J Korean Acad Nurs Adm.
2018 Mar;24(2):149-160. 10.11111/jkana.2018.24.2.149.
Role Adaptation Process of Hospice Nurses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Keimyung College University, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Keimyung University, Korea. lbs@gw.kmu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2408122
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2018.24.2.149
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was performed to identify the role adaptation process of hospice nurses and suggest a model for the process.
METHODS
Grounded theory methodology was used. Twenty nurses participated in individual in-depth interviews. Data were collected until saturated. Questions for the interviews were about phenomenon, conditions, action/interaction strategies, and consequences in the process. Data were analyzed by applying open, axial and selective coding proposed by Strauss and Corbin.
RESULTS
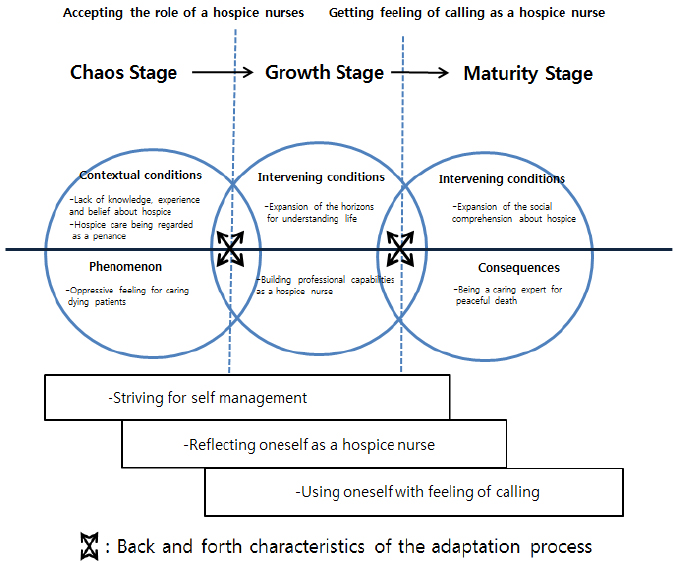
Core category of the role adaptation process was "˜building up real capabilities'. Phenomenon of the role adaptation was oppressive feelings when caring for dying patients. Contextual conditions were lack of knowledge, experience and belief about hospice and hospice care being regarded as penance. Intervening conditions were expansion of horizons in understanding life and expansion of social comprehension about hospice. Action/interaction strategies included "˜reflecting on oneself as a hospice nurse', "˜using oneself with feelings of a calling' and "˜striving for self-management'. Consequence of the process was being a caring expert for peaceful death.
CONCLUSION
The role adaptation process of hospice nurses for the participants was the process of building up real capabilities leading them to become caring experts for peaceful death through overcoming oppressive feeling when caring for dying patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi ES, Yoo YS, Kim HS, Lee SW. Curriculum development for hospice and palliative care nurses. Korean J Hosp Palliat Care. 2006; 9(2):77–85.2. Lee WH. Total pain of patient with terminal cancer. Korean J Hosp Palliat Care. 2000; 3(1):60–73.3. Shin MH, Shin SR. Predictors of burnout among oncology nurses. Asian Oncol Nurs. 2003; 3(1):75–84.4. Pereira SM, Fonseca AM, Carvlalho AS. Burnout in palliative care: A systematic review. Nurs Ethics. 2011; 18(3):317–326. DOI: 10.1177/0969733011398092.
Article5. Hawkins AC, Howard RA, Oyebode JR. Stress and coping in hospice nursing staff. The impact of attachment styles. Psychooncology. 2007; 16(6):563–572. DOI: 10.1002/pon.1064.
Article6. Sabo BM. Adverse psychosocial consequence: Compassion fatigue, burnout and vicarious traumatization: Are nurses who provide palliative and hematological cancer care vulnerable? Indian J Palliat Care. 2008; 14(1):23–29. DOI: 10.4103/0973-1075.41929.7. Kim HJ, Ku JI, Byun JH, Kim SM, Choe WS. Nurse's Experience of Changing Role in the Hospice Unit of Medical Ward. Korean J Hosp Palliat Care. 2008; 11(1):30–41.8. Choi YE. Predictors of Burnout among hospice nurses [master's thesis]. Daegu: Kyungpook National University;2013. 1–65.9. Chi KA, Kim EJ. Factors influencing nurse's attitude toward hospice. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2005; 14(3):285–291.10. Kennedy J. Demystifying the role of nurse practitioners in hospice: Nurse practitioners as an integral part of the hospice plan of care. Home Healthc Nurse. 2012; 30(1):48–51. DOI: 10.1097/NHH.0b013e31823aa87f.11. Borland R, Glackin M, Jordan J. How does involvement of a hospice nurse specialist impact on the experience on informal caring in palliative care? Perspectives of middle-aged partners bereaved through cancer. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2014; 23(5):701–711. DOI: 10.1111/ecc.12183.
Article12. Alkema K, Linton JM, Davies R. A study of the relationship between self-care, compassion satisfaction, compassion fatigue, and burnout among hospice professionals. J Soc Work End Life Palliat Care. 2008; 4(2):101–119. DOI: 10.1080/15524250802353934.
Article13. Nyatanga B. Avoiding burnout syndrome in palliative care. Br J Community Nurs. 2014; 19(10):515. DOI: 10.12968/bjcn.2014.19.10.515.
Article14. Schaffer M, Norlander L. Being present: A nurse's resource for end of life communication. Indianapolis: Sigma Theta Tau International;2009.15. Rosser M, King L. Transition experiences of qualified nurses moving into hospice nursing. J Adv Nurs. 2003; 43(2):206–215. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2003.02695.x.
Article16. Wu HL, Volker DL. Living with death and dying: The experience of Taiwanese hospice nurses. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2009; 36(5):578–584. DOI: 10.1188/09.ONF.578-584.
Article17. Kim BH, Choe SO, Chung BY, Yoo YS, Kim HS, Kang KA, et al. Job analysis for role identification of general hospice palliative nurse. Korean J Hosp Palliat Care. 2010; 13(1):13–23.
Article18. Shin KY, Koh MS, Kong BH, Kim KS, Kim MY, Kim EH, et al. A qualitative research methodology. Seoul: Ewha Womans University Press;2004.19. Jang KS. A study of establishment of clinical career development model of nurses [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2000. 1–212.20. Strauss AL, Corbin JM. Basics of qualitative research. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE;1998.21. Sandelowski M. The problem of rigor in qualitative research. ANS Adv Nurs Sci. 1986; 8(3):27–37.
Article22. Kwon SH, Yang SK, Park MH, Choe SO. Assessment for the needs to develop hospice training program for nurses. Korean J Hosp Palliat Care. 2008; 11(3):147–155.23. Kang SY, Koh MH, Choi JS. The experience of hospice nurses on spiritual care: The process of untying a knot of mind. Asian Oncol Nurs. 2008; 8(2):111–119.24. Suliman WA, Welmann E, Omer T, Thomas L. Applying Watson's nursing theory to assess patient perceptions of being cared for in a multicultural environment. J Nurs Res. 2009; 17(4):293–297. DOI: 10.1097/JNR.0b013e3181c122a3.
Article25. Son HM, Koh MH, Kim CM, Moon JH. The clinical experiences of adaptation as a new nursing staff. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2001; 31(6):988–997. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.988.
Article26. Kang SY. The role adaptation process in head nurses. [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University;2003.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role Adaptation Process of Head Nurses in the General Hospitals
- The Experience of Hospice Nurses on Spiritual Care: The Process of Untying a Knot of Mind
- Comparison of Death Orientation of Nurses before and after Hospice Training Program
- A Grounded Theory-Based Approach to Practice Adaptation Process of Hemodialysis Unit Nurses
- A Study on the Projected Manpower of Hospice and Palliative Care Nurses & APNs in Korea