Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Apr;32(2):158-159. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0135.
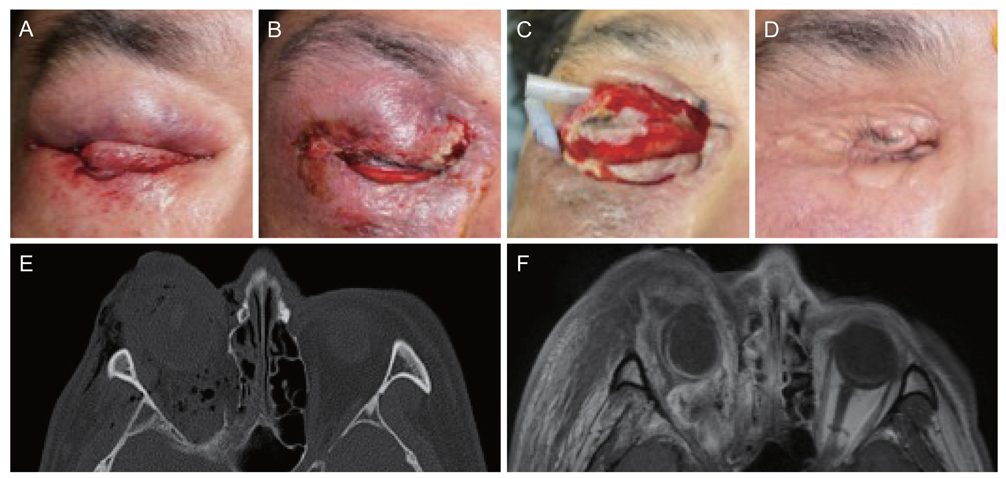
Orbital Cellulitis from an Orbital Compressed Air and Diesel Explosion Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Biomedical Research Institute, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea. ahnmin@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2408958
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0135
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Li T, Mafee MF, Edward DP. Bilateral orbital emphysema from compressed air injury. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 128:103–104.
Article2. Park JH, Jang JW, Kim SJ, Lee YJ. Traumatic optic neuropathy accompanying orbital grease gun injury. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2010; 24:134–138.
Article3. Mellington FE, Bacon AS, Abu-Bakra MA, et al. Orbital compressed air and petroleum injury mimicking necrotizing fasciitis. J Emerg Med. 2014; 47:e69–e72.
Article4. Rabinowitz MP, Goldstein SM. Diesel fuel injury to the orbit. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 29:e31–e33.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical course of compressed air injury with pneumocephlaus and orbital emphysema: a case report
- Orbital Emphysema and Pneumocephalus Caused by Compressed Air Injury
- Orbital Emphysema Causing Eye Movement Restriction Without Orbital Fractures Due to Compressed Air Injury
- Retinoblastoma Manifested by Hyphema and Orbital Cellulitis
- A Case ef Orbital Cellulitis Subdural Subdural Abscess