Imaging Sci Dent.
2016 Sep;46(3):147-157. 10.5624/isd.2016.46.3.147.
Jaw lesions associated with impacted tooth: A radiographic diagnostic guide
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Medicine, School of Dentistry, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. m-baharvand@sbmu.ac.ir
- KMID: 2408246
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2016.46.3.147
Abstract
- This review article aimed to introduce a category of jaw lesions associated with impacted tooth. General search engines and specialized databases such as Google Scholar, PubMed, PubMed Central, MedLine Plus, Science Direct, Scopus, and well-recognized textbooks were used to find relevant studies using keywords such as "jaw lesion", "jaw disease", "impacted tooth", and "unerupted tooth". More than 250 articles were found, of which approximately 80 were broadly relevant to the topic. We ultimately included 47 articles that were closely related to the topic of interest. When the relevant data were compiled, the following 10 lesions were identified as having a relationship with impacted tooth: dentigerous cysts, calcifying odontogenic cysts, unicystic (mural) ameloblastomas, ameloblastomas, ameloblastic fibromas, adenomatoid odontogenic tumors, keratocystic odontogenic tumors, calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors, ameloblastic fibro-odontomas, and odontomas. When clinicians encounter a lesion associated with an impacted tooth, they should first consider these entities in the differential diagnosis. This will help dental practitioners make more accurate diagnoses and develop better treatment plans based on patients' radiographs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
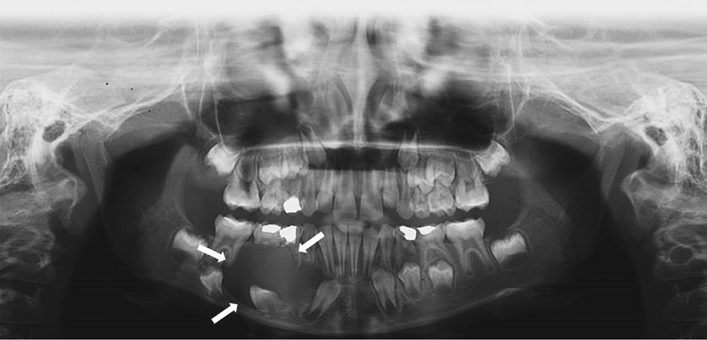
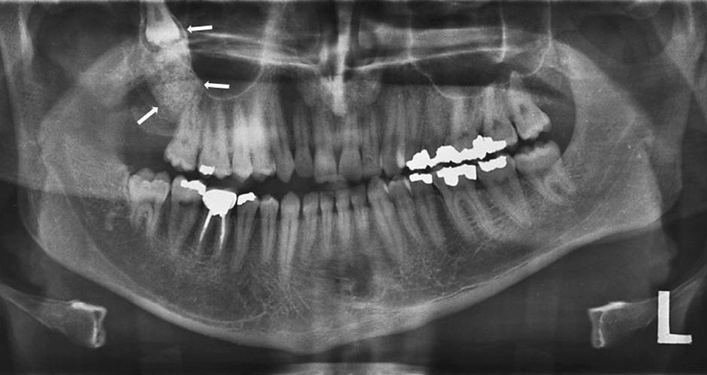
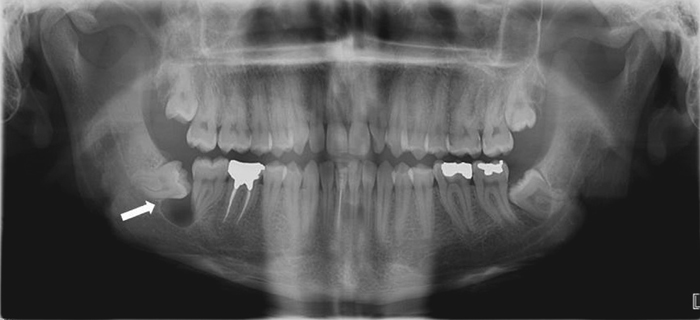
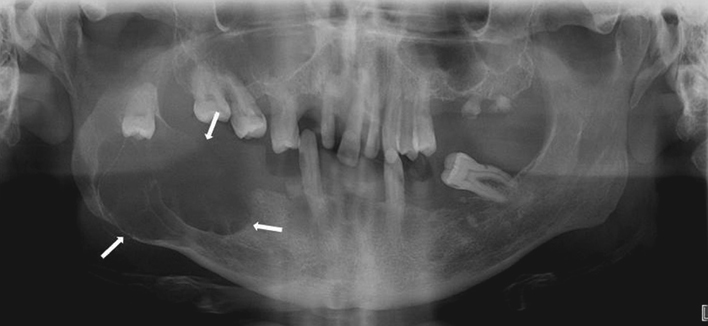
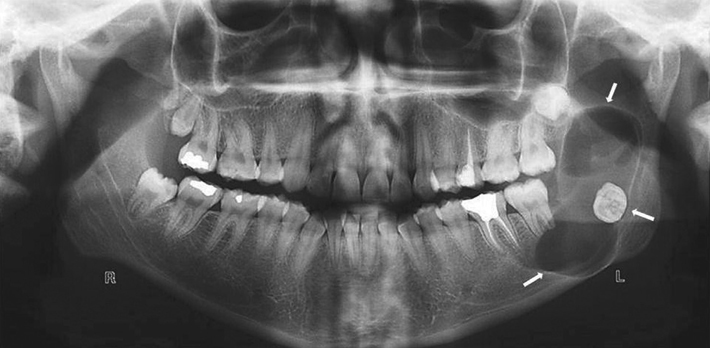
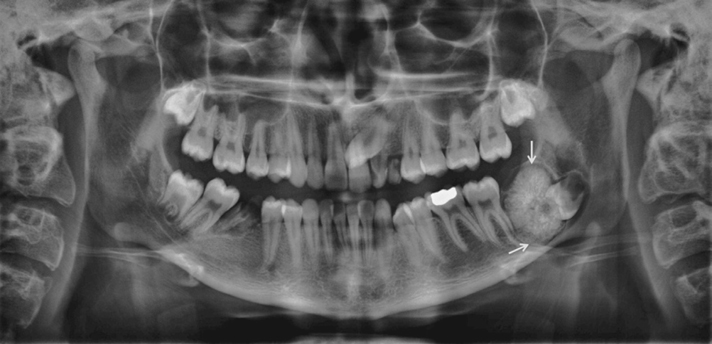
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Giant complex odontoma in the posterior mandible: A case report and literature review
Jong Chan Park, Ji Ho Yang, Sung Youn Jo, Bong Chul Kim, Jun Lee, Wan Lee
Imaging Sci Dent. 2018;48(4):289-293. doi: 10.5624/isd.2018.48.4.289.Common conditions associated with displacement of the inferior alveolar nerve canal: A radiographic diagnostic aid
Hamed Mortazavi, Maryam Baharvand, Yaser Safi, Mohammad Behnaz
Imaging Sci Dent. 2019;49(2):79-86. doi: 10.5624/isd.2019.49.2.79.
Reference
-
1. Juodzbalys G, Daugela P. Mandibular third molar impaction: review of literature and a proposal of a classification. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2013; 4:e1.
Article2. Peterson LJ. Principles of management of impacted teeth. In : Peterson LJ, Ellis E, Hupp JR, Tuker MR, editors. Contemporary oral and maxillofacial surgery. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby-Yearbook Inc;1998. p. 215–248.3. Chu FC, Li TK, Lui VK, Newsome PR, Chow RL, Cheung LK. Prevalence of impacted teeth and associated pathologies-a radiographic study of the Hong Kong Chinese population. Hong Kong Med J. 2003; 9:158–163.4. Bedoya MM, Park JH. A review of the diagnosis and management of impacted maxillary canines. J Am Dent Assoc. 2009; 140:1485–1493.
Article5. Ahlqwist M, Gröndahl HG. Prevalence of impacted teeth and associated pathology in middle-aged and older Swedish women. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1991; 19:116–119.
Article6. Hugoson A, Kugelberg CF. The prevalence of third molars in a Swedish population. An epidemiological study. Community Dent Health. 1988; 5:121–138.7. Kruger E, Thomson WM, Konthasinghe P. Third molar outcomes from age 18 to 26: findings from a population-based New Zealand longitudinal study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001; 92:150–155.
Article8. Santosh P. Impacted mandibular third molars: review of literature and a proposal of a combined clinical and radiological classification. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2015; 5:229–234.
Article9. Mortazavi H, Baharvand M, Rahmani S, Jafari S, Parvaei P. Radiolucent rim as a possible diagnostic aid for differentiating jaw lesions. Imaging Sci Dent. 2015; 45:253–261.
Article10. Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Chi AC. Oral and maxillofacial pathology. St Louis: Elsevier;2016. p. 632–690.11. White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. 7th ed. St Louis: Elsevier;2014.12. Wood NK, Goaz PW. Differential diagnosis of oral and maxillofacial lesions. 5th ed. St Louis: Mosby-Yearbook Inc;1997.13. Rohilla M, Namdev R, Dutta S. Dentigerous cyst containing multiple impacted teeth: a rare case report. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2011; 29:244–247.
Article14. Agacayak KS, Kose I, Gunes N, Bahsi E, Yaman F, Atilgan S. Dentigerous cyst with impacted canine: case report. J Int Dent Med Res. 2011; 4:21–24.15. Wali GG, Sridhar V, Shyla HN. A study on dentigerous cystic changes with radiographically normal impacted mandibular third molars. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012; 11:458–465.
Article16. Avril L, Lombardi T, Ailianou A, Burkhardt K, Varoquaux A, Scolozzi P, et al. Radiolucent lesions of the mandible: a pattern-based approach to diagnosis. Insights Imaging. 2014; 5:85–101.
Article17. Gadipelly S, Reddy VB, Sudheer M, Kumar NV, Harsha G. Bilateral calcifying odontogenic cyst: a rare entity. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2015; 14:826–831.
Article18. Rastogi V, Pandilwar PK. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic cyst associated with complex odontome of maxilla. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2013; 12:85–89.
Article19. Rajendran R, Sivapathasundharam B. Shafer's textbook of oral pathology. 5th ed. New Delhi: Elsevier;2006. p. 357–432.20. Shiva A, Nosrati K. A calcifying odontogenic cyst associated with complex odontoma: a case report. J Babol Univ Med Sci. 2015; 17:57–61.21. Wang YP, Chang YF, Wang JT, Liu BY, Sun A, Chiang CP. Characteristics of calcifying odontogenic cyst in Taiwanese. J Formos Med Assoc. 2003; 102:715–721.22. Iida S, Fukuda Y, Ueda T, Aikawa T, Arizpe JE, Okura M. Calcifying odontogenic cyst: radiologic findings in 11 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 101:356–362.
Article23. Sharma B, Balaji N, Sumathi MK, Sunitha JD. Unicystic ameloblastoma of mandible - a diagnostic dilemma. TMU J Dent. 2014; 1:131–133.24. Nagalaxmi V, Sangmesh M, Maloth KN, Kodangal S, Chappidi V, Goyal S. Unicystic mural ameloblastoma: an unusual case report. Case Rep Dent. 2013; 2013:957418.
Article25. Gupta N, Saxena S, Rathod VC, Aggarwal P. Unicystic ameloblastoma of the mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2011; 15:228–231.
Article26. Gümgüm S, Hoşgören B. Clinical and radiologic behaviour of ameloblastoma in 4 cases. J Can Dent Assoc. 2005; 71:481–484.27. More C, Tailor M, Patel HJ, Asrani M, Thakkar K, Adalja C. Radiographic analysis of ameloblastoma: a retrospective study. Indian J Dent Res. 2012; 23:698.
Article28. Santos Tde S, Piva MR, Andrade ES, Vajgel A, Vasconcelos RJ, Martins-Filho PR. Ameloblastoma in the Northeast region of Brazil: a review of 112 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2014; 18:Suppl 1. S66–S71.
Article29. Melo Lde A, Barros AC, Sardinha Sde C, Cerqueira A, dos Santos JN. Ameloblastic fibroma: a rare case report with 7-year follow-up. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2015; 143:190–194.
Article30. Chen Y, Li TJ, Gao Y, Yu SF. Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference to their nature and interrelationship. J Oral Pathol Med. 2005; 34:588–595.
Article31. JK DR, Sharma A, Sharma S, Arya V, Das R. An aggressive ameloblastic fibroma in maxilla of a 5-year-old child - reconstruction of the defect with buccal flap advancement - a conservative approach. Int J Clin Med. 2015; 6:579–585.32. John JB, John RR. Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with dentigerous cyst in posterior maxilla: a case report and review of literature. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2010; 14:59–62.
Article33. More CB, Das S, Gupta S, Bhavsar K. Mandibular adenomatoid odontogenic tumor: radiographic and pathologic correlation. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2013; 4:457–462.
Article34. Mortazavi H, Sotoode SM, Khodadoustan A, Baharvand M. Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor: report of a rare case in terms of size and location. Int J Clin Dent. 2014; 7:235–240.35. Sánchez-Burgos R, González-Martín-Moro J, Pérez-Fernández E, Burgueño-García M. Clinical, radiological and therapeutic features of keratocystic odontogenic tumours: a study over a decade. J Clin Exp Dent. 2014; 6:e259–e264.
Article36. Borgonovo AE, Bernardini L, Francinetti P, Rizza F, Re D. Odontogenic keratocyst mimicking paradental cyst. Case Rep Dent. 2014; 2014:974241.
Article37. Singh M, Gupta KC. Surgical treatment of odontogenic keratocyst by enucleation. Contemp Clin Dent. 2010; 1:263–267.38. Deboni MC, Naclério-Homem Mda G, Pinto Junior DS, Traina AA, Cavalcanti MG. Clinical, radiological and histological features of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor: case report. Braz Dent J. 2006; 17:171–174.
Article39. Müller D, Manojlović S, Luksić I, Grgurević J. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor of the maxilla (Pindborg tumor). Coll Antropol. 2012; 36:Suppl 2. 205–208.40. Kaushal S, Mathur SR, Vijay M, Rustagi A. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (Pindborg tumor) without calcification: a rare entity. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2012; 16:110–112.
Article41. Cavalcante AS, Anbinder AL, Costa NC, Lima JR, Carvalho YR. Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma: a case report. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009; 14:e650–e653.
Article42. Chang H, Precious DS, Shimizu MS. Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma: a case report. J Can Dent Assoc. 2002; 68:243–246.43. Silva GC, Jham BC, Silva EC, Horta MC, Godinho SH, Gomez RS. Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma. Oral Oncol Extra. 2006; 42:217–220.44. Buchner A, Merrell PW, Carpenter WM. Relative frequency of central odontogenic tumors: a study of 1,088 cases from Northern California and comparison to studies from other parts of the world. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 64:1343–1352.
Article45. Philipsen HP, Reichart PA, Praetorius F. Mixed odontogenic tumours and odontomas. Considerations on interrelationship. Review of the literature and presentation of 134 new cases of odontomas. Oral Oncol. 1997; 33:86–99.
Article46. Baldawa RS, Khante KC, Kalburge JV, Kasat VO. Orthodontic management of an impacted maxillary incisor due to odontoma. Contemp Clin Dent. 2011; 2:37–40.
Article47. Choudhary PJ, Gharote HP, Hegde K, Gangwal P. Compound odontoma associated with impacted teeth: a case report. IJSS Case Rep Rev. 2014; 1:12–15.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple jaw cysts not associated with basal cell nevus syndrome
- Supernumerary teeth in non-syndromic patients
- Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases
- Which factors are associated with difficult surgical extraction of impacted lower third molars?
- A comparative Ki-67 expression of odontogenic keratocysts(OKCs) with or without impacted tooth