Clin Endosc.
2018 Jan;51(1):56-60. 10.5946/ce.2017.059.
Safety of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tubes in Centenarian Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY, USA.
- 2Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY, USA. ytsirlin@maimonidesmed.org
- 3Long Island Jewish Forest Hills, Queens, NY, USA.
- 4Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, Hempstead, NY, USA.
- 5Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Yeshiva University, Bronx, NY, USA.
- KMID: 2403633
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.059
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is a relatively safe procedure; however, no study has evaluated the safety of PEG tube placement in patients over the age of 100 years.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective review of patient records for patients who underwent PEG tube placement. Thirty patients aged 100 years and older were identified and a random sample of 275 patients was selected for comparison.
RESULTS
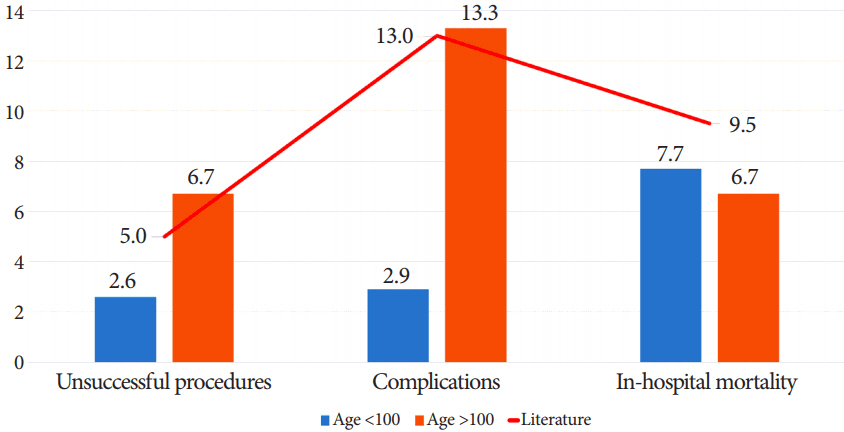
The mean age of the patients was 80.6±16.2 years. No procedure-related deaths or major complications were identified; the overall inpatient mortality rate was 7.6%. Minor complications were noted in 4% (n=12) of the patients. Centenarian patients were predominantly female (80% [n=24] vs. 54% [n=147], p=0.006), with a mean age of 100.5±0.9 years. There was no significant difference in procedural success rates (93.3% vs. 97.4%, p=0.222) or inpatient mortality (6.7% [n=2] vs. 7.7% [n=21], p=1.000) between the two groups. However, a higher minor complication rate was noted in the older patients (13.3% [n=4] vs. 2.9% [n=8], p=0.022).
CONCLUSIONS
Success rates, major complications and inpatient mortality associated with PEG tubes in patients aged over 100 years are comparable to those observed in relatively younger patients at our center; however minor complication rates are relatively higher. These findings lead us to believe that PEG tubes may be safely attempted in carefully selected patients in this subset of the population.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Clinical Course of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy: A Single-center Observational Study
Jihyun Lee, Ki-Nam Shim, Kang Hoon Lee, Ko Eun Lee, Ji Young Chang, Chung Hyun Tae, Chang Mo Moon, Seong-Eun Kim, Hye-Kyung Jung, Sung-Ae Jung
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018;71(1):24-30. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2018.71.1.24.Is Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Acceptable in Centenarian Patients?
Cheol Min Shin, Dong Ho Lee
Clin Endosc. 2018;51(1):1-2. doi: 10.5946/ce.2018.018.
Reference
-
1. Gauderer MW, Ponsky JL, Izant RJ Jr. Gastrostomy without laparotomy: a percutaneous endoscopic technique. J Pediatr Surg. 1980; 15:872–875.
Article2. McClave SA, Chang WK. Complications of enteral access. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:739–751.
Article3. Chang WK, Hsieh TY. Safety of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in high-risk patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 28 Suppl 4:118–122.
Article4. DeLegge MH, Saltzman JR, Lipman TO, Robson KM. Gastrostomy tubes: complications and their management [database on the Internet]. Alphen aan den Rijn: Wolters Kluwer Health;UpToDate; 2015 [updated 2015 Apr 15; cited 2017 Mar]. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/gastrostomy-tubes-complications-and-their-management?source=search_result&search=%22Gastrostomy%20tubes:%20complications%20and%20their%20management%22&selectedTitle=1~1.5. Larson DE, Burton DD, Schroeder KW, DiMagno EP. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Indications, success, complications, and mortality in 314 consecutive patients. Gastroenterology. 1987; 93:48–52.6. Keung EZ, Liu X, Nuzhad A, Rabinowits G, Patel V. In-hospital and long-term outcomes after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in patients with malignancy. J Am Coll Surg. 2012; 215:777–786.
Article7. Rimon E. The safety and feasibility of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy placement by a single physician. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:241–244.
Article8. Wollman B, D’Agostino HB, Walus-Wigle JR, Easter DW, Beale A. Radiologic, endoscopic, and surgical gastrostomy: an institutional evaluation and meta-analysis of the literature. Radiology. 1995; 197:699–704.
Article9. Arora G, Rockey D, Gupta S. High in-hospital mortality after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: results of a nationwide population-based study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:1437–1444.e3.
Article10. Light VL, Slezak FA, Porter JA, Gerson LW, McCord G. Predictive factors for early mortality after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995; 42:330–335.
Article11. Wirth R, Voss C, Smoliner C, Sieber CC, Bauer JM, Volkert D. Complications and mortality after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in geriatrics: a prospective multicenter observational trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012; 13:228–233.
Article12. Callahan CM, Haag KM, Weinberger M, et al. Outcomes of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy among older adults in a community setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2000; 48:1048–1054.
Article13. Gorman BK, Read JG. Why men die younger than women. Geriatr Aging. 2007; 10:182–191.14. Pender SM, Courtney MG, Rajan E, McAdam B, Fielding JF. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy--results of an Irish single unit series. Ir J Med Sci. 1993; 162:452–455.15. Wilson WR, Hariri SM. Experience with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy on an otolaryngology service. Ear Nose Throat J. 1995; 74:760–762.
Article16. Manjunath RS, Fisher NC. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube placement in patients with compound hiatus hernia and intrathoracic stomach: a case series. Gut. 2011; 60 Suppl 1:A98–A99.
Article17. Xenos ES. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in a patient with a large hiatal hernia using laparoscopy. JSLS. 2000; 4:231–233.18. Gumaste VV, Bhamidimarri KR, Bansal R, Sidhu L, Baum J, Walfish A. Factors predicting early discharge and mortality in post-percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy patients. Ann Gastroenterol. 2014; 27:42–47.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Acceptable in Centenarian Patients?
- Percutaneous Gastrostomy
- Long Term Efficacy of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
- A Case of Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in a Patient with Liver Cirrhosis Accompanied by Both Esophageal and Gastric Varices
- A Case of Buried Bumper Syndrome; A case report