J Korean Soc Radiol.
2018 Feb;78(2):81-87. 10.3348/jksr.2018.78.2.81.
Korean Clinical Imaging Guideline for Hemoptysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiolgoy, InJe University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Division of Healthcare Technology Assessment Research, National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jijung@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2408256
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.78.2.81
Abstract
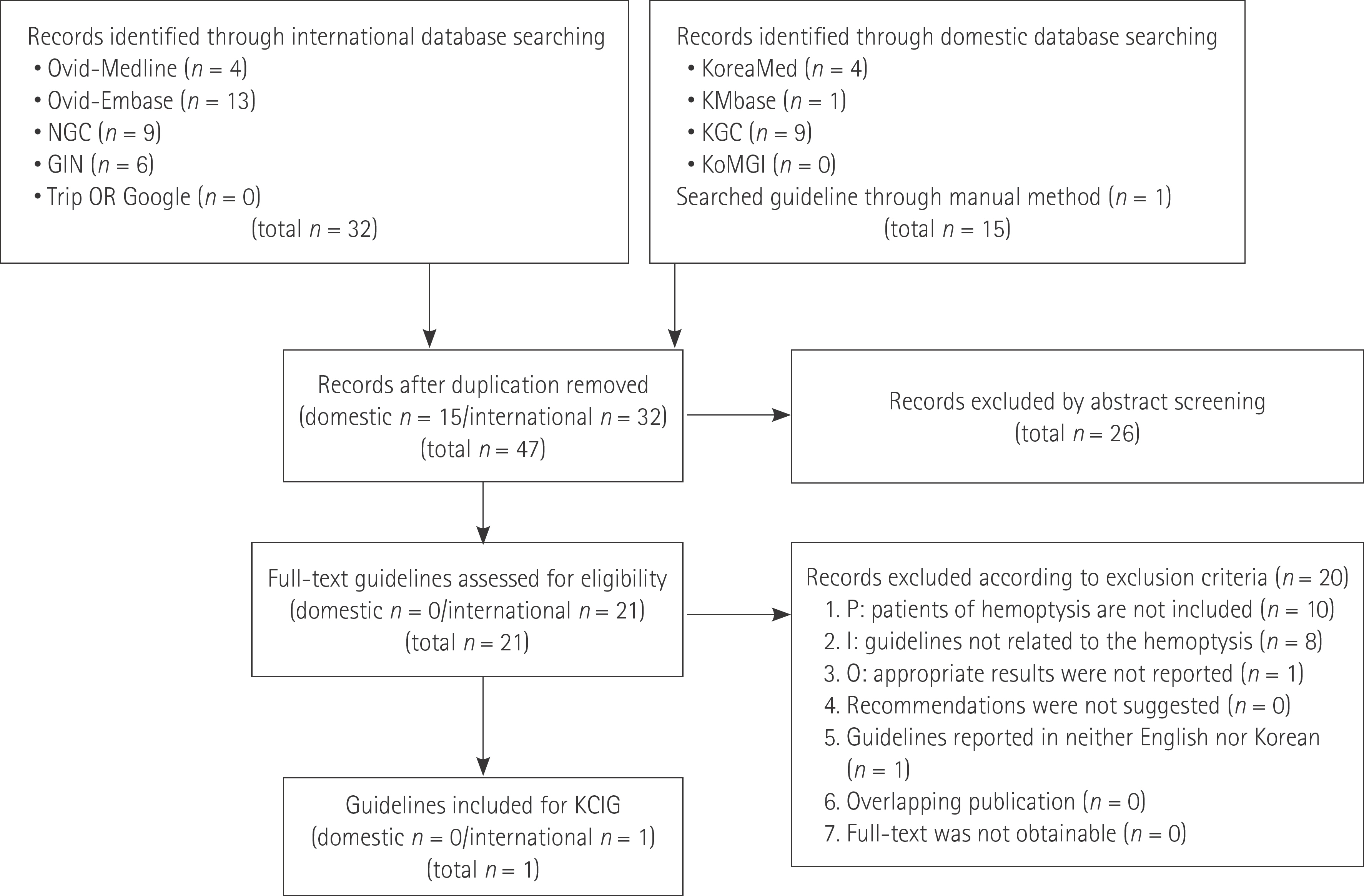
- In 2014, the American College of Radiology announced a guideline for appropriate diagnostic approach and treatment in patients with hemoptysis, according to severity of hemoptysis and risk of lung cancer. However, in Korea many patients have pulmonary fibrosis due to previous tuberculosis or have active tuberculosis. Therefore, application of this guideline is not appropriate. The Korean Society of Radiology and Korean Society of Thoracic Radiology proposed a guideline more closely matching the real state of diagnostic approach and treatment of patients with hemoptysis in Korea. The guideline was prepared in consensus by a development committee, working party, and an advisory committee. The process of the guideline proposal was based on methodology for developing evidence-based clinical imaging guidelines: joint recommendations by the Korean Society of Radiology and National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency. The clinical imaging guideline for adult patients with hemoptysis is as follows. Chest radiography is an initial imaging modality to evaluate hemoptysis. Contrast enhanced chest CT is recommended in patients with two lung cancer risks (> 40 years old and > 30 packs per year smoking history), moderate hemoptysis (> 30 cc/24 hours) or recurrent hemoptysis. Contrast enhanced chest CT is also recommended for patients with massive hemoptysis (> 400 mL/24 hours) without cardiopulmonary compromise.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® hemoptysis. Available at:. https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69449/Narrative/. Published. Aug, 2010. Accessed Jan 31, 2017.2. Choi SJ, Jeong WK, Jo AJ, Choi JA, Kim MJ, Lee M, et al. Methodology for developing evidence-based clinical imaging guidelines: joint recommendations by Korean Society of Radiology and National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency. Korean J Radiol. 2017; 18:208–216.
Article3. Tsoumakidou M, Chrysofakis G, Tsiligianni I, Maltezakis G, Siafakas NM, Tzanakis N. A prospective analysis of 184 hemoptysis cases: diagnostic impact of chest X-ray, computed tomography, bronchoscopy. Respiration. 2006; 73:808–814.4. Fidan A, Ozdog˘an S, Oruç O, Salepçi B, Ocal Z, Cag˘layan B. Hemoptysis: a retrospective analysis of 108 cases. Respir Med. 2002; 96:677–680.
Article5. Bruzzi JF, Rémy-Jardin M, Delhaye D, Teisseire A, Khalil C, Rémy J. Multi-detector row CT of hemoptysis. Radiographics. 2006; 26:3–22.
Article6. Lee SJ, Rho JY, Yoo SM, Kim MD, Lee JH, Kim EK, et al. Usefulness of multi-detector computed tomography before bronchoscopy and/or bronchial arterial embolization for hemoptysis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2010; 68:80–86.
Article7. Revel MP, Fournier LS, Hennebicque AS, Cuenod CA, Meyer G, Reynaud P, et al. Can CT replace bronchoscopy in the detection of the site and cause of bleeding in patients with large or massive hemoptysis? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 179:1217–1224.8. Delage A, Tillie-Leblond I, Cavestri B, Wallaert B, Marquette CH. Cryptogenic hemoptysis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: characteristics and outcome. Respiration. 2010; 80:387–392.
Article9. Menchini L, Remy-Jardin M, Faivre JB, Copin MC, Ramon P, Matran R, et al. Cryptogenic haemoptysis in smokers: angiography and results of embolisation in 35 patients. Eur Respir J. 2009; 34:1031–1039.
Article10. Poe RH, Israel RH, Marin MG, Ortiz CR, Dale RC, Wahl GW, et al. Utility of fiberoptic bronchoscopy in patients with hemoptysis and a nonlocalizing chest roentgenogram. Chest. 1988; 93:70–75.
Article11. Herth F, Ernst A, Becker HD. Long-term outcome and lung cancer incidence in patients with hemoptysis of unknown origin. Chest. 2001; 120:1592–1594.
Article12. Thirumaran M, Sundar R, Sutcliffe IM, Currie DC. Is investigation of patients with haemoptysis and normal chest radiograph justified? Thorax. 2009; 64:854–856.13. McGuinness G, Beacher JR, Harkin TJ, Garay SM, Rom WN, Naidich DP. Hemoptysis: prospective high-resolution CT/bronchoscopic correlation. Chest. 1994; 105:1155–1162.
Article14. Kim HB. Bronchial artery embolization. Korean Society of Interventional Radiology. ed.Interventional radiology. 2nd ed.Seoul: Ilchokak;2014. p. 321–325.15. Millar AB, Boothroyd AE, Edwards D, Hetzel MR. The role of computed tomography (CT) in the investigation of unexplained haemoptysis. Respir Med. 1992; 86:39–44.16. Khalil A, Fartoukh M, Parrot A, Bazelly B, Marsault C, Carette MF. Impact of MDCT angiography on the management of patients with hemoptysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:772–778.
Article17. Hsiao EI, Kirsch CM, Kagawa FT, Wehner JH, Jensen WA, Baxter RB. Utility of fiberoptic bronchoscopy before bronchial artery embolization for massive hemoptysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 177:861–867.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 2018 Korean Clinical Imaging Guideline for Hemoptysis
- The Causes and Clinical Course of Massive Hemoptysis
- Recurrent hemoptysis in a 26-year-old woman with a ground-glass opacity lesion of the lung
- Optimal time to localize bleeding focus and the usefulness of flexible bronchoscopy in hemoptysis
- Bronchial artery embolization: clinical analysis of 129 cases