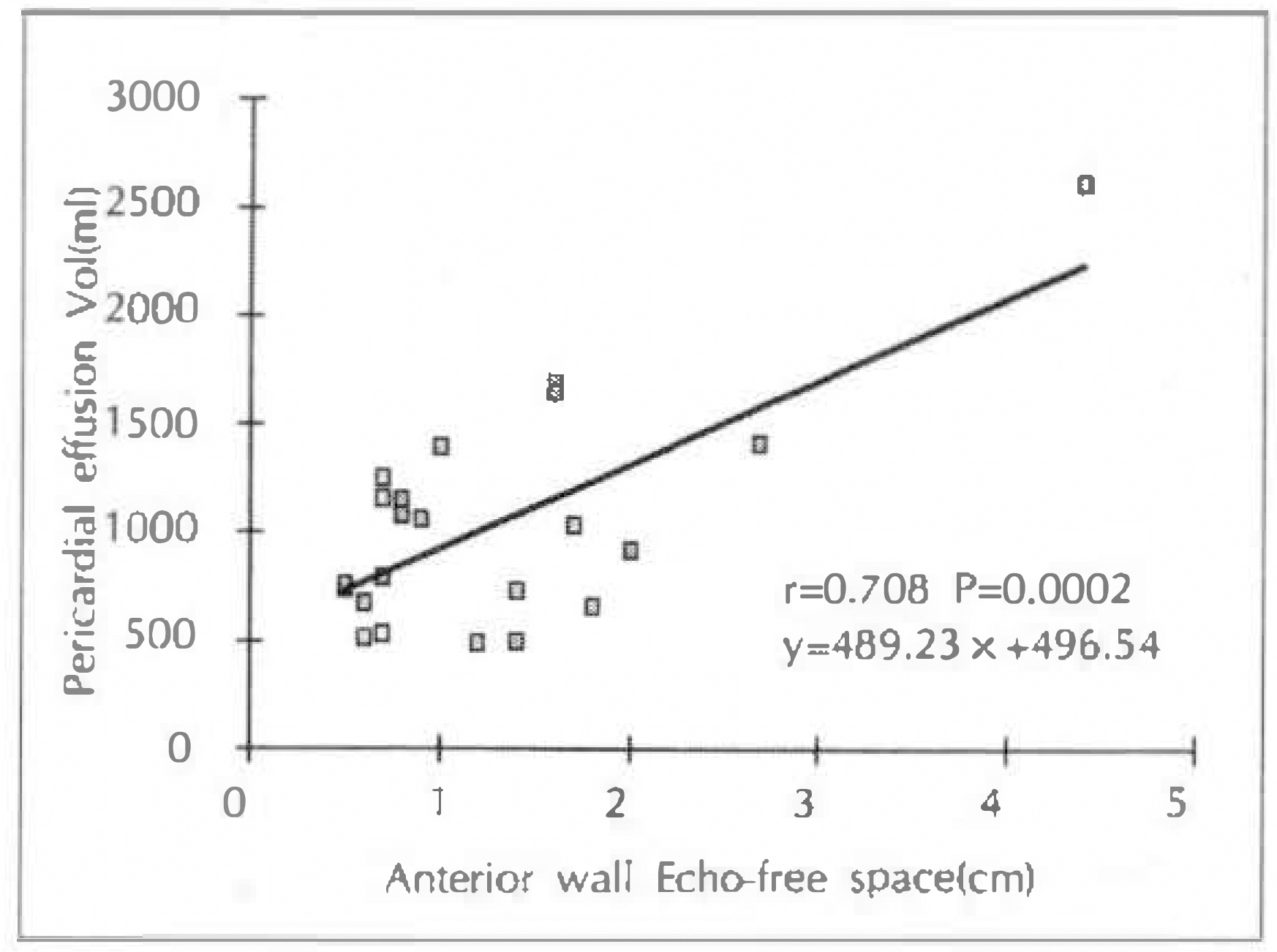
The volume of pericardial effusion calculated echocardiographically was excellently correlated with the drained volume(r=0.90, p < 0.01). The echo-free space was well correlated with the volume of pericardial effusion in the anterior aspect of the heart(r=0.71, p < 0.01), but not in the posterior aspect.
CONCLUSION
2-D echocardiographic Quantification of pericardial effusion is simple and reliable method, and its clinical efficacy may be great.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). D'cruz I, Hoffman PK. A new cross sectional echocardiographic method for estimating the volume of large pericardial effusions. Br Heart J. 66:448–451. 1991.2). Singh S, Wann LS, Schuchard GH, Klopfenstein HS, Leimgruber PP, Keelan MH, Brooks HL. Right ventricular and right atrial collapse in patients with cardiac tarnponade-a combined echocardiographic and hemodynamic study. Circulation. 70:966–971. 1984.3). Feigenbaum H, Zary a, Waldhausen JA. Use of ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion. Ann Intern Med. 65:443–452. 1966.
Article4). Horowitz MS, Schulz CS, Stinson EB, Harrison DC, Popp RL. Sensitivity and specificity of echocardiographic diagnosis of pericardial effusion. Circulation. 50:239–247. 1974.
Article5). Parameswaran R, Goldberg H. Echocardiogrphic quantitation of pericardial effusion of pericardial effusion. Chest. 83:767–770. 1983.6). Prakash R, Moorthy K, Delvicario L, Aronow WS. Reliability of echocardiography in quantitating pericardial effusion: A prospective study. JCU. 5:398–402. 1977.
Article7). Eisenberg MJ, Oken K, Guerrero S, Saniei MA, Schiller NB. Prognostic value of echocardiography in hospitalized patients with pericardial effusion. Am J Cardiol. 70:934–939. 1992.
Article8). Arvin S. Echocardiography. p. 224. New york: Churchill Livingstone;1984.
Article9). Himelman RB, Kircher B, Rockey DC, Schiller NB. Inferior vena cava plethora with blunted respiratory response: A sensitive echocardiographic sign of cardiac tamponade. J Am Coll Cardiol. 12:1470–1477. 1988.10). Menapace FJ. Two-dimensional echocardiography in pericardial disease. Giuliani E, editor. ed.Two-dimensional real-time ultrasonic imaging of the heart. p. 182. Boston: Martinus Nijhoff;1985.
Article11). Sutton MJ, Oldershaw PJ, editors. eds.:. Echocardiography and Doppler. p. 384. New York: Blackwell;1989.12). Vazquez de Prada JA, Jiang L, Handshumacher BS, Xie SW, Rivera JM, Schwammenthal E, Guerrero JL, Weyman AE, Levine RA, Picard MH J. Quantification of pericardial effusions by three-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 24:254–259. 1994.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Estimating the Volume of Pericardial Effusion by M-Mode and 2-D Echocardiographic Method
- Electrocardiographic Findings and Left Ventricular Function According to the Amount of Pericardial Effusion Measured by Echocardiography
- Pericardial Effusion and Pericardiocentesis: Role of Echocardiography
- A "Vanishing", Tuberculous, Pericardial Effusion
- Large Hypothyroidism-Induced Pericardial Effusion with Increased Serum Tumor Markers