Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Apr;32(2):126-133. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0092.
Scleral Buckling under a Slit-lamp Illumination System with a Contact Wide-angle Viewing Lens Compared with an Indirect Ophthalmoscope
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkyh@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Catholic Institute for Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2408952
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0092
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the outcomes of scleral buckling surgery performed under a slit-lamp illumination system (Visulux) with a contact wide-angle viewing lens (Mini Quad) in patients with rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) and to compare these outcomes with those of surgery performed under an indirect ophthalmoscope.
METHODS
By retrospective review of electronic medical records, patients with RRD who had undergone scleral buckling surgery were identified. Scleral buckling surgeries were performed with two illumination instruments, a slit-lamp (SL group) and an indirect ophthalmoscope (IO group). Subretinal fluid drainage, cryopexy, and intravitreal gas injection were performed optionally. At 6 months after surgery, anatomical and functional outcomes were evaluated and compared between the two groups. Operation time was also compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
Of the 45 total patients (45 eyes), 28 were included in the SL group, and 17 were included in the IO group. In the SL and IO groups, the primary anatomical success rate was 89.3% and 88.2%, respectively (p = 0.92). The logarithm of the minimal angle of resolution change, which reflects improvement in best-corrected visual acuity after surgery, was −0.19 ± 0.38 in the SL group and −0.21 ± 0.63 in the IO group; this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.91). The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the SL group (78.9 ± 11.8 minutes) than in the IO group (100.0 ± 13.9 minutes, p < 0.001), especially for patients who underwent additional procedures such as subretinal fluid drainage and cryopexy (81.4 ± 12.9 and 103.5 ± 12.3 minutes, respectively, p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Scleral buckling surgery performed under a slit-lamp illumination system yielded a similar anatomical success rate and similar functional improvement in RRD compared with surgery performed under an indirect ophthalmoscope. The slit-lamp system could save time, especially in bullous RRD, which requires additional subretinal fluid drainage.
MeSH Terms
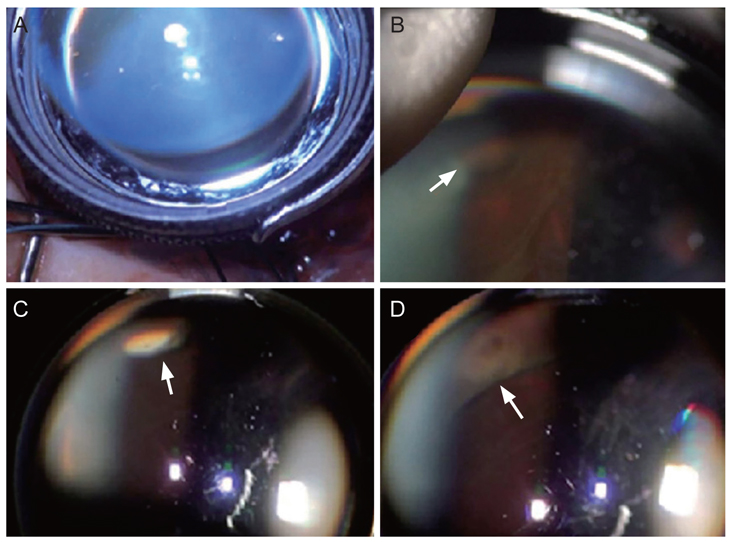
Figure
Reference
-
1. Escoffery RF, Olk RJ, Grand MG, Boniuk I. Vitrectomy without scleral buckling for primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985; 99:275–281.
Article2. Ho CL, Chen KJ, See LC. Selection of scleral buckling for primary retinal detachment. Ophthalmologica. 2002; 216:33–39.
Article3. Schwartz SG, Flynn HW. Primary retinal detachment: scleral buckle or pars plana vitrectomy? Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2006; 17:245–250.
Article4. Schepens CL, Okamura ID, Brockhurst RJ. The scleral buckling procedures. I. Surgical techniques and management. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1957; 58:797–811.5. Aras C, Ucar D, Koytak A, Yetik H. Scleral buckling with a non-contact wide-angle viewing system. Ophthalmologica. 2012; 227:107–110.
Article6. Narayanan R, Tyagi M, Hussein A, et al. Scleral buckling with wide-angled endoillumination as a surgical educational tool. Retina. 2016; 36:830–833.
Article7. Gogia V, Venkatesh P, Gupta S, et al. Endoilluminator-assisted scleral buckling: our results. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2014; 62:893–894.
Article8. Hu Y, Si S, Xu K, et al. Outcomes of scleral buckling using chandelier endoillumination. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017; 95:591–594.
Article9. Seider MI, Nomides RE, Hahn P, et al. Scleral buckling with chandelier illumination. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2016; 11:304–309.
Article10. Zhang Z, Liang X, Sun D, Peng S. The scleral buckling of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment under the surgical microscope. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2011; 42:96–101.
Article11. Ohji M, Tano Y. Vitreoretinal surgery with slit-lamp illumination combined with a wide-angle-viewing contact lens. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:955–956.
Article12. McPherson SD Jr. A modified Zeiss operating slit-lamp microscope. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1968; 66:419–420.
Article13. Bonnet M. Biomicroscopy of the fundus in retinal detachment surgery. J Fr Ophtalmol. 1979; 2:209–216.14. The repair of rhegmatogenous retinal detachments. American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:1313–1324.15. Sharma A, Grigoropoulos V, Williamson TH. Management of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with inferior breaks. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004; 88:1372–1375.
Article16. Park SW, Kwon HJ, Kim HY, et al. Comparison of scleral buckling and vitrectomy using wide angle viewing system for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in patients older than 35 years. BMC Ophthalmol. 2015; 15:121.
Article17. Setlur VJ, Rayess N, Garg SJ, et al. Combined 23-gauge PPV and scleral buckle versus 23-gauge PPV alone for primary repair of pseudophakic rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2015; 46:702–707.
Article18. Haug SJ, Jumper JM, Johnson RN, et al. Chandelier-assisted external subretinal fluid drainage in primary scleral buckling for treatment of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Retina. 2016; 36:203–205.
Article19. Li XJ, Yang XP, Lyu XB. Comparison of scleral buckling using wide-angle viewing systems and indirect ophthalmoscope for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016; 9:1310–1314.
Article20. Temkar S, Takkar B, Azad SV, Venkatesh P. Endoillumination (chandelier) assisted scleral buckling for a complex case of retinal detachment. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016; 64:845–846.
Article21. Yan H. Scleral buckling with a noncontact wide-angle viewing system in the management of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2017; 27:98–103.
Article22. Nawrocki J, Michalewska Z, Michalewski J. Optic Fibre Free Intravitreal Surgical System (OFFISS) in retinal detachment surgery. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2008; 39:466–470.
Article23. Pagot V, Mathis A, Heldenbergh O, et al. Surgery of retinal detachment of patients with pseudophakia using the panfunduscope. J Fr Ophtalmol. 1992; 15:587–591.