Nutr Res Pract.
2018 Apr;12(2):149-159. 10.4162/nrp.2018.12.2.149.
Comparison of body image perception, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes, and dietary habits between Korean and Mongolian college students
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Inha University, 100 Inha-ro, Nam-gu, Incheon 22212, Korea. kjchang@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2407812
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2018.12.2.149
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
College students are in transition from adolescence to adulthood, and it has been reported that they show poor dietary habits. This study was conducted to compare body image perception, nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes, dietary habits, and health-related lifestyles between Korean college students (KCS) and Mongolian college students (MCS).
SUBJECTS/METHODS
Subjects were 314 KCS and 280 MCS. The data includes results of self-administered questionnaires; statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 23.0 program.
RESULTS
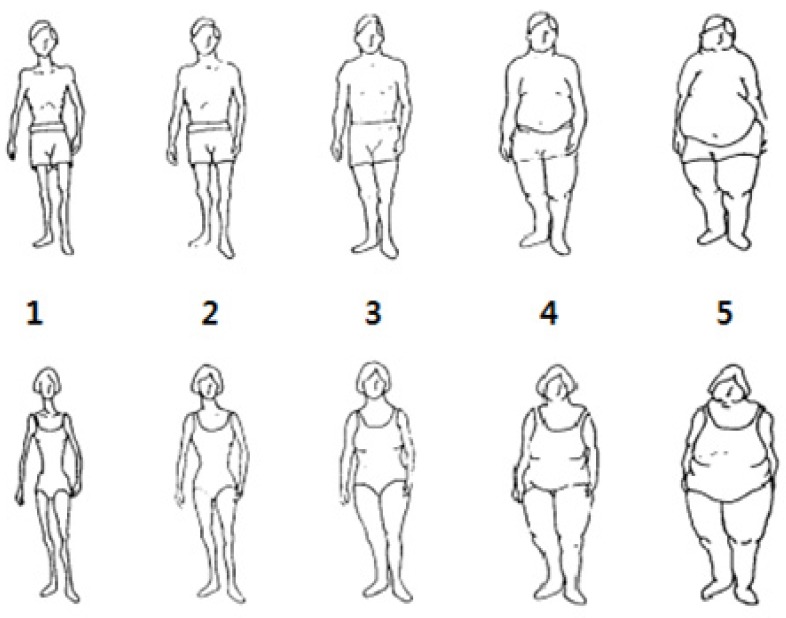
With regards to body image perception, KCS perceived themselves to be fatter on current body image than ideal body image compared to MCS; 64.0% of KCS and 34.6% of MCS desired to be thinner. Total score of nutrition knowledge in KCS (17.0) was significantly higher compared to MCS (8.4) (P < 0.001), but total score of dietary attitudes in KCS (27.0) was significantly lower compared to MCS (31.2) (P < 0.001). Nutrition knowledge had a significantly positive correlation with dietary attitudes in MCS (P < 0.01). Meal consumption among male and female subjects was 2 and 3 times, respectively, in order in KCS, and 3 and 2 times, respectively, in order in MCS (P < 0.001). Rate of skipping breakfast in both genders was significantly higher in KCS than in MCS (male: P < 0.05, female: P < 0.001). In health-related lifestyles, KCS had a significantly higher rate in frequency of alcohol drinking (P < 0.001), exercise (P < 0.01), and mobile phone usage (P < 0.001), compared to MCS.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that development of nutrition education program which is effective and proper is required to improve healthy dietary habits among college students of both countries. Essential contents should include acquirement of nutrition knowledge and a motivation for its application to actual life for KCS, and improvement of healthy dietary habits for MCS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A comparative study on nutritional knowledge and dietary behavior between Korean and Chinese postpartum women
Sohyun Kim, Heewon L Gray, Jia Li, Haeryun Park, Youngmi Lee, Kyunghee Song
Nutr Res Pract. 2019;13(6):535-542. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2019.13.6.535.Science electives in high school will improve nutrition knowledge but not enough to make accurate decisions
Takahiro Mitsui, Susumu Yamamoto, Morito Endo
Nutr Res Pract. 2023;17(4):803-811. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2023.17.4.803.
Reference
-
1. Nelson MC, Story M, Larson NI, Neumark-Sztainer D, Lytle LA. Emerging adulthood and college-aged youth: an overlooked age for weight-related behavior change. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008; 16:2205–2211. PMID: 18719665.
Article2. Poobalan AS, Aucott LS, Clarke A, Smith WC. Diet behaviour among young people in transition to adulthood (18-25 year olds): a mixed method study. Health Psychol Behav Med. 2014; 2:909–928. PMID: 25750826.
Article3. Hilger J, Loerbroks A, Diehl K. Eating behaviour of university students in Germany: dietary intake, barriers to healthy eating and changes in eating behaviour since the time of matriculation. Appetite. 2017; 109:100–107. PMID: 27864073.
Article4. Beaudry KM, Thomas AM, Falk B, Ward WE, Josse AR. Identifying changes in body weight, composition and dietary intake during first-year university. FASEB J. 2017; 31:957.27.5. Laska MN, Larson NI, Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M. Dietary patterns and home food availability during emerging adulthood: do they differ by living situation? Public Health Nutr. 2010; 13:222–228. PMID: 19691902.6. Brown C. The information trail of the ‘Freshman 15’--a systematic review of a health myth within the research and popular literature. Health Info Libr J. 2008; 25:1–12.7. Chapman CD, Nilsson VC, Thune HÅ, Cedernaes J, Le Grevès M, Hogenkamp PS, Benedict C, Schiöth HB. Watching TV and food intake: the role of content. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e100602. PMID: 24983245.
Article8. Pingali P. Westernization of Asian diets and the transformation of food systems: implications for research and policy. Food Policy. 2006; 32:281–298.
Article9. Lee JY. Korea-Mongolia economic cooperation: achievements and strategic challenges. Mong Stud. 2015; 42:187–216.10. Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Mongolia. Mongolian press articles (10.10) [Internet]. Ulaanbaatar: Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Mongolia;2017. cited 2018 February 5. Available from: http://overseas.mofa.go.kr/mn-ko/brd/m_374/view.do?seq=1331486&srchFr=&srchTo=&srchWord=&srchTp=&multi_itm_seq=0&itm_seq_1=0&itm_seq_2=0&company_cd=&company_nm=&page=5.11. namu. wiki. Developed country [Internet]. Asunción: namu.wiki;2016. cited 2018 February 8. Available from: https://namu.wiki/w/%EC%84%A0%EC%A7%84%EA%B5%AD#fn-10.12. Wholistic Interest Through Health (KR). School lunch project in Mongolia [Internet]. Seoul: Wholistic Interest Through Health;2013. cited 2018 February 5. Available from: http://www.iwith.or.kr/business_02.html.13. Joo EJ, Park ES. Comparison study of dietary behavior, nutrition knowledge, and body weight perception of female high school students in Jeonju, Korea and Jinan, China. Korean J Hum Ecol. 2016; 25:121–135.
Article14. Park JK, Nam YJ, Choi KM. A comparison of satisfaction for actual body and perceived body between Korean and Japanese female college students. J Korean Soc Clothing Text. 2004; 28:758–766.15. Kim MY, Choi EJ, Abe S, Jjang CY, Yoon JH. Comparison of nutrient criteria of school lunch programs in Korea, Japan, and Taiwan. In : 2015 Spring Conference the East Asian Society of Dietary Life; 2015 May 9; Seoul, Korea. Seoul: The East Asian Society of Dietary Life;2015. p. 195.16. Jang SH. An investigation into dietary habit and food preference by university student's nutrition knowledge [master's thesis]. Seoul: Konkuk University;2010.17. Jo HJ. A study of drinking behaviors according to diet and nutritional knowledge of university students [master's thesis]. Gimhae: Inje University;2011.18. World Health Organization Western Pacific Region. International Association for the Study of Obesity. International Obesity Task Force. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its treatment. Sydney: Health Communications Australia Pty Limited;2000.19. Stunkard A. Old and new scales for the assessment of body image. Percept Mot Skills. 2000; 90:930. PMID: 10883782.
Article20. Ambrosi-RandiXMLLink_XYZ N, Pokrajac-Bulian A, Takšić V. Nine, seven, five, or three: how many figures do we need for assessing body image? Percept Mot Skills. 2005; 100:488–492. PMID: 15974359.
Article21. Hyun H, Lee H, Ro Y, Gray HL, Song K. Body image, weight management behavior, nutritional knowledge and dietary habits in high school boys in Korea and China. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2017; 26:923–930. PMID: 28802303.22. Curran PJ, West SG, Finch JF. The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychol Methods. 1996; 1:16–29.
Article23. The Korean Labor Economic Association. Study on Strengthening Cooperation in Employment Labor Sector between Korea and Mongolia. Sejong: Ministry of Employment and Labor;2017.24. Gim WS, Kim JS. Body-related values and body-esteem in East Asian women: a cross-national study focusing on Korean, Chinese, and Japanese college students. Korean J Psychol Soc Issues. 2007; 13:113–134.25. Song L, An NY, Ryu HK. A comparative study of dietary and weight control behavior of female college students in Korea and China. Korean J Community Living Sci. 2015; 26:761–774.
Article26. Lee Y, Sun L. The study of perception in body somatotype and dietary behaviors: the comparative study between Korean and Chinese college students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2013; 18:25–44.27. Lee SG, Koh AR. Formation models of body image, self-esteem, and clothing attitudes as related to pubertal physical growth. J Korean Soc Clothing Text. 2005; 29:438–448.28. Jang HS, Kim TR. The effect of mass media on body perception and state esteem of body image. Stud Korean Youth. 2006; 17:57–83.29. Shin YH, Lee HW, Jeon SH, Lee MJ, Kim SH, Kim S, Kim HG, Shin KM. Korean Cultural Wave in East Asia. Yongin: Jeonyewon;2006.30. Yoon CH. Analysis of health status and health behavior among school children in Mongolia [master's thesis]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2009.31. Wholistic Interest Through Health (KR). Sung Keun Haigu State Health Center ‘Nutrition Education Center’ handover ceremony [Internet]. Seoul: Wholistic Interest Through Health;2014. cited 2018 February 5. Available from: http://www.iwith.or.kr/community_02.html?actobj=news&acttype=VIEWINFO&bbs_code=news&bbs_key=79859397795173_538c648a45802.32. Shuchen G, Kim H, Kim M. A cross-cultural investigation of nutrition knowledge, dietary behaviors, and checking behaviors of food and nutrition labels between Korean and Chinese university students. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2015; 25:942–951.33. Yang SG. Analysis of School Meal Program in Korea in OECD Countries. Seoul: Korean Educational Development Institute;2010.34. Minister of Health and Sports (MN). Third national STEPS Survey on the prevalence of noncommunicable disease and injury risk factors-2013 [Internet]. Ulaanbaatar: Minister of Health And Sports;2013. cited 2017 December 10. Available from: http://www.who.int/chp/steps/Mongolia_2013_STEPS_Report.pdf?ua=1.35. Campo S, Mastin T. Placing the burden on the individual: overweight and obesity in African American and mainstream women's magazines. Health Commun. 2007; 22:229–240. PMID: 17967145.
Article36. Babbie ER. The Basics of Social Research. Boston (MA): Cengage Learning;2007.37. Park YS, Lee JW, Seo JS, Lee BK, Lee HS, Lee SK. Nutrition Education & Counseling. 5th ed. Paju: Kyomunsa;2013.38. Son S, Ro Y, Hyun H, Lee H, Song K. A comparative study on dietary behavior, nutritional knowledge and life stress between Korean and Chinese female high school students. Nutr Res Pract. 2014; 8:205–212. PMID: 24741406.
Article39. Sakamaki R, Amamoto R, Mochida Y, Shinfuku N, Toyama K. A comparative study of food habits and body shape perception of university students in Japan and Korea. Nutr J. 2005; 4:31. PMID: 16255785.
Article40. Choi SH. Effects of self esteem, dietary self-efficacy and life stress on dietary behavior of female nursing students. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2017; 18:366–374.41. Korea Foundation for International Culture Exchange. Korean food culture spreading to Mongolia [Internet]. Seoul: Korea Foundation for International Culture Exchange;2017. cited 2017 December 7. Available from: http://kofice.or.kr/c30correspondent/c30_correspondent_02_view.asp?seq=14879.42. Lum C, Corliss HL, Mays VM, Cochran SD, Lui CK. Differences in the drinking behaviors of Chinese, Filipino, Korean, and Vietnamese college students. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2009; 70:568–574. PMID: 19515297.
Article43. YTN (KR). People who drinks alcohol are being problem more than alcohol consumption [Internet]. Seoul: YTN;2017. cited 2017 December 7. Available from: http://www.ytn.co.kr/_ln/0102_201705291657474174.44. HuffingtonPostKorea. Korean male smoking rate tops 30% for the first time [Internet]. Seoul: HuffingtonPostKorea;2016. cited 2018 December 7. Available from: http://www.huffingtonpost.kr/2016/05/10/story_n_9878846.html.45. Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Mongolia. Tobacco production in Mongolia, smoking rates and key regulations [Internet]. Ulaanbaatar: Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Mongolia;2015. cited 2017 December 7. Available from: http://overseas.mofa.go.kr/mn-ko/brd/m_378/view.do?seq=1156735&srchFr=&srchTo=&srchWord=&srchTp=&multi_itm_seq=0&itm_seq_1=0&itm_seq_2=0&company_cd=&company_nm=&page=13.46. Oranisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. World Health Organization. Health at a Glance: Asia/Pacific 2014: Measuring Progress towards Universal Health Coverage. Paris: OECD Publishing;2014.47. Kim MO, Sawano K. Comparison of Korean and Japanese female college students' obesity recognition and life style. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2010; 39:699–708.
Article48. Amarsanaa N. Mongolian telecommunication equipment market growth [Internet]. Seoul: KOTRA;2017. cited 2017 December 10. Available from: https://news.kotra.or.kr/user/globalBbs/kotranews/4/globalBbsDataView.do?setIdx=243&dataIdx=161646.49. Yonhapnews (KR). The world's smartphone penetration surpassed the first 50% … Korea 85% [Internet]. Seoul: Yonhapnews;2017. cited 2017 December 10. Available from: http://www.yonhapnews.co.kr/bulletin/2017/02/08/0200000000AKR20170208052100017.HTML.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Comparison Study on Perception of Body Image and Dietary Habits of High School Students between Urban and Rural Areas
- Effect of Two-year Course of Food and Nutrition on Improving Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitudes and Food Habits of Junior College Female Students
- A Study on Dietary Habits, Dietary Behaviors and Body Image Recognition of Nutrition Knowledge after Nutrition Education for Obese Children in Seoul
- Effects of Nutrition Education on Nutrition Knowledge, Dietary Attitudes, and Food Behavior of College Students
- Nutrition Knowledge, Food Habit Problems and Dietary Attitudes of Nursing Students