J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2018 Apr;53(2):180-184. 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.2.180.
Iatrogenic Sciatic Nerve Injury after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. cwk1009@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2410067
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.2.180
Abstract
- Sciatic nerve palsy after total knee arthroplasty, accompanied by motor power weakness and electromyographic evidence, is a rare occurrence. In a 78-year-old female, pneumatic tourniquet was used for 72 minutes, with a pressure of 300 mmHg. The time and pressure are generally accepted values. We noticed sciatic nerve palsy showing motor power weakness and electromyographic evidence. One year after the operation, she recovered full motor power, but complained about a tingling sensation below the knee. Given that the nerve injury after using tourniquet was due to neural ischemia, and since our patient had vascular circulation problems such as atrial fibrillation and clip insertion due to internal carotid artery aneurysm, our patient can be considered as a high-risk patient with weakness to neural ischemic damage, even with the use of conventional tourniquet. Therefore, surgeons should be cautious when using tourniquet in patients with vascular circulation problems.
MeSH Terms
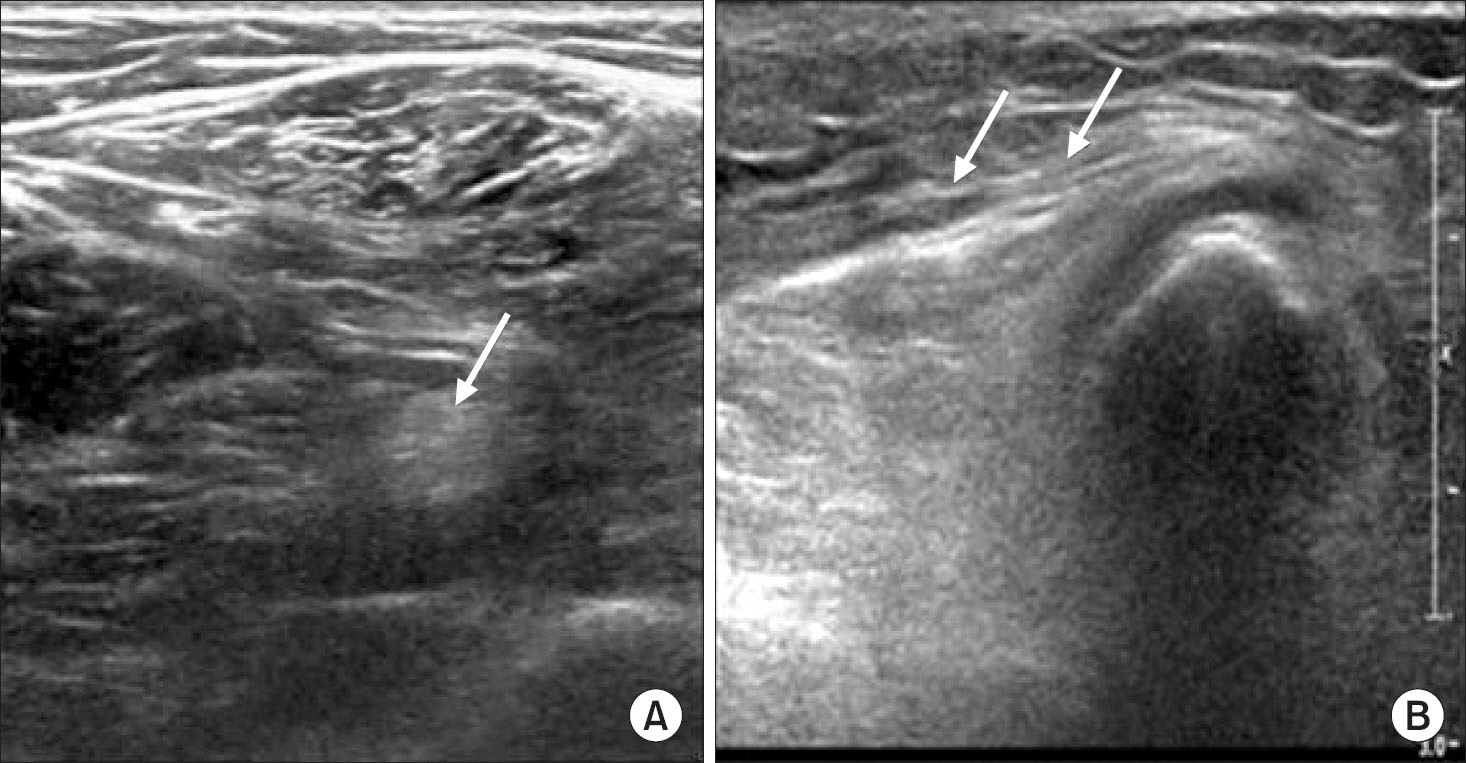
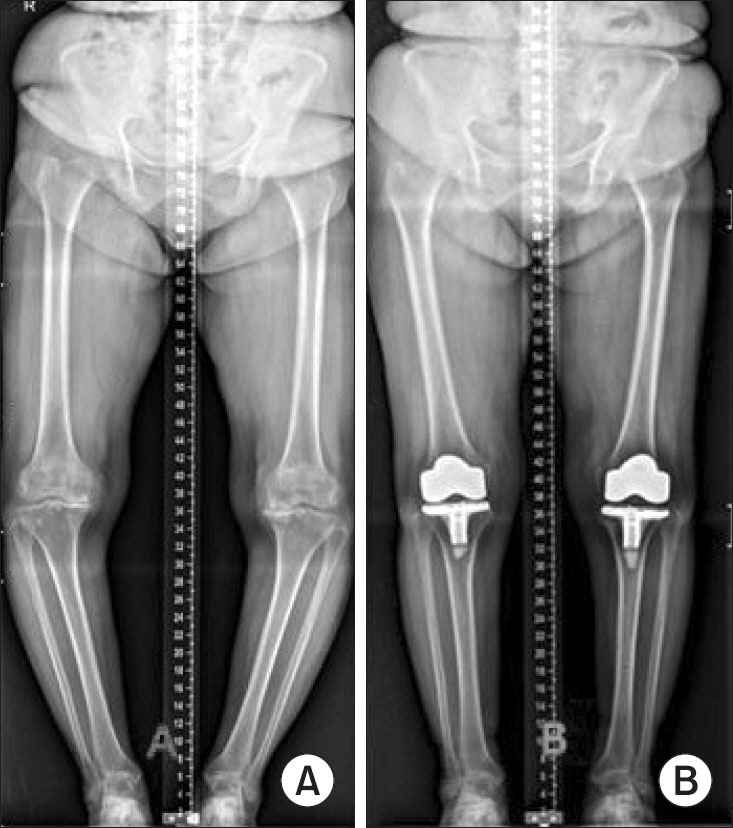
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schinsky MF, Macaulay W, Parks ML, Kiernan H, Nercessian OA. Nerve injury after primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001; 16:1048–54.
Article2. Park JH, Restrepo C, Norton R, Mandel S, Sharkey PF, Parvizi J. Common peroneal nerve palsy following total knee arthroplasty: prognostic factors and course of recovery. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:1538–42.3. Olivecrona C, Blomfeldt R, Ponzer S, Stanford BR, Nilsson BY. Tourniquet cuff pressure and nerve injury in knee arthroplasty in a bloodless field: a neurophysiological study. Acta Orthop. 2013; 84:159–64.4. Asp JP, Rand JA. Peroneal nerve palsy after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 261:233–7.5. Myers MA, Harmon RL. Sacral plexopathy and sciatic neuropathy after total knee arthroplasty. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1998; 38:423–6.6. Horlocker TT, Cabanela ME, Wedel DJ. Does postoperative epidural analgesia increase the risk of peroneal nerve palsy after total knee arthroplasty? Anesth Analg. 1994; 79:495–500.
Article7. Johanson NA. Neurovascular complications following total knee replacement: causes, treatment, and prevention. Instr Course Lect. 1997; 46:181–4.8. Horlocker TT, Hebl JR, Gali B. . Anesthetic, patient, and surgical risk factors for neurologic complications after prolonged total tourniquet time during total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg. 2006; 102:950–5.
Article9. Wyse DG, Waldo AL, DiMarco JP. . A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1825–33.
Article10. Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation: a major contributor to stroke in the elderly. The Framingham study. Arch Intern Med. 1987; 147:1561–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sciatic Nerve Injury in Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Entrapment of the Sciatic Nerve in Femoral Subtrochanteric Fracture : A Case Report
- Sciatic Nerve Palsy Due to Hematoma Following Anticoagulation Therapy for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism after Total Hip Arthroplasty - A Case Report -
- Peroneal Nerve Palsy Induced by Impingement of the Screw in Tibial Component Subsidence -Case Report-
- Nerve Palsy and Delayed Arterial Occlusion after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Case Report