Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2018 Feb;22(1):11-18. 10.14701/ahbps.2018.22.1.11.
Gas-forming pyogenic liver abscess: A world review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore.
- 2Department of General Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore, Singapore. vishal_g_shelat@ttsh.com.sg
- KMID: 2409075
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2018.22.1.11
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
Gas-forming pyogenic liver abscess (GFPLA) has an incidence of up to 30% of all pyogenic liver abscesses (PLA). GFPLA has higher mortality compared to non-GFPLA. Mere presence of gas within abscess may not determine clinical outcome. Hence it is important to study biologic characteristics that make GFPLA a distinct clinical entity. The aim of this study was to conduct a world review on GFPLA.
METHODS
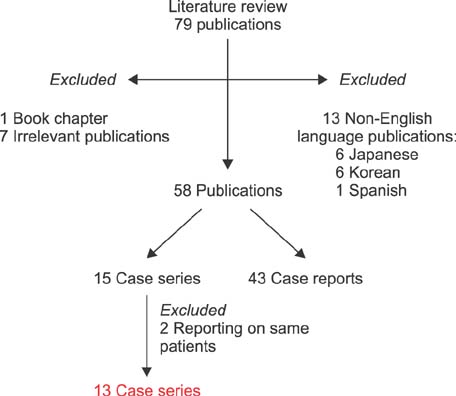
We conducted literature searches in PubMed using the following MeSH terms: "gas forming" AND "Liver abscess, pyogenic", "gas" AND "Liver abscess, pyogenic", "gas" AND "Liver abscess", "gas forming" AND "Liver abscess". Thirteen case series including 313 GFPLA patients were included. Age, gender, diabetes mellitus (DM), bacteriology, underlying etiology, symptoms, investigations, operative indications, and mortality rates were tabulated.
RESULTS
GFPLA is often cryptogenic. There was no difference in age, gender, or symptomatology between GFPLA and non-GFPLA patients. DM was more common in patients with GFPLA compared to that in non-GFPLA patients (mean: 83.5% vs. 38.3%). Klebsiella pneumoniae is the most common causative pathogen. GFPLA has higher mortality compared to non-GFPLA (mean: 30.3% vs. 9%).
CONCLUSIONS
GFPLA is associated with DM and monomicrobial Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. GFPLA has high mortality. It needs to be recognized as a distinct clinical entity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
간농양 파열로 인한 복막염의 비수술적 치료 증례
Hee Jun Myung, Soo Hyung Ryu, Chung Hao Liu, Jung Hoon Yoo, Seo Hyun Kim, Seung Hyuk Kim, Won Eui Yoon, Tae Young Park, Jeong Seop Moon
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2021;77(4):190-193. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2021.005.
Reference
-
1. Mohsen AH, Green ST, Read RC, McKendrick MW. Liver abscess in adults: ten years experience in a UK centre. QJM. 2002; 95:797–802.
Article2. Smith RS. Pyogenic liver abscess in the aged. Am J Surg. 1944; 63:206–213.
Article3. Yang CC, Chen CY, Lin XZ, Chang TT, Shin JS, Lin CY. Pyogenic liver abscess in Taiwan: emphasis on gas-forming liver abscess in diabetics. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993; 88:1911–1915.4. Lee TY, Wan YL, Tsai CC. Gas-containing liver abscess: radiological findings and clinical significance. Abdom Imaging. 1994; 19:47–52.
Article5. Shiina S, Tateishi R, Arano T, Uchino K, Enooku K, Nakagawa H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year outcome and prognostic factors. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:569–577.
Article6. Huang SF, Ko CW, Chang CS, Chen GH. Liver abscess formation after transarterial chemoembolization for malignant hepatic tumor. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003; 50:1115–1118.7. Shelat VG, Chia CL, Yeo CS, Qiao W, Woon W, Junnarkar SP. Pyogenic liver abscess: Does Escherichia coli cause more adverse outcomes than Klebsiella pneumoniae? World J Surg. 2015; 39:2535–2542.
Article8. Ahmed S, Chia CL, Junnarkar SP, Woon W, Shelat VG. Percutaneous drainage for giant pyogenic liver abscess--is it safe and sufficient? Am J Surg. 2016; 211:95–101.
Article9. Chou FF, Sheen-Chen SM, Chen YS, Chen MC, Chen FC, Tai DI. Prognostic factors for pyogenic abscess of the liver. J Am Coll Surg. 1994; 179:727–732.10. Chou FF, Sheen-Chen SM, Chen YS, Lee TY. The comparison of clinical course and results of treatment between gas-forming and non-gas-forming pyogenic liver abscess. Arch Surg. 1995; 130:401–405.
Article11. Chen SC, Tsai SJ, Chen CH, Huang CC, Lin DB, Wang PH, et al. Predictors of mortality in patients with pyogenic liver abscess. Neth J Med. 2008; 66:196–203.12. Chen SC, Huang CC, Tsai SJ, Yen CH, Lin DB, Wang PH, et al. Severity of disease as main predictor for mortality in patients with pyogenic liver abscess. Am J Surg. 2009; 198:164–172.
Article13. Lee HL, Lee HC, Guo HR, Ko WC, Chen KW. Clinical significance and mechanism of gas formation of pyogenic liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:2783–2785.14. Foo NP, Chen KT, Lin HJ, Guo HR. Characteristics of pyogenic liver abscess patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:328–335.
Article15. Lin YT, Wang FD, Wu PF, Fung CP. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in diabetic patients: association of glycemic control with the clinical characteristics. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:56.
Article16. Wang J, Yan Y, Xue X, Wang K, Shen D. Comparison of pyogenic liver abscesses caused by hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae and non-Klebsiella pneumoniae pathogens in Beijing: a retrospective analysis. J Int Med Res. 2013; 41:1088–1097.
Article17. Jun CH, Yoon JH, Wi JW, Park SY, Lee WS, Jung SI, et al. Risk factors and clinical outcomes for spontaneous rupture of pyogenic liver abscess. J Dig Dis. 2015; 16:31–36.
Article18. Chen C, Chen PJ, Yang PM, Huang GT, Lai MY, Tsang YM, et al. Clinical and microbiological features of liver abscess after transarterial embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92:2257–2259.19. Li J, Fu Y, Wang JY, Tu CT, Shen XZ, Li L, et al. Early diagnosis and therapeutic choice of Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess. Front Med China. 2010; 4:308–316.
Article20. Alkofer B, Dufay C, Parienti JJ, Lepennec V, Dargere S, Chiche L. Are pyogenic liver abscesses still a surgical concern? A Western experience. HPB Surg. 2012; 2012:316013.
Article21. Shelat VG, Wang Q, Chia CL, Wang Z, Low JK, Woon WW. Patients with culture negative pyogenic liver abscess have the same outcomes compared to those with Klebsiella pneumoniae pyogenic liver abscess. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2016; 15:504–511.
Article22. Chemaly RF, Hall GS, Keys TF, Procop GW. Microbiology of liver abscesses and the predictive value of abscess gram stain and associated blood cultures. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2003; 46:245–248.
Article23. Lo JZ, Leow JJ, Ng PL, Lee HQ, Mohd Noor NA, Low JK, et al. Predictors of therapy failure in a series of 741 adult pyogenic liver abscesses. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015; 22:156–165.
Article24. Sartelli M, Weber DG, Ruppé E, Bassetti M, Wright BJ, Ansaloni L, et al. Antimicrobials: a global alliance for optimizing their rational use in intra-abdominal infections (AGORA). World J Emerg Surg. 2016; 11:33.25. Koti RS, Kanoria S, Davidson BR. The liver. In : Williams NS, Bulstrode CJK, O'Connell PR, editors. Bailey & Love's short practice of surgery. 26th ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press;2013. p. 1080.26. Sartelli M, Abu-Zidan FM, Catena F, Griffiths EA, Di Saverio S, Coimbra R, et al. Global validation of the WSES Sepsis Severity Score for patients with complicated intra-abdominal infections: a prospective multicentre study (WISS Study). World J Emerg Surg. 2015; 10:61.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases Of Gas-Forming Liver Abscesses Successfully Treated By Early Pigtail Catheter Drainage
- A Case of Gas-forming Pyogenic Liver Abscess in a Diabetic Patient
- Comparison of Liver Abscess between Diabetic Patients and Non-Diabetic Patients
- Clinical features of gas-forming liver abscesses: comparison between diabetic and nondiabetic patients
- Ruptured Gas-forming Pyogenic Liver Abscess into the Peritoneal Cavity Treated Successfully with Medical Treatment