Korean Circ J.
2018 Apr;48(4):325-328. 10.4070/kcj.2018.0057.
You're Not under Arrest: Worry-free with β-arrestin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Sciences and Technology, BK21 Plus Project Team, Graduate School of Inje University, Busan, Korea. phyhanj@inje.ac.kr
- 2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Center, BK21 Plus Project Team, National Research Laboratory for Mitochondrial Signaling, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2407902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2018.0057
Abstract
- No abstract available.
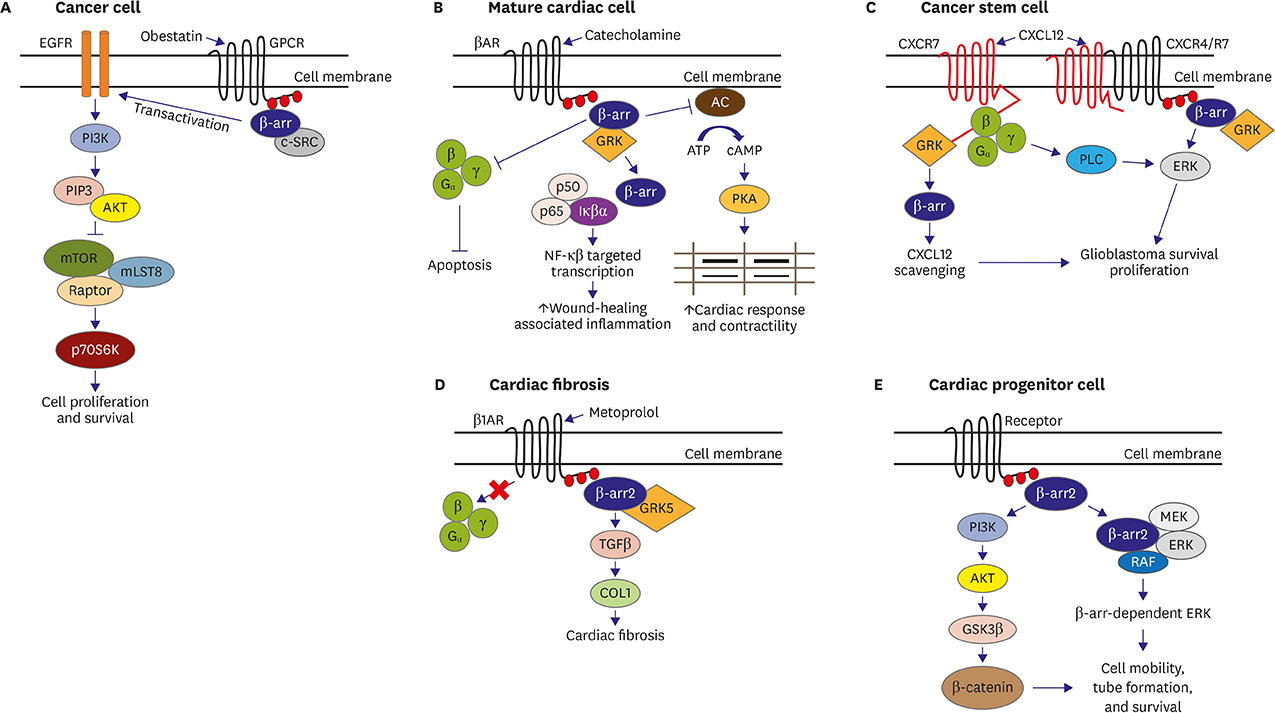
Figure
Reference
-
1. Savarese G, Lund LH. Global public health burden of heart failure. Card Fail Rev. 2017; 3:7–11.
Article2. Le T, Chong J. Cardiac progenitor cells for heart repair. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 2:16052.
Article3. Noor N, Patel CB, Rockman HA. β-arrestin: a signaling molecule and potential therapeutic target for heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011; 51:534–541.
Article4. Würth R, Bajetto A, Harrison JK, Barbieri F, Florio T. CXCL12 modulation of CXCR4 and CXCR7 activity in human glioblastoma stem-like cells and regulation of the tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014; 8:144.
Article5. Nakaya M, Chikura S, Watari K, et al. Induction of cardiac fibrosis by β-blocker in G protein-independent and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5/β-arrestin2-dependent signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:35669–35677.
Article6. Bathgate-Siryk A, Dabul S, Pandya K, et al. Negative impact of β-arrestin-1 on post-myocardial infarction heart failure via cardiac and adrenal-dependent neurohormonal mechanisms. Hypertension. 2014; 63:404–412.
Article7. Seo SK, Kim N, Lee JH, et al. β-arrestin2 affects cardiac progenitor cell survival through cell mobility and tube formation in severe hypoxia. Korean Circ J. 2018; 48:296–309.
Article8. McCrink KA, Maning J, Vu A, et al. β-arrestin2 improves post-myocardial infarction heart failure via sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase-dependent positive inotropy in cardiomyocytes. Hypertension. 2017; 70:972–981.9. Bolli R, Chugh AR, D'Amario D, et al. Cardiac stem cells in patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy (SCIPIO): initial results of a randomised phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2011; 378:1847–1857.
Article10. Hu S, Wang D, Wu J, et al. Involvement of β-arrestins in cancer progression. Mol Biol Rep. 2013; 40:1065–1071.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular Signature That Determines the Acute Tolerance of G Protein-Coupled Receptors
- Biased G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling: New Player in Modulating Physiology and Pathology
- Roles of Dopamine D₂ Receptor Subregions in Interactions with β-Arrestin2
- Effects of chronic alcohol exposure on ischemia–reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in mice: the role of β-arrestin 2 and glycogen synthase kinase 3
- Role of Helix 8 in Dopamine Receptor Signaling