Korean J Radiol.
2018 Apr;19(2):230-236. 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.230.
Double-Stent System with Long Duodenal Extension for Palliative Treatment of Malignant Extrahepatic Biliary Obstructions: A Prospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul 05505, Korea. radgwon@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2404919
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.230
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the technical safety and clinical efficacy of a double-stent system with long duodenal extension in patients with malignant extrahepatic biliary obstruction.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
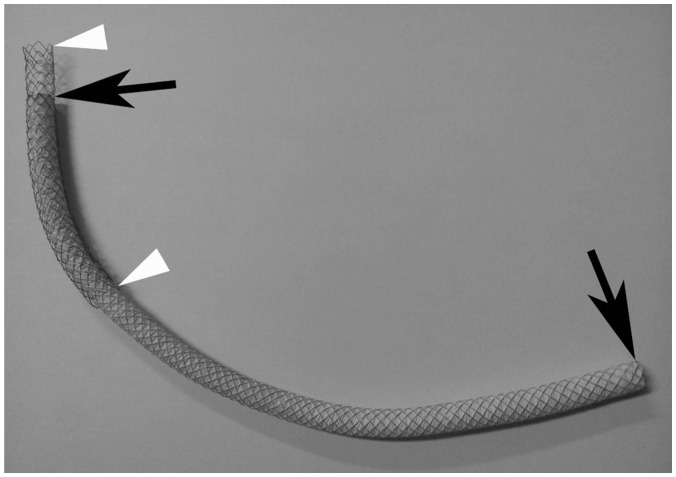
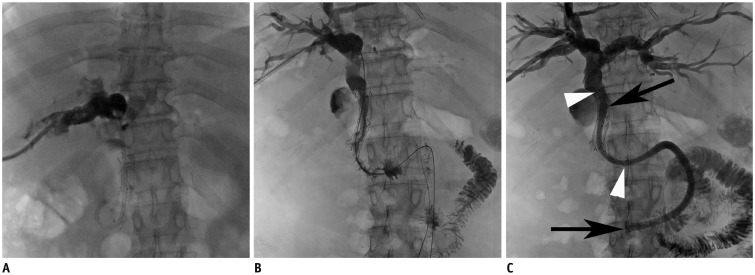
This prospective study enrolled 48 consecutive patients (31 men, 17 women; mean age, 61 years; age range, 31-77 years) with malignant extrahepatic biliary obstructions from May 2013 to December 2015. All patients were treated with a double-stent system with long duodenal covered extension (16 cm or 21 cm).
RESULTS
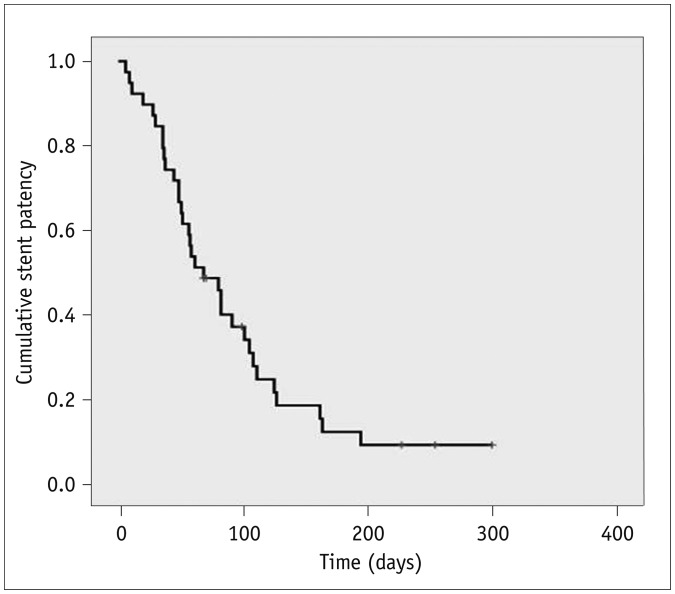
The stents were successfully placed in all 48 patients. There were five (10.4%) procedure-related complications. Minor complications were self-limiting hemobilia (n = 2). Major complications included acute pancreatitis (n = 1) and acute cholecystitis (n = 2). Successful internal drainage was achieved in 42 (87.5%) patients. Median patient survival and stent patency times were 92 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 61-123 days) and 83 days (95% CI, 46-120 days), respectively. Ten (23.8%) of the 42 patients presented with stent occlusion due to food impaction with biliary sludge, and required repeat intervention. Stent occlusion was more frequent in metastatic gastric cancer patients with pervious gastrectomy, but did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.069).
CONCLUSION
Percutaneous placement of a double-stent system with long duodenal extension is feasible and safe. However, this stent system does not completely prevent stent occlusion caused by food reflux.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gillams A, Dick R, Dooley JS, Wallsten H, el-Din A. Self-expandable stainless steel braided endoprosthesis for biliary strictures. Radiology. 1990; 174:137–140. PMID: 2294541.
Article2. Lammer J, Hausegger KA, Flückiger F, Winkelbauer FW, Wildling R, Klein GE, et al. Common bile duct obstruction due to malignancy: treatment with plastic versus metal stents. Radiology. 1996; 201:167–172. PMID: 8816539.
Article3. Lee BH, Choe DH, Lee JH, Kim KH, Chin SY. Metallic stents in malignant biliary obstruction: prospective long-term clinical results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:741–745. PMID: 9057527.
Article4. Ho CS, Warkentin AE. Evidence-based decompression in malignant biliary obstruction. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:S56–S61. PMID: 22563288.
Article5. Thurnher SA, Lammer J, Thurnher MM, Winkelbauer F, Graf O, Wildling R. Covered self-expanding transhepatic biliary stents: clinical pilot study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1996; 19:10–14. PMID: 8653739.
Article6. Hausegger KA, Thurnher S, Bodendörfer G, Zollikofer CL, Uggowitzer M, Kugler C, et al. Treatment of malignant biliary obstruction with polyurethane-covered Wallstents. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 170:403–408. PMID: 9456954.
Article7. Rossi P, Bezzi M, Salvatori FM, Panzetti C, Rossi M, Pavia G. Clinical experience with covered wallstents for biliary malignancies: 23-month follow-Up. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1997; 20:441–447. PMID: 9354713.
Article8. Kanasaki S, Furukawa A, Kane T, Murata K. Polyurethane-covered Nitinol Strecker stents as primary palliative treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2000; 23:114–120. PMID: 10795835.9. Schoder M, Rossi P, Uflacker R, Bezzi M, Stadler A, Funovics MA, et al. Malignant biliary obstruction: treatment with ePTFE-FEP-covered endoprostheses initial technical and clinical experiences in a multicenter trial. Radiology. 2002; 225:35–42. PMID: 12354981.10. Bezzi M, Zolovkins A, Cantisani V, Salvatori FM, Rossi M, Fanelli F, et al. New ePTFE/FEP-covered stent in the palliative treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13:581–589. PMID: 12050298.
Article11. Hatzidakis A, Krokidis M, Kalbakis K, Romanos J, Petrakis I, Gourtsoyiannis N. ePTFE/FEP-covered metallic stents for palliation of malignant biliary disease: can tumor ingrowth be prevented? Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007; 30:950–958. PMID: 17508236.
Article12. Han YM, Kwak HS, Jin GY, Lee SO, Chung GH. Treatment of malignant biliary obstruction with a PTFE-covered self-expandable nitinol stent. Korean J Radiol. 2007; 8:410–417. PMID: 17923784.
Article13. Fanelli F, Orgera G, Bezzi M, Rossi P, Allegritti M, Passariello R. Management of malignant biliary obstruction: technical and clinical results using an expanded polytetrafluoroethylene fluorinated ethylene propylene (ePTFE/FEP)-covered metallic stent after 6-year experience. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:911–919. PMID: 18204844.
Article14. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Kim JH, Yoon HK, Lee IS, Kim KA, et al. A comparative analysis of PTFE-covered and uncovered stents for palliative treatment of malignant extrahepatic biliary obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:W463–W469. PMID: 21098180.
Article15. Kim JW, Gwon D, Han YM, Won JH, Hong HP, Ko GY, et al. A prospective, multicenter study of a double stent system for palliative treatment of malignant extrahepatic biliary obstructions. Acta Radiol. 2015; 56:1209–1215. PMID: 25260418.
Article16. Guaglianone E, Cardines R, Vuotto C, Di Rosa R, Babini V, Mastrantonio P, et al. Microbial biofilms associated with biliary stent clogging. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010; 59:410–420. PMID: 20482630.
Article17. Leung JW, Ling TK, Kung JL, Vallance-Owen J. The role of bacteria in the blockage of biliary stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988; 34:19–22. PMID: 3280393.
Article18. van Berkel AM, van Marle J, Groen AK, Bruno MJ. Mechanisms of biliary stent clogging: confocal laser scanning and scanning electron microscopy. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:729–734. PMID: 16032491.
Article19. Hu B, Wang TT, Shi ZM, Wang SZ, Lu R, Pan YM, et al. A novel antireflux metal stent for the palliation of biliary malignancies: a pilot feasibility study (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:143–148. PMID: 20970788.
Article20. Kim DU, Kwon CI, Kang DH, Ko KH, Hong SP. New antireflux self-expandable metal stent for malignant lower biliary obstruction: in vitro and in vivo preliminary study. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25:60–66. PMID: 23286258.21. Hamada T, Isayama H, Nakai Y, Kogure H, Togawa O, Kawakubo K, et al. Novel antireflux covered metal stent for recurrent occlusion of biliary metal stents: a pilot study. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26:264–269. PMID: 23621525.
Article22. Hu B, Wang TT, Wu J, Shi ZM, Gao DJ, Pan YM. Antireflux stents to reduce the risk of cholangitis in patients with malignant biliary strictures: a randomized trial. Endoscopy. 2014; 46:120–126. PMID: 24477367.
Article23. Lee YN, Moon JH, Choi HJ, Choi MH, Lee TH, Cha SW, et al. Effectiveness of a newly designed antireflux valve metal stent to reduce duodenobiliary reflux in patients with unresectable distal malignant biliary obstruction: a randomized, controlled pilot study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:404–412. PMID: 26385187.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Stent Placement in the Palliation of Malignant Biliary Obstruction
- Malignant Duodenal Obstructions: Palliative Treatment with Covered Expandable Nitinol Stent
- Two Double Stents Insertion for Commen Bile Duct and Duodenal Obstruction Caused by Pancreatic Cancer
- Clinical outcomes of biliary and duodenal self-expandable metal stent placements for palliative treatment in patients with periampullary cancer
- Simultaneous Duodenal Metal Stent Placement and EUS-Guided Choledochoduodenostomy for Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer