Blood Res.
2017 Dec;52(4):329-332. 10.5045/br.2017.52.4.329.
A young man with acute respiratory distress syndrome: eosinophilia is not always “benignâ€
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Nehru Hospital, PGIMER, Chandigarh, India. hematpgi@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Nehru Hospital, PGIMER, Chandigarh, India.
- 3Department of Histopathology, Nehru Hospital, PGIMER, Chandigarh, India.
- KMID: 2405075
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2017.52.4.329
Abstract
- No abstract available.
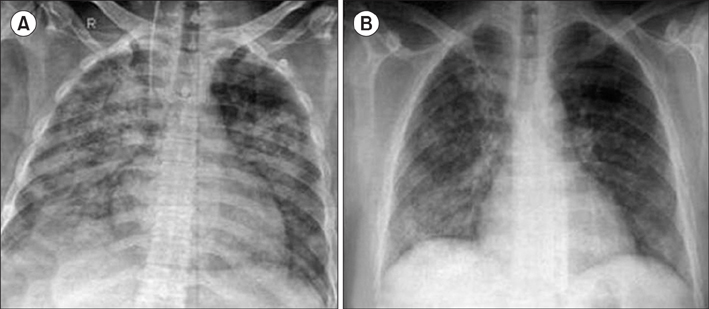
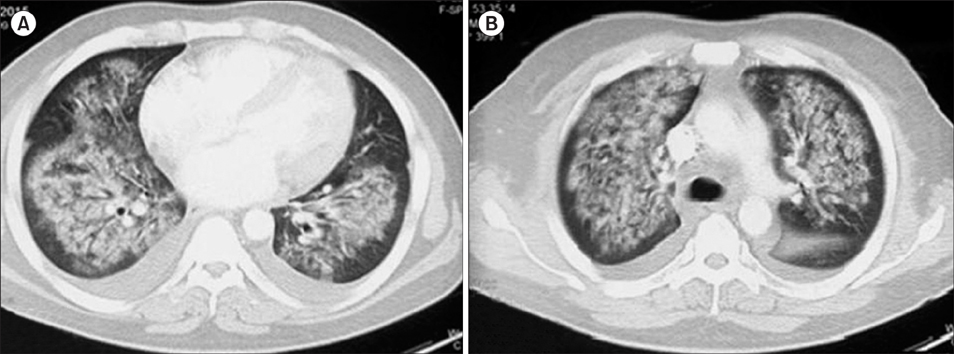
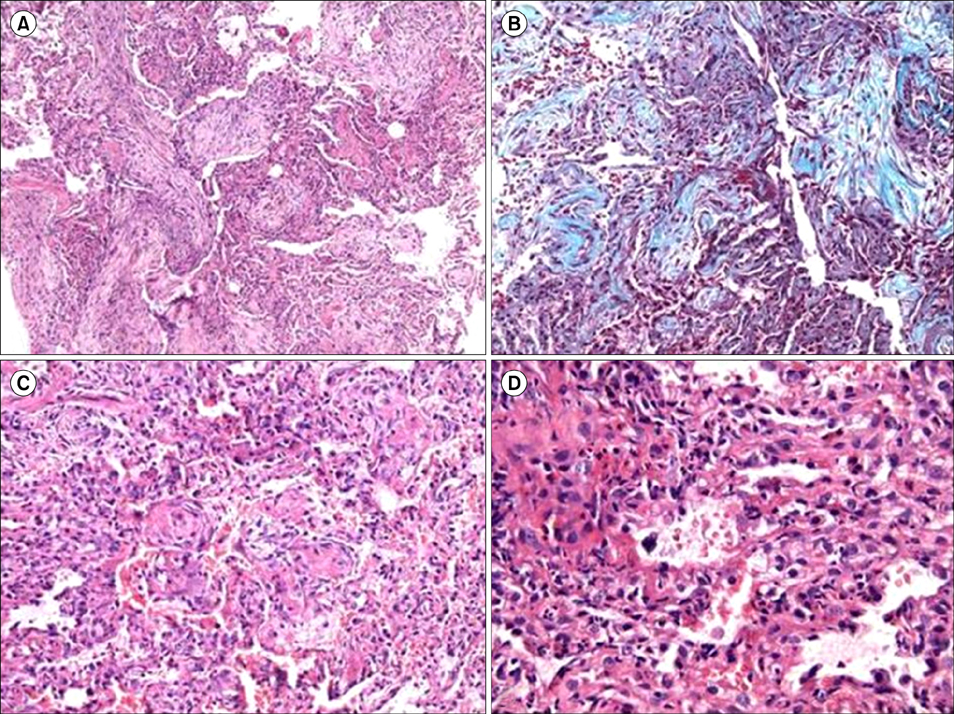
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fowler AA, Hamman RF, Good JT, et al. Adult respiratory distress syndrome: risk with common predispositions. Ann Intern Med. 1983; 98:593–597.
Article2. Chusid MJ, Dale DC, West BC, Wolff SM. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1975; 54:1–27.3. Roufosse FE, Goldman M, Cogan E. Hypereosinophilic syndromes. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007; 2:37.
Article4. Gotlib J. World Health Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2014 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2014; 89:325–337.
Article5. Gotlib J, Cools J, Malone JM 3rd, Schrier SL, Gilliland DG, Coutré SE. The FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha fusion tyrosine kinase in hypereosinophilic syndrome and chronic eosinophilic leukemia: implications for diagnosis, classification, and management. Blood. 2004; 103:2879–2891.
Article6. Dulohery MM, Patel RR, Schneider F, Ryu JH. Lung involvement in hypereosinophilic syndromes. Respir Med. 2011; 105:114–121.
Article7. Winn RE, Kollef MH, Meyer JI. Pulmonary involvement in the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Chest. 1994; 105:656–660.
Article8. Savage N, George TI, Gotlib J. Myeloid neoplasms associated with eosinophilia and rearrangement of PDGFRA, PDGFRB, and FGFR1: a review. Int J Lab Hematol. 2013; 35:491–500.
Article