J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2018 Apr;56(2):166-172. 10.4047/jkap.2018.56.2.166.
Aesthetic restoration n patients with unaesthetic maxillary anterior teeth using double scan : A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea. ykd@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2410121
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2018.56.2.166
Abstract
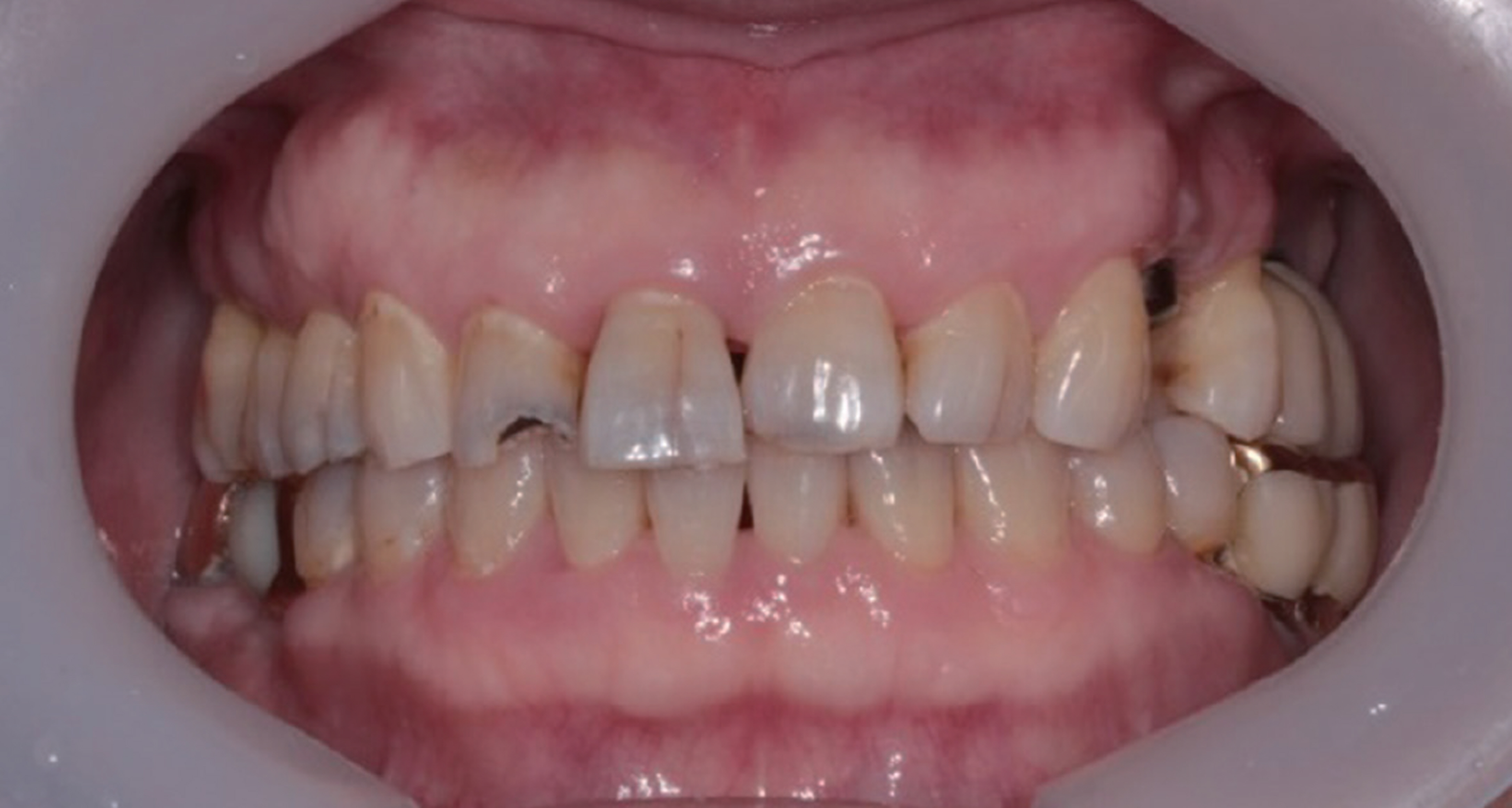
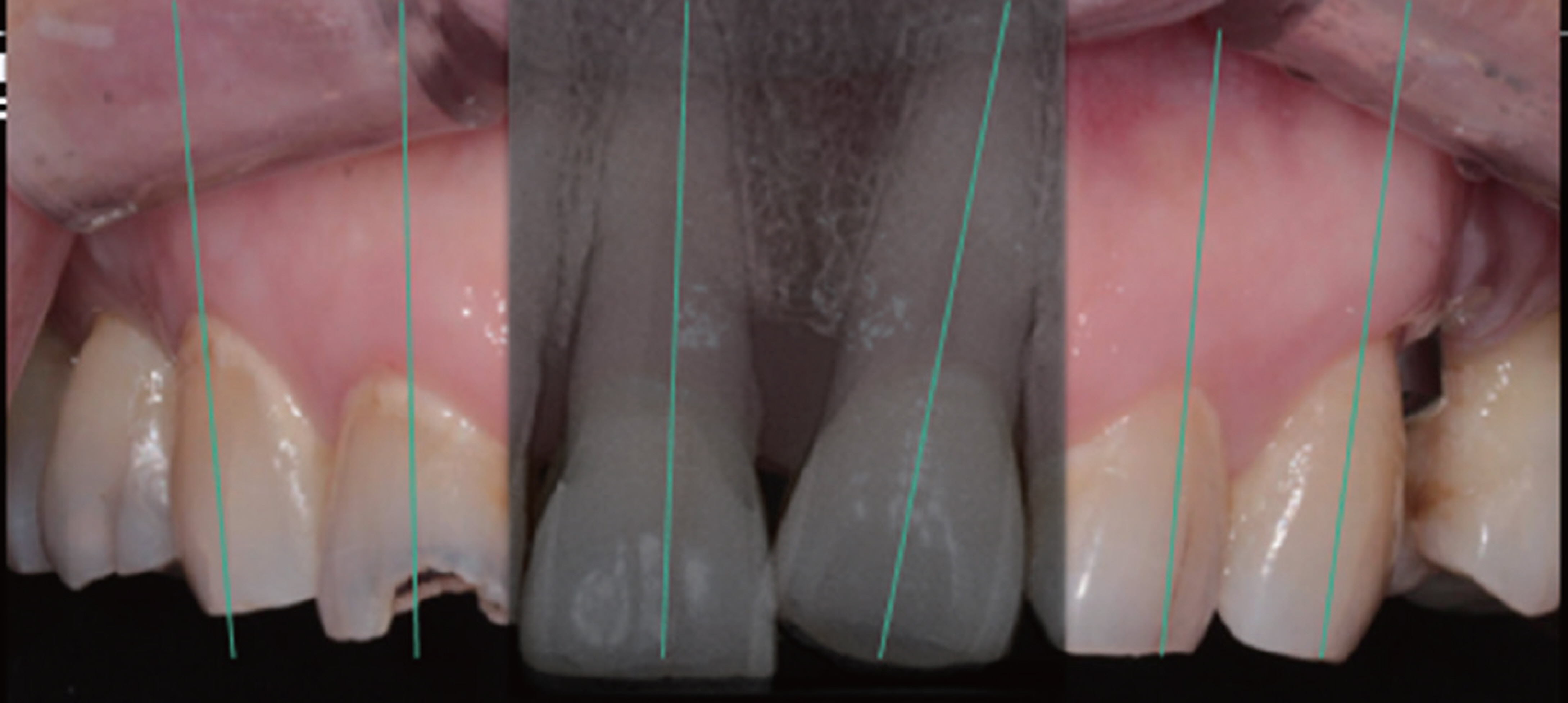
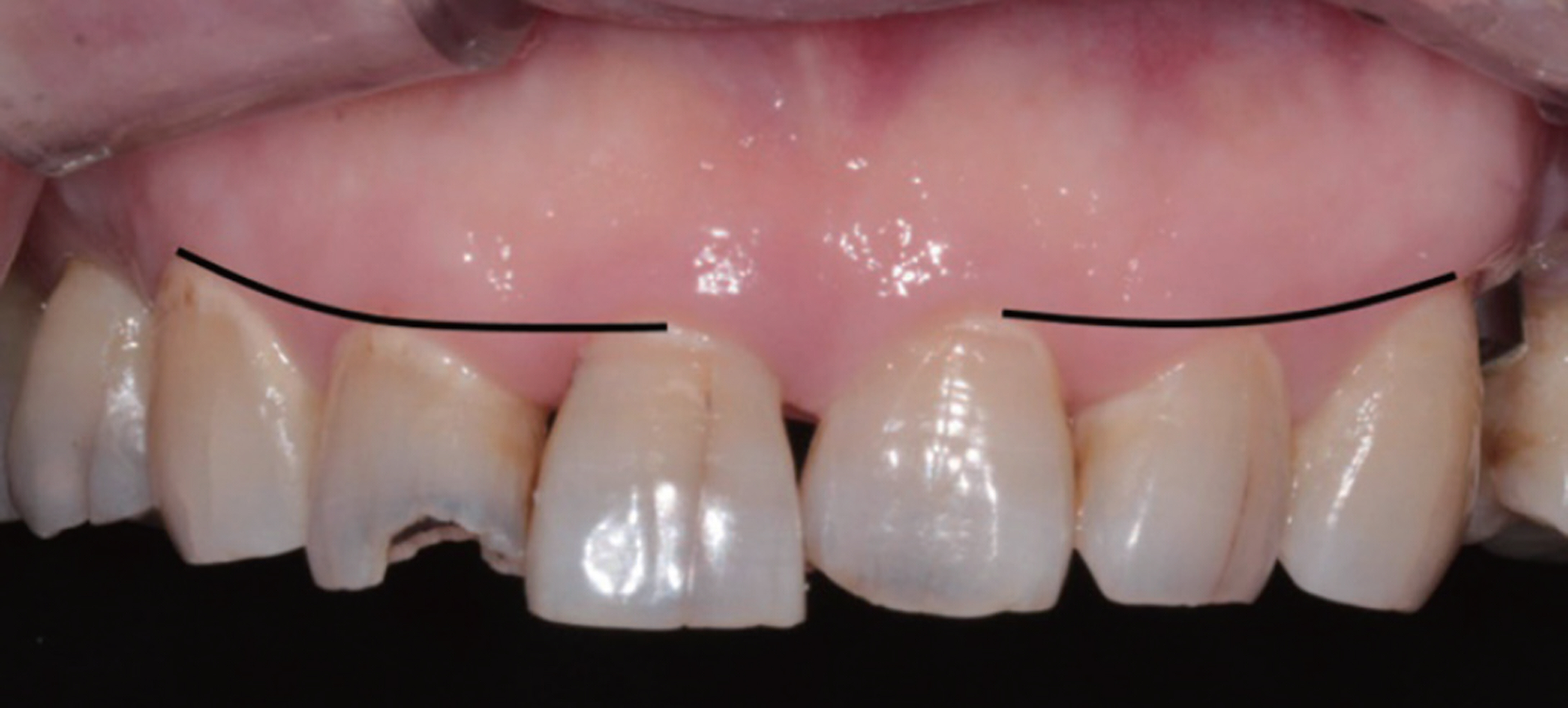
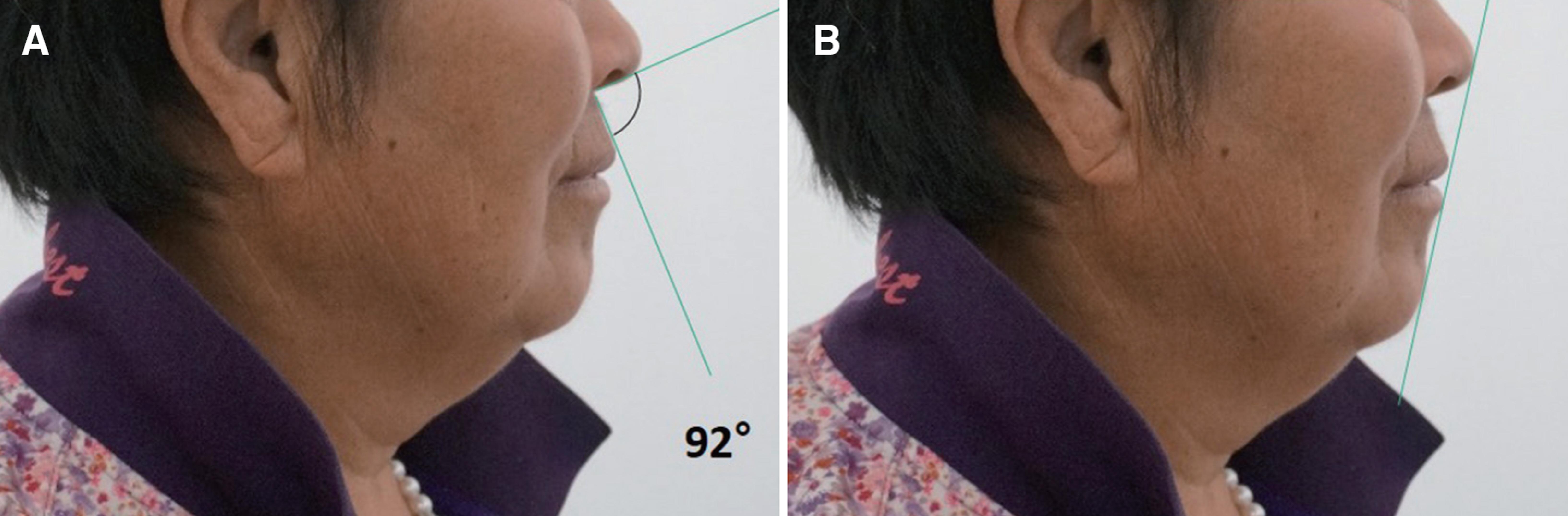
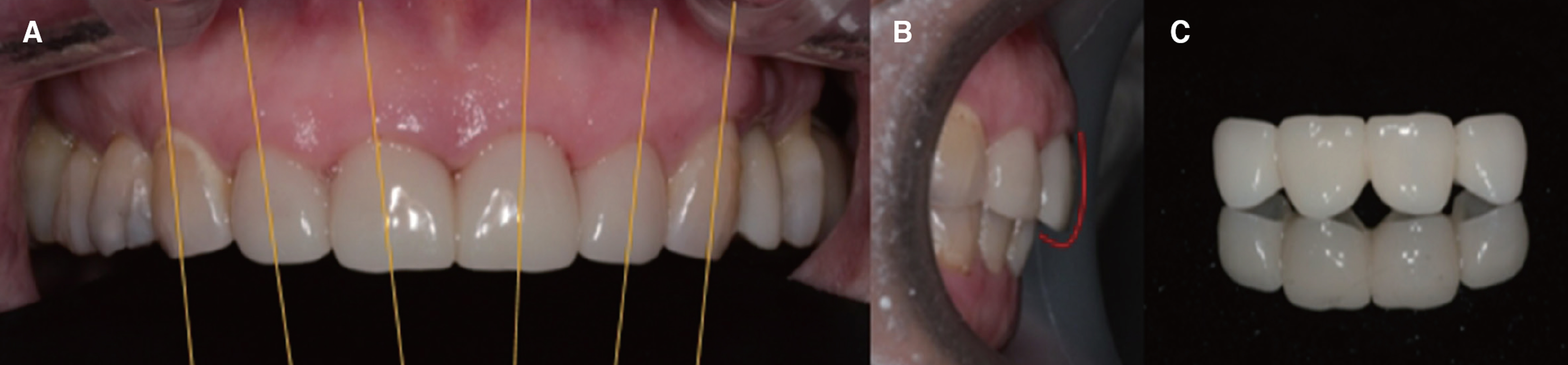
- In case of the treatment of maxillary anterior teeth, it should be taken into account the proper morphology, arrangement and color satisfying patient's esthetic demands. For this purpose, facial composition, dentofacial composition, dental composition and dentogingival composition should be considered making diagnosis and treatment plan in an esthetic point of view. In adjustable temporary crown state, careful evaluation and correction of the esthetic and functional aspect were performed, and the definite restoration was reproduced using double scan.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Functional and esthetic improvement through reconstruction of anterior guidance using the modified Dahl principle and copy-milled technique of CAD/CAM system: A case report
Sung-Ho Kim, Yu-Sung Choi
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2019;57(2):160-170. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2019.57.2.160.
Reference
-
1.Davis LG., Ashworth PD., Spriggs LS. Psychological effects of aesthetic dental treatment. J Dent. 1998. 26:547–54.
Article2.Ahmad I. Geometric considerations in anterior dental aesthetics: restorative principles. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent. 1998. 10:813–22.3.Ahmad I. Anterior dental aesthetics: facial perspective. Br Dent J. 2005. 199:15–21.
Article4.Ahmad I. Anterior dental aesthetics: gingival perspective. Br Dent J. 2005. 199:195–202.
Article5.Dawson PE. Determining the determinants of occlusion. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1983. 3:8–21.6.Yang DH., Yang HS., Park SW., Lim HP., Yun KD., Vang MS. Full mouth implant rehabilitation with double scanning of provisional restoration. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2014. 52:252–7.
Article7.Karl M., Graef F., Wichmann M., Krafft T. Passivity of fit of CAD/CAM and copy-milled frameworks, veneered frameworks, and anatomically contoured, zirconia ceramic, implant-supported fixed prostheses. J Prosthet Dent. 2012. 107:232–8.
Article8.Fradeani M. Estehtic rehabilitation in fixed prosthodontics. Volume 1. Estehtic analysis: a systematic approach to pros-theric treatment. Chicago: Quintessence;2004. p. 16–31.9.Matthews TG. The anatomy of a smile. J Prosthet Dent. 1978. 39:128–34.
Article10.Seo JM. Full mouth rehabilitation in a patient with severely worn dentition. J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci. 2010. 26:463–76.11.Triwatana P., Nagaviroj N., Tulapornchai C. Clinical performance and failures of zirconia-based fixed partial dentures: a review literature. J Adv Prosthodont. 2012. 4:76–83.
Article12.Herrguth M., Wichmann M., Reich S. The aesthetics of all-ceramic veneered and monolithic CAD/CAM crowns. J Oral Rehabil. 2005. 32:747–52.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Functional and esthetic improvement through systematic diagnosis and treatment procedures in patient with unaesthetic anterior teeth proportion because of tooth wear: A case report
- Aesthetic restoration of maxillary anterior teeth in patient with tilted occlusal plane on both posterior parts and asymmetry of the chin using virtual patient: a case report
- Immediate restoration through gingiva conditioning of maxillary anterior implant installed labially: A case report
- Anterior esthetic restoration using DSD (digital smile design) for a patient with congenital missing tooth of maxillary central incisor
- Single-tooth implant restoration with alveolar bone augmentation in the maxillary anterior tooth region: a case report