J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2018 Mar;25(1):9-17. 10.4184/jkss.2018.25.1.9.
Treatment of Multiple Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Spine Fractures: Comparison of Contiguous and Non-Contiguous Fractures in Non-Osteoporotic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. hmsohn@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2408302
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2018.25.1.9
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the outcomes of multiple thoracolumbar and lumbar fractures depending on whether the fractures were contiguous. SUMMARY OF THE LITERATURE REVIEW: The treatment of multiple spine fractures in patients without osteoporosis has rarely been reported.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
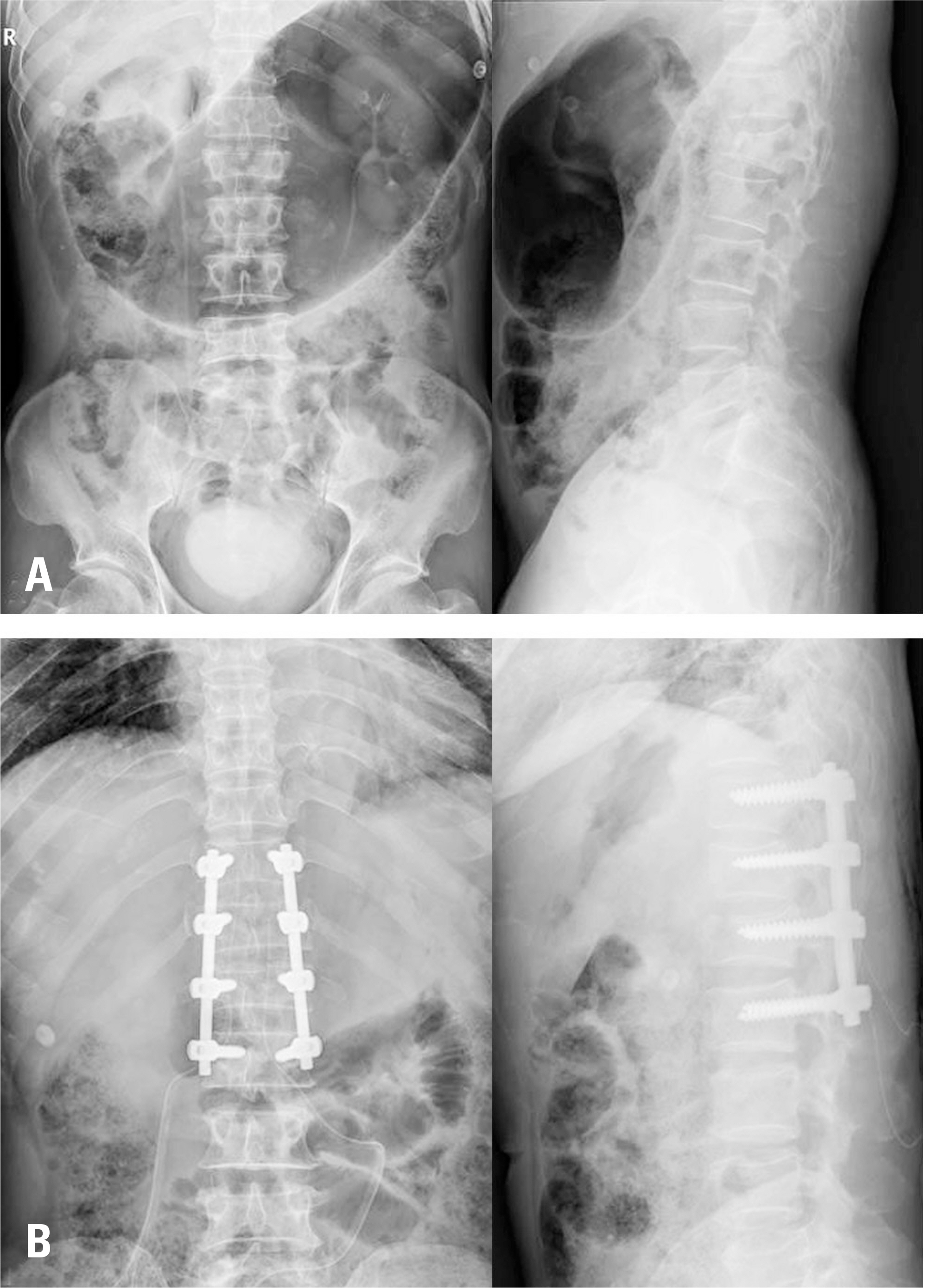
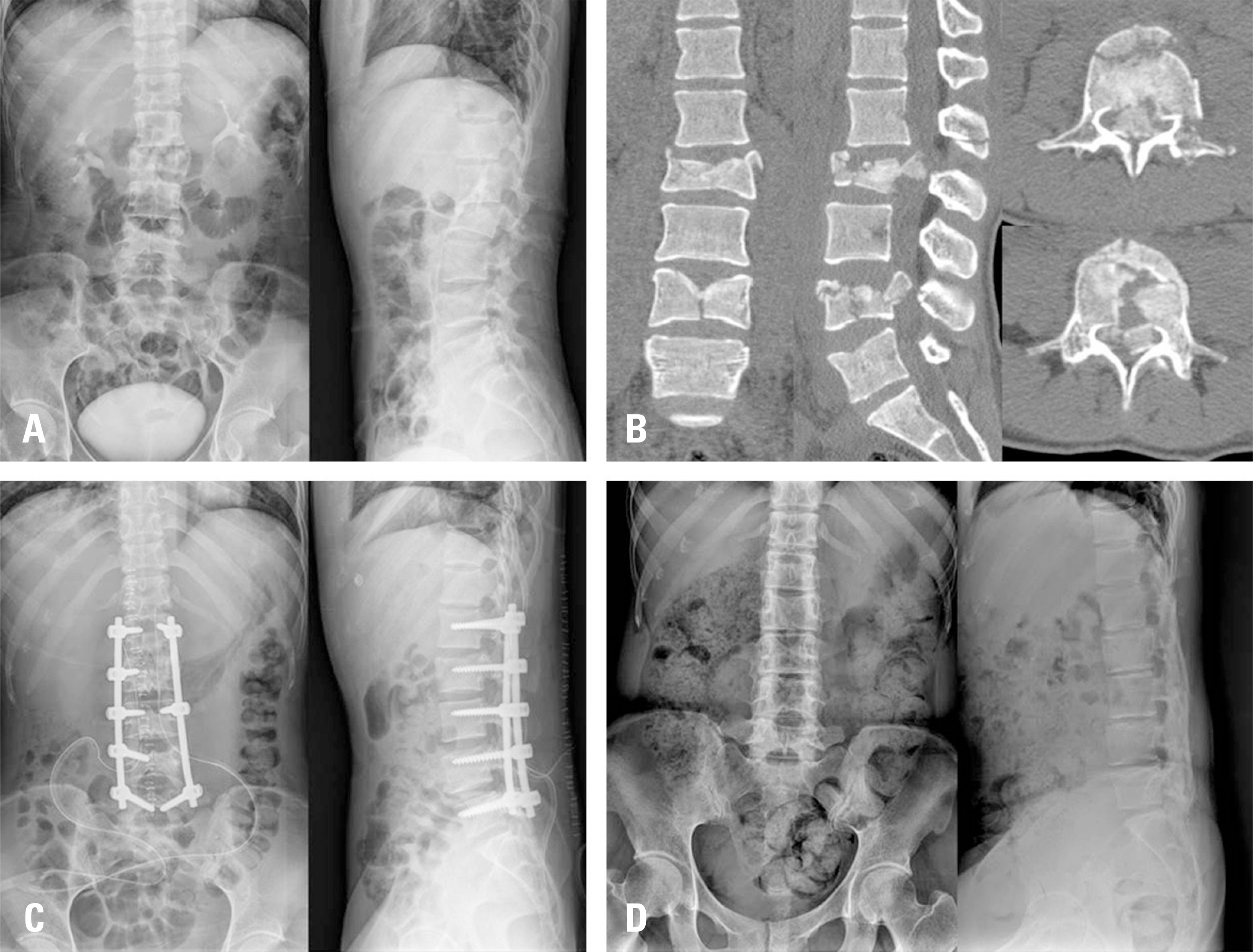
From February 2004 to January 2016, 81 patients without osteoporosis who had acute thoracolumbar and lumbar fractures and underwent posterior fusion surgery were evaluated. Patients were divided into 2 groups (group A: contiguous, group B: non-contiguous). We investigated the causes of the injuries, the locations of the injuries within the spine, the range of fusion levels, and functional outcomes based on the patients' general characteristics.
RESULTS
Group A comprised 37 patients and group B comprised 44 patients. In most patients, the fusion included 3 segments (group A: 12, group B: 14) or 4 segments (group A: 9, group B: 10). Group A scored 21.2 and group B scored 19.0 on the Korean Oswestry Disability Index. In both groups, longer fusion was associated with poorer clinical results. In the clinical evaluation of the fusion rate, there was no statistically significant difference between the 2 groups (p=0.446).
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, patients with multiple vertebral fractures showed more fusion segments and poor clinical outcomes in contiguous fractures. In the patients with non-contiguous fractures, the clinical results were better when a minimal number of segments was fused. Therefore, the authors recommend conservative treatment to minimize the number of segments that are fused in non-contiguous multiple thoracolumbar and lumbar fractures when decompression is not necessary.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wittenberg RH, Hargus S, Steffen R, et al. Noncontiguous unstable spine fractures. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2002 Feb; 27(3):254–7. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-200202010-00010.
Article2. Kano S, Tanikawa H, Mogami Y, et al. Comparison between continuous and discontinuous multiple vertebral compression fractures. Eur Spine J. 2012 Sep; 21(9):186772. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-012-2210-6.
Article3. Dai LY, Jia LS. Multiple non-contiguous injuries of the spine. Injury. 1996 Oct; 27(8):573–5. DOI: 10.1016/s0020-1383 (96)00074-5.
Article4. McAfee PC, Yuan HA, Fredrickson BE, et al. The value of computed tomography in thoracolumbar fractures. An analysis of one hundred consecutive cases and a new classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983 Apr; 65(4):461–73. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-198365040-00006.
Article5. Yoon SP, Lee SH, Ki CH, et al. Quality of life in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Asian Spine J. 2014 Oct; 8(5):653–8. DOI: 10.4184/asj.2014.8.5.653.
Article6. Calenoff L, Chessare JW, Rogers LF, Toerge J, Rosen JS. Multiple level spinal injuries: importance of early recognition. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978 Apr; 130(4):665–9. DOI: DOI:10.2214/ajr.130.4.665.
Article7. Powell JN, Waddell JP, Tucker WS, et al. Multiple-level noncontiguous spinal fractures. J Trauma. 1989 Aug; 29(8):1146–50. DOI: 10.1097/00005373-198908000-00013.
Article8. Chang HG, Kim YW, Kim YC, et al. Multiple spine fractures of young adult(over 3 vertebrae). J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2005 Sep; 12(3):206–13. DOI: 10.4184/jkss.2005.12.3.206.9. Seçer M, Alagöz F, Uçkun O, et al. Multilevel Noncontiguous Spinal Fractures: Surgical Approach towards Clinical Characteristics. Asian Spine J. 2015 Dec; 9(6):889–94. DOI: 10.4184/asj.2015.9.6.889.
Article10. Lian XF, Zhao J, Hou TS, Yuan JD, Jin GY, Li ZH. The treatment for multilevel noncontiguous spinal fractures. Int Orthop. 2007 Oct; 31(5):647–52. DOI: DOI:10.1007/s00264-006-0241-5.
Article11. Jorgensen DR, Joseph J Jr. Multiple noncontiguous spine fractures at four levels in a neurologically intact patient. J Trauma. 1996 Oct; 41(4):750–3. DOI: 10.1097/00005373-199610000-00027.
Article12. Korres DS, Boscainos PJ, Papagelopoulos PJ, et al. Multiple level noncontiguous fractures of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003 Jun; 411:95–102. DOI: 10.1097/01. blo.0000068362.47147.a2.
Article13. Henderson RL, Reid DC, Saboe LA. Multiple noncontiguous spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991 Feb; 16(2):128–31. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199116020-00005.
Article14. Thomas KC, Lalonde F, O'Neil J, et al. Multiple-level thoracolumbar burst fractures in teenaged patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003 Jan-Feb; 23(1):119–23. DOI: 10.1097/01241398-200301000-00024.
Article15. Korres DS, Katsaros A, Pantazopoulos T, et al. Double or multiple level fractures of the spine. Injury. 1981 Sep; 13(2):147–52. DOI: 10.1016/0020-1383 (81)90050-4.
Article16. Cho JL, Choi SW, Lee JM, et al. The changes of adjacent segments after long segment posterolateral fusion: comparative study of 3 year versus over the 7 year follow-up patients. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2005 Feb; 40(1):38–43. DOI: 10.4055/jkoa.2005.40.1.38.
Article17. Guven O, Kocaoglu B, Bezer M, et al. The use of screw at the fracture level in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009 Aug; 22(6):417–21. DOI: 10.1097/BSD.0b013e3181870385.
Article18. Jeong ST, Cho SH, Song HR, et al. Comparison of short and long-segment fusion in thoracic and lumbar fractures. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999 May; 6(1):73–80.19. Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, et al. Comparison of short fusion versus long fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2007 Dec; 42(6):795–802. DOI: 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.6.795.
Article20. Farcy JP, Weidenbaum M, Glassman SD. Sagittal index in management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1990 Sep; 15(9):958–65. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199009000-00022.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple Non-contiguous Spine Fractures with Concomitant Injuries: A Case Report
- Eleven Levels of Spinous Process Fractures in Thoracolumbar Spine
- Multiple Lumbar Osteoporotic Compression Fractures in a Patient in Her 20s - A Case Report -
- Non - Contiguous Multiple Spine Fracture
- Twelve Contiguous Spinous Process Fracture of Cervico-Thoracic Spine