Korean J Adult Nurs.
2017 Feb;29(1):51-62. 10.7475/kjan.2017.29.1.51.
A Meta-analysis of the Risk Factors related to Falls among Elderly Patients with Dementia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Teagu Science University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Assistant Professor, College of Nursing, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea. hopark@kmu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2406336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2017.29.1.51
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to provide data about the risk factors related to falls among elderly patients with dementia using meta-analysis.
METHODS
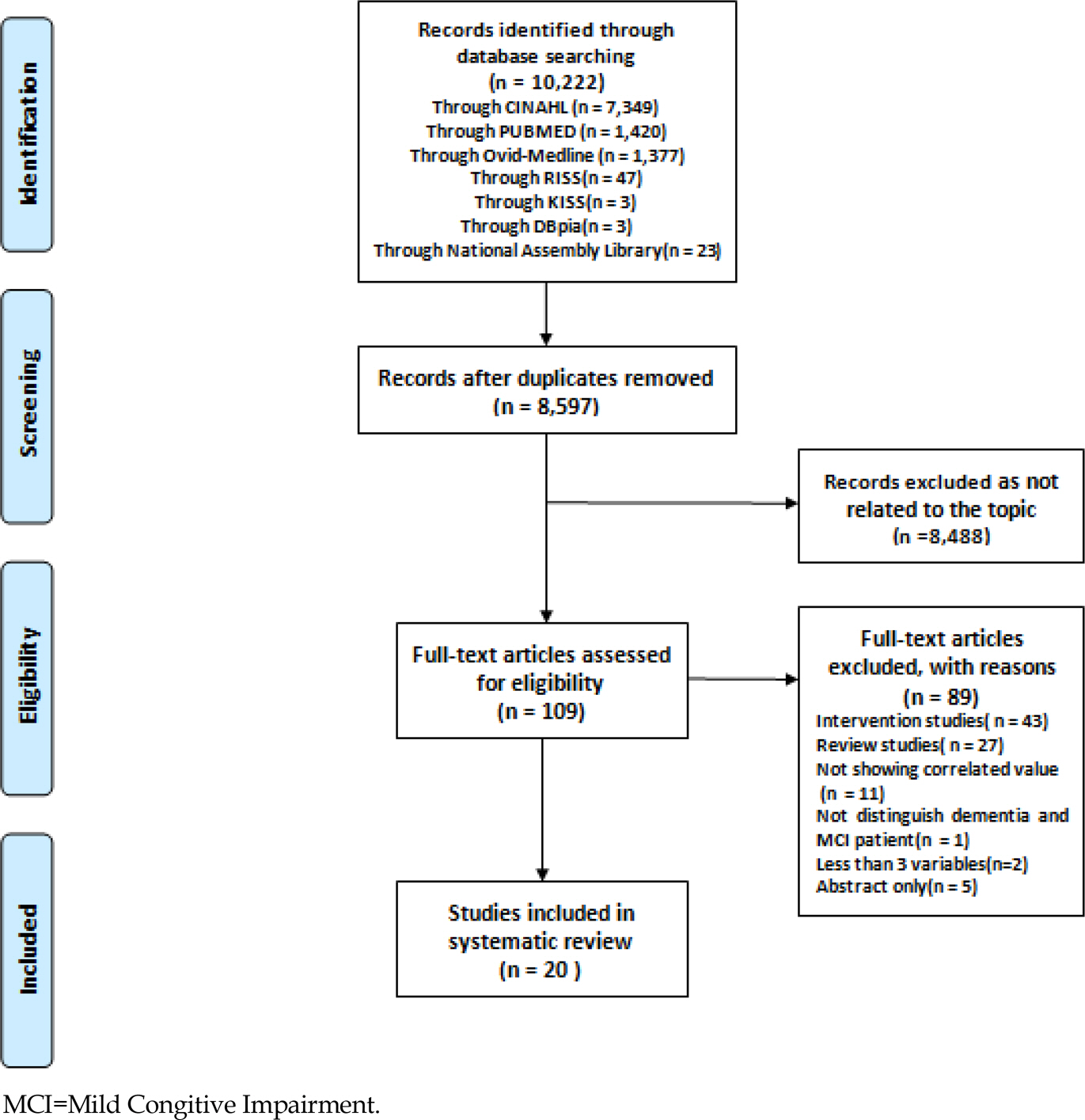
Key words used for search through electronic database (CINAHL, PubMed, Ovid-MEDLINE, RISS, KISS, DBPIA, National Assembly Library) included "˜ dementia', "˜ Alzheimer', "˜ fall'. Twenty studies met the inclusion criteria for the meta-analysis and "˜ R' version 3.2.2 was used to analyze the correlated effect size.
RESULTS
Study results showed that risk factors related to falls were identified as the demographic (age, gender, education), dementia-related (disease duration, cognition), physical (body mass index, walking, balance, activity of daily living, use of walking aids, number of medications including psychotropic drugs, musculoskeletal problems, parkinsonism, comorbidity), psychological (neuropsychiatric symptom, depression), environmental (Physical environment), and fall-related (fall history, high risk group of fall) factors. The effect size of risk factors such as high risk group of fall (r=.35), use of walking aids (r=.33), depression (r=.31), psychotropic drugs (r=.27), Musculoskeletal problems (r=.25) were higher than the other risk factors.
CONCLUSION
Based on the findings of this study, strategies to improve elderly patient's depression, intensive care for high risk group of fall, and adequate training with walking aids are needed for prevention of falls in elderly patients with dementia
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Kannus P., Sievänen H., Palvanen M., Järvinen T., Parkkari J. Prevention of falls and consequent injuries in elderly people. The Lancet. 2005. 366:1885–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(05)67604-0.
Article2.Allan LM., Ballard CG., Rowan EN., Kenny RA. Incidence and prediction of falls in dementia: a prospective study in older people. Plos One. 2009. 4(5):e5521. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005521.
Article3.Ambrose AF., Paul G., Hausdorff JM. Risk factors for falls among older adults: a review of the literature. [Review]. Maturitas. 2013. 75(1):51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.02.009.4.Boelens C., Hekman EE. Verkerke GJ. Risk factors for falls of older citizens. Technology and Health Care. 2013. 21(5):521–33. https://doi.org/10.3233/THC-130748.5.Salonen L., Kivelä SL. Eye diseases and impaired vision as possible risk factors for recurrent falls in the aged: a systematic review. Current Gerontology and Geriatrics Research. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/271481.
Article6.Voort VD., Geusens PP., Dinant GJ. Risk factors for osteoporosis related to their outcome: fractures. Osteoporosis International. 2001. 12(8):630–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980170062.
Article7.Paskulin LMG., Molzahn A. Quality of life of older adults in Canada and Brazil. Western Journal of Nursing Research. 2007. 29(1):10–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193945906292550.
Article8.Welmerink DB., Longstreth WT Jr., Lyles MF., Fitzpatrick AL. Cognition and the risk of hospitalization for serious falls in the elderly: results from the Cardiovascular Health Study. Journals of Gerontology Series A-Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2010. 65(11):1242–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glq115.
Article9.Sai AJ., Gallagher JC., Smith LM., Logsdon S. Fall predictors in the community dwelling elderly: a cross sectional and prospective cohort study. Journal of Musculoskelet Neuronal Interactions. 2010. 10(2):142–50.10.Kim YH., Yang KH., Park KS. Fall experience and risk factors for falls among the community-dwelling elderly. Journal of Muscle and Joint Health. 2013. 20(2):91–101. https://doi.org/10.5953/JMJH.2013.20.2.91.
Article11.Jang IS., Park EO. The prevalence and factors of falls among the community-dwelling elderly. Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing. 2013. 27(1):89–101. https://doi.org/10.5932/JKPHN.2013.27.1.89.
Article12.Agostini JV., Tinetti ME. Drugs and falls: rethinking the approach to medication risk in older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2002. 50(10):1744–5. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50472.x.
Article13.Carter SE., Campbell EM., Sanson-Fisher RW., Gillespie WJ. Accidents in older people living at home: a community-based study assessing prevalence, type, location and injuries. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health. 2000. 24(6):633–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-842X.2000.tb00532.x.
Article14.Park YH., Moon JS. Home environmental hazards of falling accident in the elderly. Journal of Korean Society for Health Education and Promotion. 2005. 22(4):203–13.15.Bongue B., Dupré C., Beauchet O., Rossat A., Fantino B., Colvez A. A screening tool with five risk factors was developed for fall-risk prediction in community-dwelling elderly. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2011. 64(10):1152–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.12.014.
Article16.Deandrea S., Bravi F., Turati F., Lucenteforte E., La Vecchia C., Negri E. Risk factors for falls in older people in nursing homes and hospitals. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2013. 56(3):407–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2012.12.006.
Article17.Swanenburg J., de Bruin ED., Uebelhart D., Mulder T. Falls prediction in elderly people: a 1-year prospective study. Gait and Posture. 2010. 31(3):317–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2009.11.013.
Article18.Rubenstein LZ., Josephson KR. Falls and their prevention in elderly people: what does the evidence show? Medical Clinics of North America. 2006. 90(5):807–24. https://doi.org/doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2006.05.013.
Article19.Estabrooks CA., Floyd JA., Scott-Findlay S., O'Leary KA., Gushta M. Individual determinants of research utilization: a systematic review. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2003. 43(5):506–20. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2648.2003.02748.x.
Article20.Cicolini G., Comparcini D., Simonetti V. Workplace empowerment and nurses' job satisfaction: a systematic literature review. Journal of Nursing Management. 2014. 22(7):855–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.12028.
Article21.Kosse NM., de Groot MH., Vuillerme N., Hortobagyi T., Lamoth CJ. Factors related to the high fall rate in long-term care residents with dementia. International Psychogeriatrics. 2015. 27(5):803–14. https://doi.org/10.1017/S104161021400249X.
Article22.Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed.Hilsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;1988.23.Higgins J., Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [Internet]. London, UK. The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. [cited 2016 March 15]. Available from:. http://handbook.cochrane.org/.24.Deandrea S., Lucenteforte E., Bravi F., Foschi R., La Vecchia C., Negri E. Risk factors for falls in community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiology. 2010. 21(5):658–68. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181e89905.25.Bateni H., Maki BE. Assistive devices for balance and mobility: benefits, demands, and adverse consequences. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2005. 86(1):134–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2004.04.023.
Article26.Murphy CF., Alexopoulos GS. Longitudinal association of ini-tiation/perseveration and severity of geriatric depression. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2004. 12(1):50–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/00019442-200401000-00007.
Article27.Barca ML., Engedal K., Selbaek G., Knapskog AB., Laks J., Coutinho E, et al. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Cornell scale for depression in dementia among patient with dementia of various degrees. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2015. 188:173–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.08.062.
Article28.Nijk RM., Zuidema SU., Koopmans RT. Prevalence and correlates of psychotropic drug use in Dutch nursing-home patients with dementia. International Psychogeriatrics. 2009. 21(3):485–93. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610209008916.
Article29.Kim SH., Lee BH. Risperidone for psychogeriatric patients. The Korean Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2003. 14(Suppl1):101–11.30.Kim NC., Kim JH., Lim YM. A study on community-dwelling elders with dementia, their primary caregiver, and living environments. Journal of Korea Community Health Nursing Academic Society. 2002. 16(1):13–29.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Risk Factors of Falls for Home Staying Elderly People in a Rural Community
- Effects of Walking Program with Dance on Gait, Cognition, and Risk of Falls of Elderly with Dementia in a Long-term Care Hospital
- Predictors of Fall Prevention Behaviors in Elderly Inpatients
- Risk Factors of Dementia
- Effects of Horticultural Therapy on Korean Elderly with Dementia: A Meta-analysis