Korean J Crit Care Med.
2017 Nov;32(4):340-346. 10.4266/kjccm.2017.00255.
Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II Score and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score as Predictors for Severe Trauma Patients in the Intensive Care Unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Trauma, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. nonajugi@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2405120
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2017.00255
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II scoring system and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scoring system are widely used for critically ill patients. We evaluated whether APACHE II score and SOFA score predict the outcome for trauma patients in the intensive care unit (ICU).
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed trauma patients admitted to the ICU in a single trauma center between January 2014 and December 2015. The APACHE II score was figured out based on the data acquired from the first 24 hours of admission; the SOFA score was evaluated based on the first 3 days in the ICU. A total of 241 patients were available for analysis. Injury Severity score, APACHE II score, and SOFA score were evaluated.
RESULTS
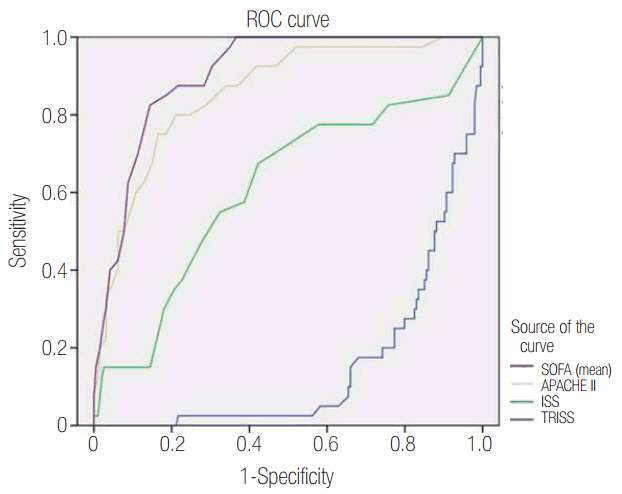
The overall survival rate was 83.4%. The non-survival group had a significantly high APACHE II score (24.1 ± 8.1 vs. 12.3 ± 7.2, P < 0.001) and SOFA score (7.7 ± 1.7 vs. 4.3 ± 1.9, P < 0.001) at admission. SOFA score had the highest areas under the curve (0.904). During the first 3 days, SOFA score remained high in the non-survival group. In the non-survival group, cardiovascular system, neurological system, renal system, and coagulation system scores were significantly higher.
CONCLUSIONS
In ICU trauma patients, both SOFA and APACHE II scores were good predictors of outcome, with the SOFA score being the most effective. In trauma ICU patients, the trauma scoring system should be complemented, recognizing that multi-organ failure is an important factor for mortality.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Evans JA, van Wessem KJ, McDougall D, Lee KA, Lyons T, Balogh ZJ. Epidemiology of traumatic deaths: comprehensive population-based assessment. World J Surg. 2010; 34:158–63.
Article2. Lefering R, Goris RJ, van Nieuwenhoven EJ, Neugebauer E. Revision of the multiple organ failure score. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2002; 387:14–20.
Article3. Moreno R, Vincent JL, Matos R, Mendonça A, Cantraine F, Thijs L, et al. The use of maximum SOFA score to quantify organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care: results of a prospective, multicentre study. Working group on sepsis related problems of the ESICM. Intensive Care Med. 1999; 25:686–96.4. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985; 13:818–29.5. Dewar DC, White A, Attia J, Tarrant SM, King KL, Balogh ZJ. Comparison of postinjury multiple-organ failure scoring systems: Denver versus Sequential Organ Failure Assessment. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014; 77:624–9.6. Ferreira FL, Bota DP, Bross A, Mélot C, Vincent JL. Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. JAMA. 2001; 286:1754–8.
Article7. Ciesla DJ, Moore EE, Johnson JL, Burch JM, Cothren CC, Sauaia A. A 12-year prospective study of postinjury multiple organ failure: has anything changed? Arch Surg. 2005; 140:432–8.8. Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonça A, Bruining H, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the working group on sepsis-related problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996; 22:707–10.9. Chawda MN, Hildebrand F, Pape HC, Giannoudis PV. Predicting outcome after multiple trauma: which scoring system? Injury. 2004; 35:347–58.
Article10. Baker SP, O’Neill B. The Injury Severity score: an update. J Trauma. 1976; 16:882–5.11. Champion HR, Copes WS, Sacco WJ, Frey CF, Holcroft JW, Hoyt DB, et al. Improved predictions from a severity characterization of trauma (ASCOT) over Trauma and Injury Severity score (TRISS): results of an independent evaluation. J Trauma. 1996; 40:42–8.12. Kajdacsy-Balla Amaral AC, Andrade FM, Moreno R, Artigas A, Cantraine F, Vincent JL. Use of the sequential organ failure assessment score as a severity score. Intensive Care Med. 2005; 31:243–9.
Article13. Antonelli M, Moreno R, Vincent JL, Sprung CL, Mendoça A, Passariello M, et al. Application of SOFA score to trauma patients: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment. Intensive Care Med. 1999; 25:389–94.14. Hwang SY, Lee JH, Lee YH, Hong CK, Sung AJ, Choi YC. Comparison of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II scoring system, and Trauma and Injury Severity score method for predicting the outcomes of intensive care unit trauma patients. Am J Emerg Med. 2012; 30:749–53.
Article15. Wong DT, Barrow PM, Gomez M, McGuire GP. A comparison of the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score and the Trauma-Injury Severity score (TRISS) for outcome assessment in intensive care unit trauma patients. Crit Care Med. 1996; 24:1642–8.
Article16. Knaus WA. Why measure severity? Reanim Urgences. 1994; 3:159–63.
Article17. Milzman DP, Boulanger BR, Rodriguez A, Soderstrom CA, Mitchell KA, Magnant CM. Pre-existing disease in trauma patients: a predictor of fate independent of age and injury severity score. J Trauma. 1992; 32:236–43.18. McAnena OJ, Moore FA, Moore EE, Mattox KL, Marx JA, Pepe P. Invalidation of the APACHE II scoring system for patients with acute trauma. J Trauma. 1992; 33:504–6.
Article19. Boyd CR, Tolson MA, Copes WS. Evaluating trauma care: the TRISS method--Trauma Score and the Injury Severity score. J Trauma. 1987; 27:370–8.20. Dewar D, Moore FA, Moore EE, Balogh Z. Postinjury multiple organ failure. Injury. 2009; 40:912–8.
Article21. Norris R, Woods R, Harbrecht B, Fabian T, Rhodes M, Morris J, et al. TRISS unexpected survivors: an outdated standard? J Trauma. 2002; 52:229–34.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lung Injury Score in Predicting the Outcome of the Patients in the Intensive Care Unit
- The Prognostic Utility of the Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II) and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Score for Hemato-Oncology Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit
- APACHE II Score and Evaluation of Intensive Care Unit Patients
- Severity Assessment of Acute Pancreatitis
- Tissue Perfusion and the Braden Scale as Predictors of Pressure Injury Risk in the Intensive Care Unit Patient