Ann Lab Med.
2018 Jul;38(4):381-383. 10.3343/alm.2018.38.4.381.
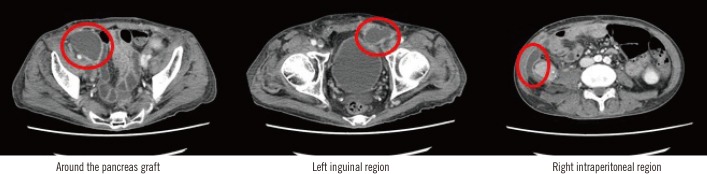
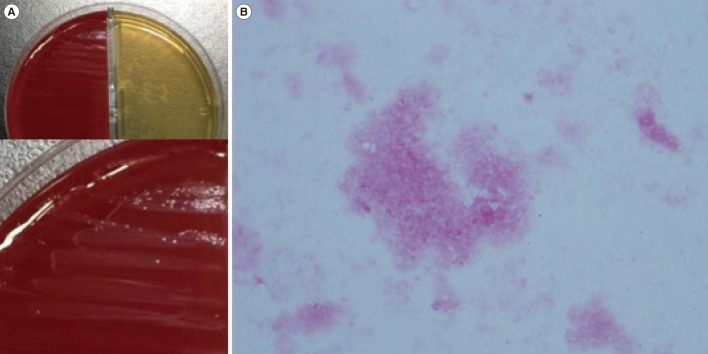
Multiple Intraabdominal Abscesses Caused by Mycoplasma hominis Infection Following Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Project Research Center for Nosocomial Infectious Diseases, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan. jyumiko@hiroshima-u.ac.jp
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases Laboratory, Department of Clinical Practice and Support, Hiroshima University Hospital, Hiroshima, Japan.
- 3Division of Laboratory Medicine, Hiroshima University Hospital, Hiroshima, Japan.
- 4Department of Infectious Diseases, Hiroshima University Hospital, Hiroshima, Japan.
- 5Hiroshima and Department of Gastroenterological and Transplant Surgery, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan.
- KMID: 2408081
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.4.381
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Meyer RD, Clough W. Extragenital Mycoplasma hominis infection in adults: emphasis on immunosuppression. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 17:S243–S249. PMID: 8399923.2. Blanchard A, Yañez A, Dybvig K, Watson HL, Griffiths G, Cassell GH. Evaluation of intraspecies genetic variation within the 16S rRNA gene of Mycoplasma hominis and detection by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1993; 31:1358–1361. PMID: 7684753.3. Sampath R, Patel R, Cunningham SA, Arif S, Daly RC, Badley AD, et al. Cardiothoracic transplant recipient Mycoplasma hominis: an uncommon infection with probable donor transmission. EBioMedicine. 2017; 19:84–90. PMID: 28438507.4. Horiuchi K, Matsumoto T, Ohno Y, Kasuga E, Negishi T, Yaguchi T, et al. Intra-abdominal Mycoplasma hominis infection in a liver transplant recipient: a case report. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2014; 67:232–233. PMID: 24858617.5. Camara B, Mouzin M, Ribes D, Esposito L, Guitard J, Game X, et al. Perihepatitis and perinephric abscess due to Mycoplasma hominis in a kidney transplant patient. Exp Clin Transplant. 2007; 5:708–709. PMID: 18194127.6. Geissdörfer W, Schörner C, Lohoff M. Systemic Mycoplasma hominis infection in a patient immunocompromised due to combined transplantation of kidney and pancreas. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2001; 20:511–512. PMID: 11561812.7. Loupy A, Join-Lambert OF, Bébéar CM, Legendre C, Anglicheau D. Urogenital mycoplasma: an emerging cause of deep wound infection after kidney transplantation? NDT Plus. 2008; 1:239–240. PMID: 25983892.8. Pastural M, Audard V, Bralet MP, Rémy P, Salomon L, Tankovic J, et al. Mycoplasma hominis infection in renal transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002; 17:495–496. PMID: 11865099.9. Rohner P, Schnyder I, Ninet B, Schrenzel J, Lew D, Ramla T, et al. Severe Mycoplasma hominis infections in two renal transplant patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004; 23:203–204. PMID: 14986166.10. Pereyre S, Gonzalez P, De Barbeyrac B, Darnige A, Renaudin H, Charron A, et al. Mutations in 23S rRNA account for intrinsic resistance to macrolides in Mycoplasma hominis and Mycoplasma fermentans and for acquired resistance to macrolides in M. hominis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002; 46:3142–3150. PMID: 12234836.