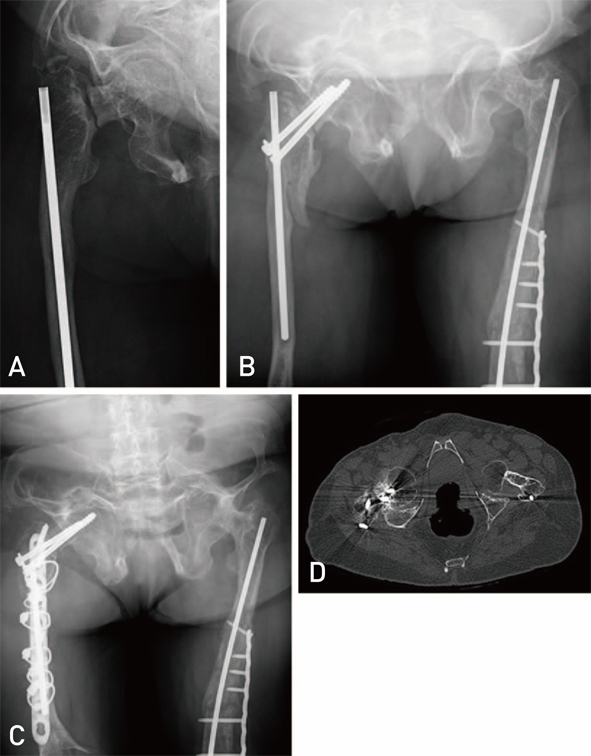
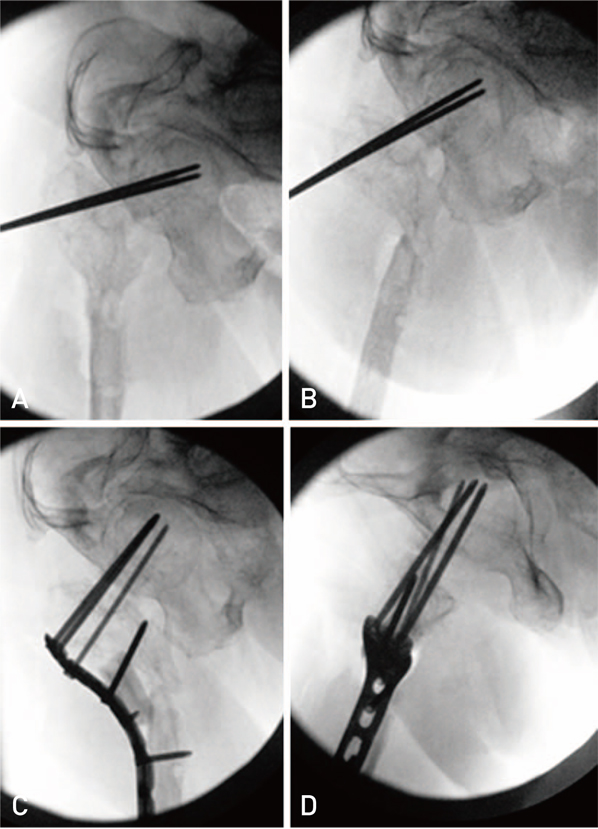
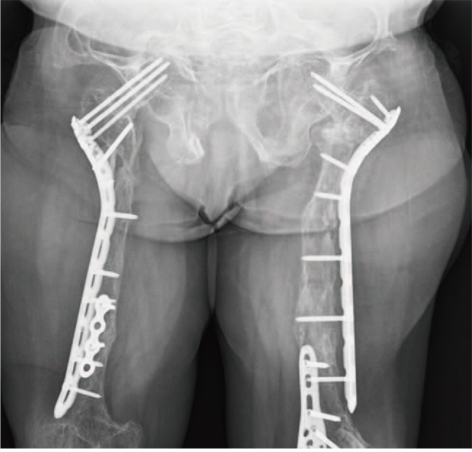
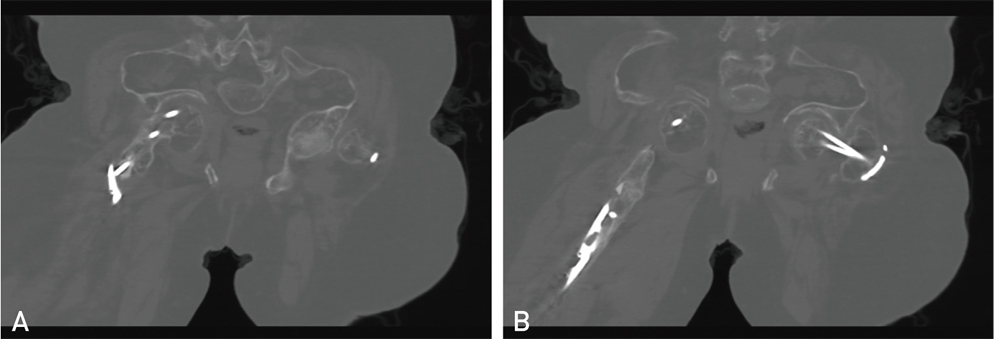
Hip Pelvis.
2018 Mar;30(1):53-59. 10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.53.
Pauwels Osteotomy for Femoral Neck Nonunion in Two Adult Siblings with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam Movement Sciences, Amsterdam, the Netherlands. p.kloen@amc.uva.nl
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Section Endocrinology, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
- 3Division of Orthopaedics, Shriners Hospital for Children, McGill University, Montreal, QU, Canada.
- KMID: 2408186
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.53
Abstract
- This is a retrospective review of two adult siblings with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) type III (according to Sillence classification), who sustained a spontaneous femoral neck fracture and subsequent nonunion. The diagnosis of OI in these two patients was made based on clinical, radiological and genetic findings. The fracture was most likely caused by femoroacetabular impingement secondary to OI induced acetabular protrusio. A valgus osteotomy according to Pauwels'principles and fixation of the osteotomy and nonunion with a locking plate resulted in healing despite compromised bone quality and limited bone stock. Long-term follow up (4.5 years and 6.5 years, respectively) is provided. When treating this difficult problem, improving the mechanobiological environment and decreasing the femoroacetabular impingement by a Pauwels type osteotomy should be considered.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Van Dijk FS, Sillence DO. Osteogenesis imperfecta: clinical diagnosis, nomenclature and severity assessment. Am J Med Genet A. 2014; 164A:1470–1481.
Article2. Gil JA, DeFroda SF, Sindhu K, Cruz AI Jr, Daniels AH. Challenges of fracture management for adults with osteogenesis imperfecta. Orthopedics. 2017; 40:e17–e22.
Article3. Violas P, Fassier F, Hamdy R, Duhaime M, Glorieux FH. Acetabular protrusion in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002; 22:622–625.
Article4. Aarabi M, Rauch F, Hamdy RC, Fassier F. High prevalence of coxa vara in patients with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006; 26:24–28.
Article5. Trehan SK, Morakis E, Raggio CL, Twomey KD, Green DW. Acetabular protrusio and proximal femur fractures in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Orthop. 2015; 35:645–649.
Article6. Pauwels F. [Basics of indication and technique of rearrangement in femoral neck pseudarthrosis]. Arch Klin Chir. 1949; 262:404–422. German.7. Chow W, Negandhi R, Kuong E, To M. Management pitfalls of fractured neck of femur in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Child Orthop. 2013; 7:195–203.
Article8. Papanna MC, Tafazal S, Bell MJ, Giles SN, Fernandes JA. Femoral neck fractures in osteogenesis imperfecta treated with bisphosphonates. J Child Orthop. 2017; 11:191–194.
Article9. Beck M, Leunig M, Clarke E, Ganz R. Femoroacetabular impingement as a factor in the development of nonunion of the femoral neck: a report of three cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:425–430.
Article10. Sanz-Ruiz P, Villanueva-Martinez M, Calvo-Haro JA, Carbo-Laso E, Vaquero-Martin J. Total femur arthroplasty for revision hip failure in osteogenesis imperfecta: limits of biology. Arthroplast Today. 2017; 3:154–159.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A radiologic study about effects of multiple osteotomy and intramedullary nail fixation upon changes of diaphyseal thickness in osteogenesis imperfecta
- Osteogenesis imperfecta and combined orthodontics and orthognathic surgery: a case report on two siblings
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Case Report
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta (Correction of Anterior Tibial Bowing): A case report
- A Case of Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Diagnosed in Uterus by Ultrasonogram