Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2018 Apr;6(1):13-21. 10.14791/btrt.2018.6.e3.
Cystic Meningiomas: Correlation between Radiologic and Histopathologic Features
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea. gnuhjjm@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2410233
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2018.6.e3
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Tumors with cysts often correlate with gliomas, metastatic tumors, or hemangioblastomas, which require differentiation.
METHODS
Thirty-eight cases of cyst associated-meningioma based on preoperative radiologic studies and histologic confirmations were reviewed from November 1998 to July 2017.
RESULTS
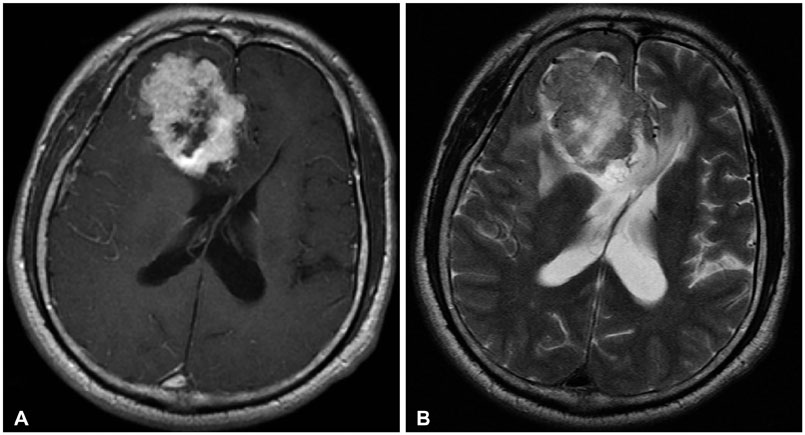
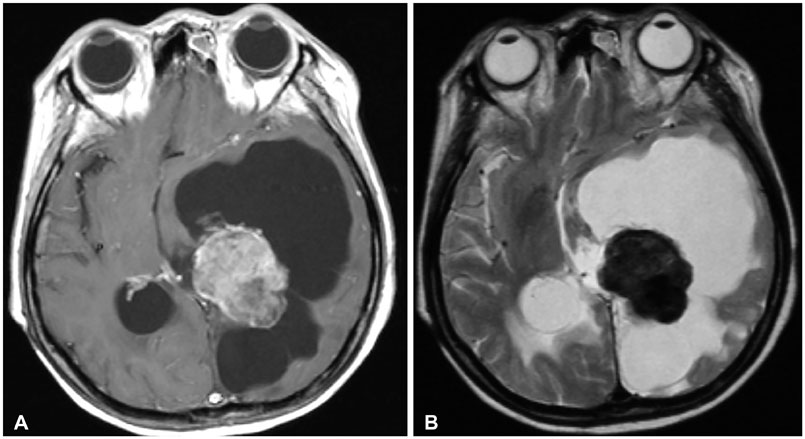
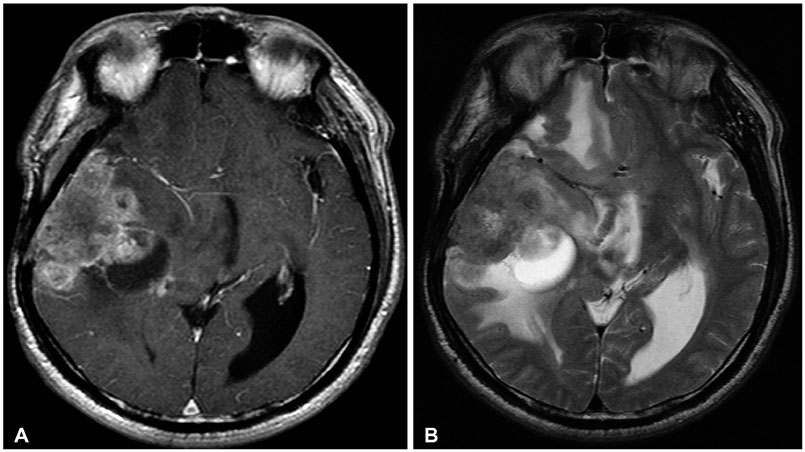
A total of 395 cases of meningioma were observed in the 20 years, and surgical treatment of intracranial meningioma was performed in 120 cases. Thirty-eight (9.6%) cases of cyst associated meningiomas were analyzed. Nauta type I was the most common type of cyst (39.5%) and the most frequent histopathological subtype was meningothelial type (36.8%).
CONCLUSION
Statistically there were no significant associations between meningioma histopathological type and associated cysts; however, the rate of World Health Organization grade II was higher in cyst associated meningiomas than in unrelated meningiomas. This correlation was weak, in accordance with the meningioma grade.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fortuna A, Ferrante L, Acqui M, Guglielmi G, Mastronardi L. Cystic meningiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1988; 90:23–30.
Article2. Nauta HJ, Tucker WS, Horsey WJ, Bilbao JM, Gonsalves C. Xanthochromic cysts associated with meningioma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979; 42:529–535.
Article3. Odake G. Cystic meningioma: report of three patients. Neurosurgery. 1992; 30:935–940.4. Parisi G, Tropea R, Giuffrida S, Lombardo M, Giuffrè F. Cystic meningiomas. Report of seven cases. J Neurosurg. 1986; 64:35–38.5. Rengachary S, Batnitzky S, Kepes JJ, Morantz RA, O'Boynick P, Watanabe I. Cystic lesions associated with intracranial meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 1979; 4:107–114.
Article6. Worthington C, Caron JL, Melanson D, Leblanc R. Meningioma cysts. Neurology. 1985; 35:1720–1724.
Article7. Zee CS, Chen T, Hinton DR, Tan M, Segall HD, Apuzzo ML. Magnetic resonance imaging of cystic meningiomas and its surgical implications. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:482–488.
Article8. Zhang D, Hu LB, Zhen JW, et al. MRI findings of intracranial cystic meningiomas. Clin Radiol. 2009; 64:792–800.
Article9. Bowen JH, Burger PC, Odom GL, Dubois PJ, Blue JM. Meningiomas associated with large cysts with neoplastic cells in the cysts walls. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1981; 55:473–478.
Article10. Moraci A, Cioffi F. [Cystic meningioma. An aspect of “forme humide” of Masson]. Neurochirurgie. 1976; 22:701–710.11. Russell EJ, George AE, Kricheff II, Budzilovich G. Atypical computed tomography features of intracranial meningioma: radiological-pathological correlation in a series of 131 consecutive cases. Radiology. 1980; 135:673–682.
Article12. Amano K, Miura N, Tajika Y, et al. Cystic meningioma in a 10-monthold infant: case report. J Neurosurg. 1980; 52:829–833.13. Dell S, Ganti SR, Steinberger A, McMurtry J 3rd. Cystic meningiomas: a clinicoradiological study. J Neurosurg. 1982; 57:8–13.
Article14. Goran A, Cimenello VJ, Fisher RG. Hemorrhage into Meningiomas. Arch Neurol. 1965; 13:65–69.
Article15. Tapas JN. Intracranial meningioma in a four-month-old infant simulating subdural hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1961; 18:120–121.
Article16. Lapresle J, Netsky MG, Zimmerman HM. [The pathology of meningiomas; a study of 121 cases]. Am J Pathol. 1952; 28:757–791.17. Becker D, Norman D, Wilson CB. Computerized tomography and pathological correlation in cystic meningiomas. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1979; 50:103–105.
Article18. Sigel RM, Messina AV. Computed tomography; the anatomic basis of the zone of diminished density surrounding meningiomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976; 127:139–141.
Article19. Paxton R, Ambrose J. The EMI scanner. A brief review of the first 650 patients. Br J Radiol. 1974; 47:530–565.
Article20. Sridhar K, Ravi R, Ramamurthi B, Vasudevan MC. Cystic meningiomas. Surg Neurol. 1995; 43:235–239.
Article21. Liu M, Liu Y, Li X, Zhu S, Wu C. Cystic meninigioma. J Clin Neurosci. 2007; 14:856–859.
Article22. Ambrose J, Gooding MR, Richardson AE. An assessment of the accuracy of computerized transverse axial scanning (EMI scanner) in the diagnosis of intracranial tumour. A review of 366 patients. Brain. 1975; 98:569–582.
Article23. Claveria LE, Sutton D, Tress BM. The radiological diagnosis of meningiomas, the impact of EMI scanning. Br J Radiol. 1977; 50:15–22.
Article24. Handa J, Nakano Y, Handa H. Computed tomography in the differential diagnosis of low-density intracranial lesions. Surg Neurol. 1978; 10:179–185.
Article25. Bonneville F, Sarrazin JL, Marsot-Dupuch K, et al. Unusual lesions of the cerebellopontine angle: a segmental approach. RadioGraphics. 2001; 21:419–438.
Article26. Pinna G, Beltramello A, Buffatti P, et al. Cystic meningiomas—an update. Surg Neurol. 1986; 26:441–452.
Article27. Kwan AL, Howng SL, Hwang SL. Cystic intracranial meningioma. Gaoxiong Yi Xue Ke Xue Za Zhi. 1992; 8:591–596.28. Chan RC, Thompson GB. Intracranial meningiomas in childhood. Surg Neurol. 1984; 21:319–322.
Article29. Cushing H, Eisenhardt L. Meningiomas. Their classification, regional behaviour, life history, and surgical end results. Springfield: Charles C Thomas;1938.30. Kono K, Inoue Y, Nakayama K, et al. The role of diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1081–1088.31. Filippi CG, Edgar MA, Uluğ AM, Prowda JC, Heier LA, Zimmerman RD. Appearance of meningiomas on diffusion-weighted images: correlating diffusion constants with histopathologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:65–72.32. Sanverdi SE, Ozgen B, Oguz KK, et al. Is diffusion-weighted imaging useful in grading and differentiating histopathological subtypes of meningiomas? Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:2389–2395.
Article33. Chen TY, Lai PH, Ho JT, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion-weighted images of cystic meningioma: correlating with histopathology. Clin Imaging. 2004; 28:10–19.
Article34. Surov A, Ginat DT, Sanverdi E, et al. Use of diffusion weighted imaging in differentiating between maligant and benign meningiomas. A multicenter analysis. World Neurosurg. 2016; 88:598–602.
Article35. Boukobza M, Cebula H, Pop R, et al. Cystic meningioma: radiological, histological, and surgical particularities in 43 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016; 158:1955–1964.
Article36. Jung TY, Jung S, Shin SR, et al. Clinical and histopathological analysis of cystic meningiomas. J Clin Neurosci. 2005; 12:651–655.
Article37. Batra A, Tripathi RP. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the evaluation of focal cerebral tubercular lesions. Acta Radiol. 2004; 45:679–688.
Article38. Kulah A, Ilçayto R, Fiskeci C. Cystic meningiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1991; 111:108–113.
Article39. Maiuri F, Benvenuti D, De Simone MR, Cirillo S, Corriero G, Giamundo A. Cystic lesions associated with meningiomas. Surg Neurol. 1986; 26:591–597.
Article40. Imagawa K, Nomura T, Asai A, et al. [2 Cases of cystic meningioma]. No Shinkei Geka. 1983; 11:513–518.41. Lake P, Heiden JS, Minckler J. Cystic meningioma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1973; 38:638–641.42. Matsushima T, Kinoshita K, Numaguchi Y, Oda K. [Cystic meningioma--a case report (author's transl)]. No Shinkei Geka. 1978; 6:167–171.43. Kolluri VR, Reddy DR, Reddy PK, Naidu MR, Devi S. CT-findings in cystic meningiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1987; 87:31–33.
Article44. Wasenko JJ, Hochhauser L, Stopa EG, Winfield JA. Cystic meningiomas: MR characteristics and surgical correlations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994; 15:1959–1965.45. Ferrante L, Acqui M, Lunardi P, Qasho R, Fortuna A. MRI in the diagnosis of cystic meningiomas: surgical implications. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1997; 139:8–11.
Article46. Souei Mhiri M, Ben Rhouma K, Tlili-Graiess K, et al. [Magnetic resonance imaging features of cystic meningiomas. Report of four cases]. J Neuroradiol. 2005; 32:54–58.47. Borovich B, Guilburd JN, Doron Y, et al. Cystic meningiomas. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 1988; 42:147–151.
Article48. Carvalho GA, Vorkapic P, Biewener G, Samii M. Cystic meningiomas resembling glial tumors. Surg Neurol. 1997; 47:284–289. discussion 289-90.
Article49. Weber J, Gassel AM, Hoch A, Kilisek L, Spring A. Intraoperative management of cystic meningiomas. Neurosurg Rev. 2003; 26:62–66.
Article50. Ghani E, Al-Yamany M. Intracranial cystic meningiomas: a rare type of tumours. Br J Neurosurg. 2015; 29:396–400.
Article51. Henry JM, Schwartz FT, Sartawi MA, Fox JL. Cystic meningiomas simulating astrocytomas. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg. 1974; 40:647–650.52. el-Fiki M, el-Henawy Y, Abdel-Rahman N. Cystic meningioma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996; 138:811–817.
Article53. el Abbassi Skalli A, Chikhaoui N, el Hajjam M, Kadiri R. [Cystic meningioma. Apropos of 6 cases]. J Neuroradiol. 1998; 25:275–280.54. Mena IX, Noboa CA, Leone-Stay G, Vásconez JV, Cárdenas-Mera B. [Cystic meningiomas: unusual forms of intracranial neoplasms]. Rev Neurol. 1998; 27:50–55.55. Demir MK, Müslüman M, Kilicoglu G, Hakan T, Aker FV. Imaging features of unusual intracranial cystic meningiomas. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2007; 58:109–115.56. Wan X, Jiang B, Ma Z, Wang J, Hou Y, Liu Y. [Diagnosis and treatment of cystic meningioma]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010; 35:1009–1012.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis of meningiomas by computed tomography
- Cystic Meningioma: A case report
- Atypical C-T Features of Intracranial Meningiomas and Pathological Correlation
- Correlation of histopathologic classification with proliferative activity and DNA ploidy in 120 intracranial meningiomas, with special reference to atypical meningioma
- Cystic Meningiomas