J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2018 Apr;53(2):103-111. 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.2.103.
Arthroscopic Modified Broström Operation for Lateral Ankle Instability
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. brain0808@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, VHS Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul Bumin Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2410057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.2.103
Abstract
- Lateral ankle sprain is the most common ankle injuries. Patients who fail conservative treatments are candidates for modified Broström operation (MBO). Traditionally, the primary surgical treatment performed is the open MBO. Recently, there has been an evolution in the arthroscopic treatment of lateral ankle injury. Several reports reveal biomechanically equivalent results of arthroscopic vs . open MBO when using matched cadaver pairs. Also there was no difference in the clinical or radiologic outcomes between the arthroscopic and open MBO in randomized controlled trial. Therefore, arthroscopic MBO is reasonable and good alternative treatment for lateral ankle injury. Actually new techniques of arthroscopic treatment for ankle injury is introduced about arthroscopic syndesmotic repair and arthroscopic deltoid repair. Arthroscopic techniques for ankle injuries seem to develop further in the future.
MeSH Terms
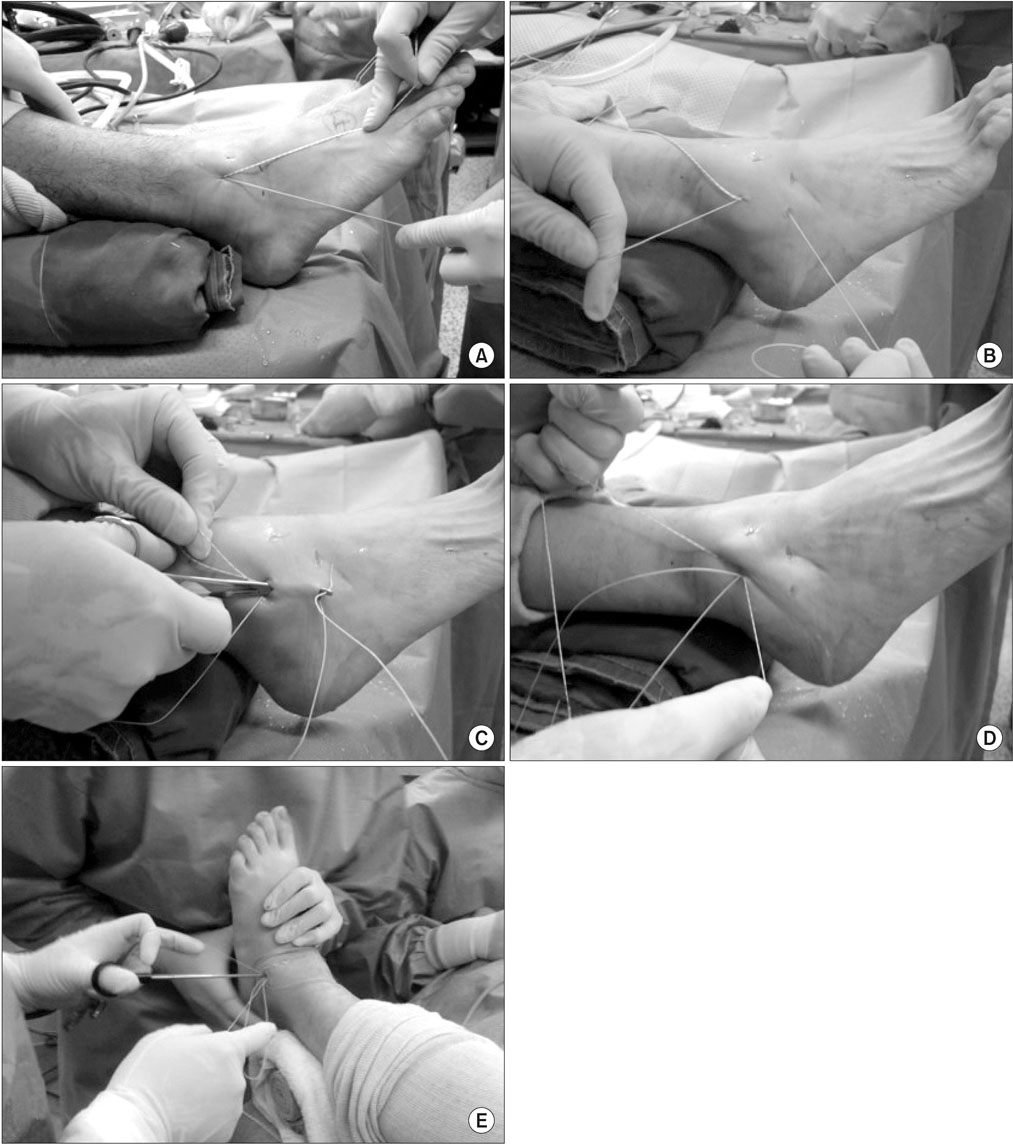
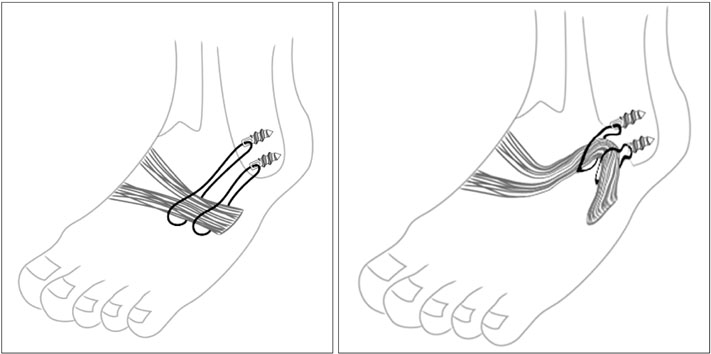
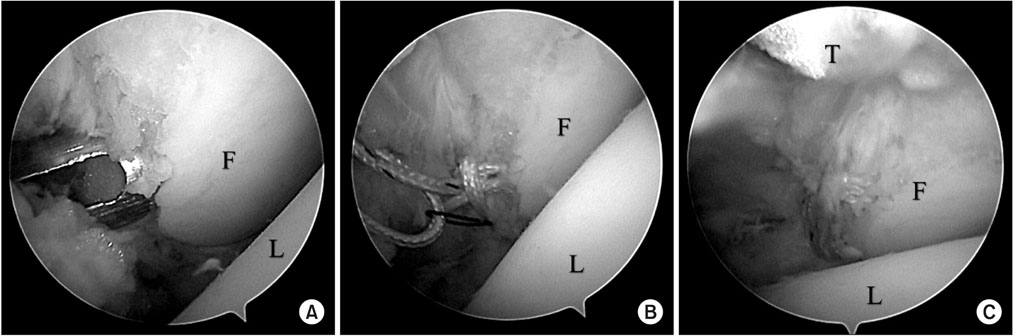
Figure
Reference
-
1. Acevedo JI, Mangone P. Arthroscopic brostrom technique. Foot Ankle Int. 2015; 36:465–473.
Article2. Corte-Real NM, Moreira RM. Arthroscopic repair of chronic lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2009; 30:213–217.3. Hu CY, Lee KB, Song EK, Kim MS, Park KS. Comparison of bone tunnel and suture anchor techniques in the modified Broström procedure for chronic lateral ankle instability. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:1877–1884.
Article4. Kim ES, Lee KT, Park JS, Lee YK. Arthroscopic anterior talofibular ligament repair for chronic ankle instability with a suture anchor technique. Orthopedics. 2011; 34:273.
Article5. Brostroem L. Sprained ankles. I. Anatomic lesions in recent sprains. Acta Chir Scand. 1964; 128:483–495.6. Lee KT, Park YU, Kim JS, Kim JB, Kim KC, Kang SK. Longterm results after modified Brostrom procedure without calcaneofibular ligament reconstruction. Foot Ankle Int. 2011; 32:153–157.
Article7. Lee KT, Kim ES, Kim YH, Ryu JS, Rhyu IJ, Lee YK. All-inside arthroscopic modified Bröstrom operation for chronic ankle instability: a biomechanical study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24:1096–1100.8. Yeo ED, Lee KT, Sung IH, Lee SG, Lee YK. Comparison of all-inside arthroscopic and open techniques for the modified Bröstrom procedure for ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2016; 37:1037–1045.9. Godin J, Sekiya JK. Systematic review of arthroscopic versus open repair for recurrent anterior shoulder dislocations. Sports Health. 2011; 3:396–404.
Article10. Strauss JE, Forsberg JA, Lippert FG 3rd. Chronic lateral ankle instability and associated conditions: a rationale for treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:1041–1044.
Article11. Hawkins RB. Arthroscopic stapling repair for chronic lateral instability. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 1987; 4:875–883.12. Gould N, Seligson D, Gassman J. Early and late repair of lateral ligament of the ankle. Foot Ankle. 1980; 1:84–89.
Article13. Hamilton WG, Thompson FM, Snow SW. The modified Brostrom procedure for lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle. 1993; 14:1–7.
Article14. Scranton PE Jr, McDermott JE, Rogers JV. The relationship between chronic ankle instability and variations in mortise anatomy and impingement spurs. Foot Ankle Int. 2000; 21:657–664.
Article15. Komenda GA, Ferkel RD. Arthroscopic findings associated with the unstable ankle. Foot Ankle Int. 1999; 20:708–713.
Article16. Hintermann B, Boss A, Schäfer D. Arthroscopic findings in patients with chronic ankle instability. Am J Sports Med. 2002; 30:402–409.
Article17. Thomas B, Yeo JM, Slater GL. Chronic pain after ankle fracture: an arthroscopic assessment case series. Foot Ankle Int. 2005; 26:1012–1016.
Article18. Hua Y, Chen S, Li Y, Chen J, Li H. Combination of modified Broström procedure with ankle arthroscopy for chronic ankle instability accompanied by intra-articular symptoms. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26:524–528.
Article19. Yeo ED, Rhyu IJ, Kim HJ, Kim DS, Ahn JH, Lee YK. Can Bassett's ligament be removed? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24:1236–1242.
Article20. Nery C, Raduan F, Del Buono A, Asaumi ID, Cohen M, Maffulli N. Arthroscopic-assisted Broström-Gould for chronic ankle instability: a long-term follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2011; 39:2381–2388.21. Acevedo JI, Mangone P. Ankle instability and arthroscopic lateral ligament repair. Foot Ankle Clin. 2015; 20:59–69.
Article22. Giza E, Shin EC, Wong SE, et al. Arthroscopic suture anchor repair of the lateral ligament ankle complex: a cadaveric study. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:2567–2572.23. Lee SH, Kim ES, Lee YK, Yeo ED, Oh SR. Arthroscopic syndesmotic repair: technical tip. Foot Ankle Int. 2015; 36:229–231.24. Han SH, Lee JW, Kim S, Suh JS, Choi YR. Chronic tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: the diagnostic efficiency of magnetic resonance imaging and comparative analysis of operative treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:336–342.
Article25. Lee TH, Jang KS, Choi GW, et al. The contribution of anterior deltoid ligament to ankle stability in isolated lateral malleolar fractures. Injury. 2016; 47:1581–1585.
Article26. Kim JG, Gwak HC, Lee MJ, et al. Arthroscopic deltoid repair: a technical tip. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017; 56:1253–1256.
Article27. Matsui K, Takao M, Miyamoto W, Innami K, Matsushita T. Arthroscopic Broström repair with Gould augmentation via an accessory anterolateral port for lateral instability of the ankle. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014; 134:1461–1467.
Article28. Takao M, Matsui K, Stone JW, et al. Arthroscopic anterior talofibular ligament repair for lateral instability of the ankle. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24:1003–1006.
Article29. Behrens SB, Drakos M, Lee BJ, et al. Biomechanical analysis of Brostrom versus Brostrom-Gould lateral ankle instability repairs. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34:587–592.
Article30. Lee KT, Lee JI, Sung KS, et al. Biomechanical evaluation against calcaneofibular ligament repair in the Brostrom procedure: a cadaveric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008; 16:781–786.
Article31. Aydogan U, Glisson RR, Nunley JA. Extensor retinaculum augmentation reinforces anterior talofibular ligament repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 442:210–215.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ligament Repair in Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability: Efficacy and Technique of Broström Procedures
- Risk Factors for Failure after Lateral Ankle Ligament Repair
- Surgical Outcomes of Arthroscopic Modified Brostrom Procedure in Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability
- Arthroscopic Procedure in the Treatment of Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability
- Arthroscopic Findings and Treatment of Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability