J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2018 Jan;61(1):42-50. 10.3340/jkns.2017.0224.
Compare the Intracranial Pressure Trend after the Decompressive Craniectomy between Massive Intracerebral Hemorrhagic and Major Ischemic Stroke Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Myungji St. Mary’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, Uijeongbu, Korea. yooman@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, St. Paul’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurosurgery, Incheon St. Mary’s Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurosurgery, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2403522
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0224
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Massive intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) and major infarction (MI) are devastating cerebral vascular diseases. Decompression craniectomy (DC) is a common treatment approach for these diseases and acceptable clinical results have been reported. Author experienced the postoperative intracranaial pressure (ICP) trend is somewhat different between the ICH and MI patients. In this study, we compare the ICP trend following DC and evaluate the clinical significance.
METHODS
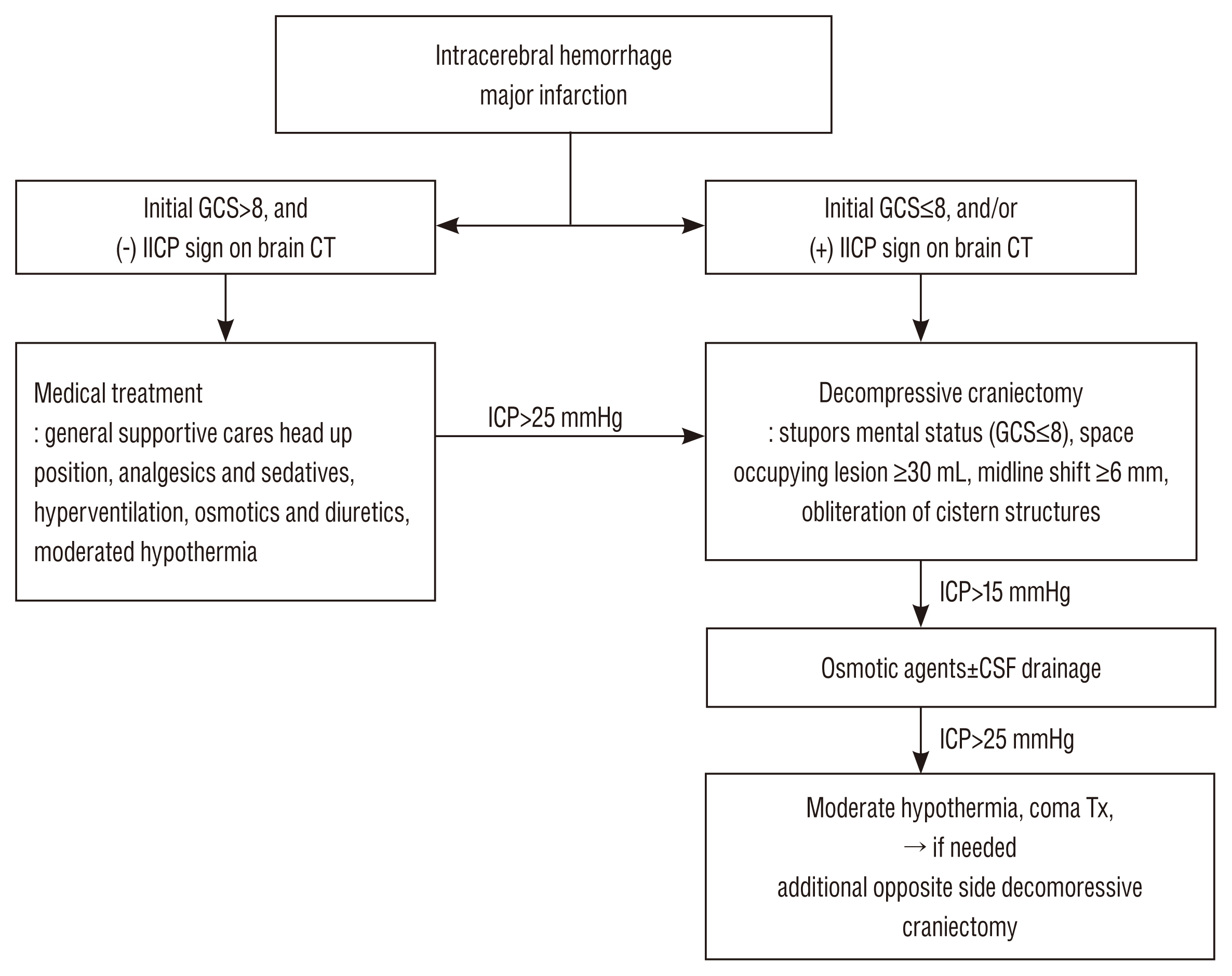
One hundred forty-three patients who underwent DC following massive ICH (81 cases) or MI (62 cases) were analyzed retrospectively. The mean age was 56.3±14.3 (median=57, male : female=89 : 54). DC was applied using consistent criteria in both diseases patients; Glasgow coma scale (GCS) score less than 8 and a midline shift more than 6 mm on brain computed tomography. In all patients, ventricular puncture was done before the DC and ICP trends were monitored during and after the surgery. Outcome comparisons included the ictus to operation time (OP-time), postoperative ICP trend, favorable outcomes and mortality.
RESULTS
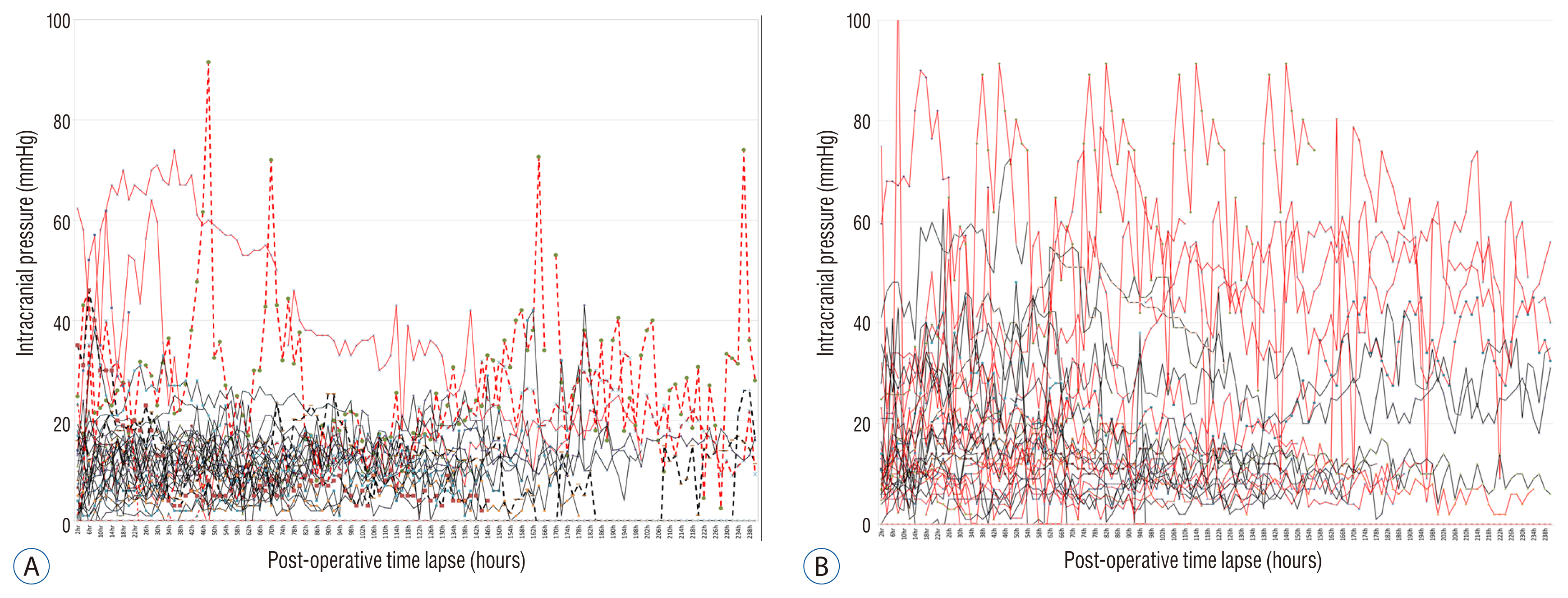
Initial GCS (p=0.364) and initial ventricular ICP (p=0.783) were similar among the ICH and MI patients. The postoperative ICP of ICH patients were drop rapidly and maintained within physiological range if greater than 80% of the hematoma was removed. While in MI patients, the postoperative ICP were not drop rapidly and maintained above the physiologic range (MI=18.8 vs. ICH=13.6 mmHg, p=0.000). The OP-times were faster in ICH patients (ICH=7.3 vs. MI=40.9 hours, p=0.000) and the mortality rate was higher in MI patients (MI=37.1% vs. ICH=17.3%, p=0.007).
CONCLUSION
The results of this study suggest that if greater than 80% of the hematoma was removed in ICH patients, the postoperative ICP rarely over the physiologic range. But in MI patients, the postoperative ICP was above the physiologic range for several days after the DC. Authors propose that DC is no need for the massive ICH patient if a significant portion of their hematoma is removed. But DC might be essential to improve the MI patients' outcome and timely treatment decision.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Al-Jehani H, Petrecca K, Martel P, Sinclair D, Sirhan D. Decompressive craniectomy for ischemic stroke: effect of hemorrhagic transformation on outcome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 25:2177–2183. 2016.
Article2. Anderson CS, Chakera TM, Stewart-Wynne EG, Jamrozik KD. Spectrum of primary intracerebral haemorrhage in Perth, Western Australia, 1989–90: incidence and outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 57:936–940. 1994.
Article3. Arac A, Blanchard V, Lee M, Steinberg GK. Assessment of outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction in patients older than 60 years of age. Neurosurg Focus. 26:E3. 2009.
Article4. Brain Trauma Foundation; American Association of Neurological Surgeons; Congress of Neurological Surgeons; Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care, AANS/CNS. Bratton SL, Chestnut RM, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. VIII Intracranial pressure thresholds. J Neurotrauma. 24:Suppl 1. S55–S58. 2007.5. Broderick JP, Adams HP Jr, Barsan W, Feinberg W, Feldmann E, Grotta J, et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the stroke council, American Heart Association. Stroke. 30:905–915. 1999.
Article6. Broderick JP, Brott T, Tomsick T, Miller R, Huster G. Intracerebral hemorrhage more than twice as common as subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 78:188–191. 1993.
Article7. Brott T, Broderick J, Kothari R, Barsan W, Tomsick T, Sauerbeck L, et al. Early hemorrhage growth in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 28:1–5. 1997.
Article8. Carney N, Totten AM, O’Reilly C, Ullman JS, Hawryluk GW, Bell MJ, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury, fourth edition. Neurosurgery. 80:6–15. 2017.
Article9. Cooper PR, Rovit RL, Ransohoff J. Hemicraniectomy in the treatment of acute subdural hematoma: a re-appraisal. Surg Neurol. 5:25–28. 1976.10. Csókay A, Pataki G, Nagy L, Belán K. Vascular tunnel construction in the treatment of severe brain swelling caused by trauma and SAH. (evidence based on intra-operative blood flow measure). Neurol Res. 24:157–160. 2002.
Article11. Dierssen G, Carda R, Coca JM. The influence of large decompressive craniectomy on the outcome of surgical treatment in spontaneous intracerebral haematomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 69:53–60. 1983.
Article12. Fung C, Murek M, Z’Graggen WJ, Krähenbühl AK, Gautschi OP, Schucht P, et al. Decompressive hemicraniectomy in patients with supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 43:3207–3211. 2012.
Article13. Gaab MR, Rittierodt M, Lorenz M, Heissler HE. Traumatic brain swelling and operative decompression: a prospective investigation. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien). 51:326–328. 1990.
Article14. Güresir E, Schuss P, Vatter H, Raabe A, Seifert V, Beck J. Decompressive craniectomy in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg Focus. 26:E4. 2009.
Article15. Hatashita S, Hoff JT. The effect of craniectomy on the biomechanics of normal brain. J Neurosurg. 67:573–548. 1987.
Article16. Hofmeijer J, Kappelle LJ, Algra A, Amelink GJ, van Gijn J, van der Worp HB. Surgical decompression for space-occupying cerebral infarction (the hemicraniectomy after middle cerebral artery infarction with life-threatening edema trial [HAMLET]): a multicentre, open, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 8:326–333. 2009.
Article17. Hutchinson PJ, Kolias AG, Timofeev IS, Corteen EA, Czosnyka M, Timothy J, et al. Trial of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic intracranial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 375:1119–1130. 2016.
Article18. Jaeger M, Soehle M, Meixensberger J. Effects of decompressive craniectomy on brain tissue oxygen in patients with intracranial hypertension. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 74:513–515. 2003.
Article19. Jüttler E, Schwab S, Schmiedek P, Unterberg A, Hennerici M, Woitzik J, et al. Decompressive surgery for the treatment of malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery (DESTINY): a randomized, controlled trial. Stroke. 38:2518–2525. 2007.
Article20. Kazui S, Naritomi H, Yamamoto H, Sawada T, Yamaguchi T. Enlargement of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Incidence and time course Stroke. 27:1783–1787. 1996.
Article21. Kenning TJ, Gooch MR, Gandhi RH, Shaikh MP, Boulos AS, German JW. Cranial decompression for the treatment of malignant intracranial hypertension after ischemic cerebral infarction: decompressive craniectomy and hinge craniotomy. J Neurosurg. 116:1289–1298. 2012.
Article22. Kim KT, Park JK, Kang SG, Cho KS, Yoo DS, Jang DK, et al. Comparison of the effect of decompressive craniectomy on different neurosurgical diseases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 151:21–30. 2009.
Article23. Kurzbuch AR. Does size matter? Decompressive surgery under review. Neurosurg Rev. 38:629–640. 2015.
Article24. Macdonell RAL, Kalnins RM, Donnan GA. Cerebellar infarction: natural history, prognosis, and pathology. Stroke. 18:849–855. 1987.
Article25. Maira G, Anile C, Colosimo C, Rossi GF. Surgical treatment of primary supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage in stuporous and comatose patients. Neurol Res. 24:54–60. 2002.
Article26. Maramattom BV, Bahn MM, Wijdicks EF. Which patient fares worse after early deterioration due to swelling from hemispheric stroke? Neurology. 63:2142–2145. 2004.
Article27. Marinkovic I, Strbian D, Pedrono E, Vekovischeva OY, Shekhar S, Durukan A, et al. Decompressive craniectomy for intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 65:780–786. 2009.
Article28. Mayer SA, Brun NC, Begtrup K, Broderick J, Davis S, Diringer MN, et al. Recombinant activated factor VII intracerebral hemorrhage Trial Investigators: Recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 352:777–785. 2005.
Article29. Mitchell P, Gregson BA, Vindlacheruvu RR, Mendelow AD. Surgical options in ICH including decompressive craniectomy. J Neurol Sci. 261:89–98. 2007.
Article30. Otani N, Takasato Y, Masaoka H, Hayakawa T, Yoshino Y, Yatsushige H, et al. Surgical outcome following decompressive craniectomy for poor-grade aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in patients with associated massive intracerebral or sylvian hematomas. Cerebrovasc Dis. 26:612–617. 2008.
Article31. Paldor I, Rosenthal G, Cohen JE, Leker R, Harnof S, Shoshan Y, et al. Intracranial pressure monitoring following decompressive hemicraniectomy for malignant cerebral infarction. J Clin Neurosci. 22:79–82. 2015.
Article32. Rothwell PM, Fowkes FG, Belch JF, Ogawa H, Warlow CP, Meade TW. Effect of daily aspirin on long-term risk of death due to cancer: analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet. 377:31–41. 2011.
Article33. Schirmer CM, Hoit DA, Malek AM. Decompressive hemicraniectomy for the treatment of intractable intracranial hypertension after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 38:987–992. 2007.
Article34. Slotty PJ, Kamp MA, Beez T, Beenen H, Steiger HJ, Turowski B, et al. The influence of decompressive craniectomy for major stroke on early cerebral perfusion. J Neurosurg. 123:59–64. 2015.
Article35. Smith ER, Carter BS, Ogilvy CS. Proposed use of prophylactic decompressive craniectomy in poor-grade aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients presenting with associated large sylvian hematomas. Neurosurgery. 51:117–124. 2002.
Article36. Strege RJ, Lang EW, Stark AM, Scheffner H, Fritsch MJ, Barth H, et al. Cerebral edema leading to decompressive craniectomy: an assessment of the preceding clinical and neuromonitoring trends. Neurol Res. 25:510–515. 2003.
Article37. Toni D, Fiorelli M, Gentile M, Bastianello S, Sacchetti ML, Argentino C, et al. Progressing neurological deficit secondary to acute ischemic stroke. A study on predictability, pathogenesis, and prognosis. Arch Neurol. 52:670–675. 1995.
Article38. Tagliaferri F, Zani G, Iaccarino C, Ferro S, Ridolfi L, Basaglia N, et al. Decompressive craniectomies, facts and fiction: a retrospective analysis of 526 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 154:919–926. 2012.
Article39. Vahedi K, Vicaut E, Mateo J, Kurtz A, Orabi M, Guichard JP, et al. Sequential-design, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of early decompressive craniectomy in malignant middle cerebral artery infarction (DECIMAL Trial). Stroke. 38:2506–2517. 2007.
Article40. Xiao B, Wu FF, Zhang H, Ma YB. A randomized study of urgent computed tomography-based hematoma puncture and aspiration in the emergency department and subsequent evacuation using craniectomy versus craniectomy only. J Neurosurg. 117:566–573. 2012.
Article41. Yamakami I, Yamaura A. effects of decompressive craniectomy on regional cerebral blood flow in severe head trauma patients. Neruol Med Chir (Tokyo). 33:616–620. 1993.
Article42. Yoo DS, Kim DS, Cho KS, Huh PW, Park CK, Kang JK. Ventricular pressure monitoring during bilateral decompression with dural expansion. J Neurosurg. 91:953–959. 1999.
Article43. Zazulia AR, Diringer MN, Derdeyn CP, Powers WJ. Progression of mass effect after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 30:1167–1173. 1999.
Article44. Ziai WC, Port JD, Cowan JA, Garonzik IM, Bhardwaj A, Rigamonti D. Decompressive craniectomy for intractable cerebral edema: experience of a single center. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 15:25–32. 2003.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Decompressive Craniectomy on Massive Brain Swelling Patients According to the Diseases
- ICP Trend in Massive ICH Patients After Decompressive Craniectomy
- Paradoxical Herniation after Decompressive Craniectomy for Acute Subdural Hematoma
- Bilateral Multiple Intracerebral Hemorrhagic Infarction after Cranioplasty in a Patient with Cerebral Infarction: Case Report
- Surgical Management of Acute Stroke