Ann Lab Med.
2018 May;38(3):274-276. 10.3343/alm.2018.38.3.274.
Circulating Microparticles and Coagulation Profiles in Patients with Advanced Stage Solid Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. bbonui@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2403464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.3.274
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
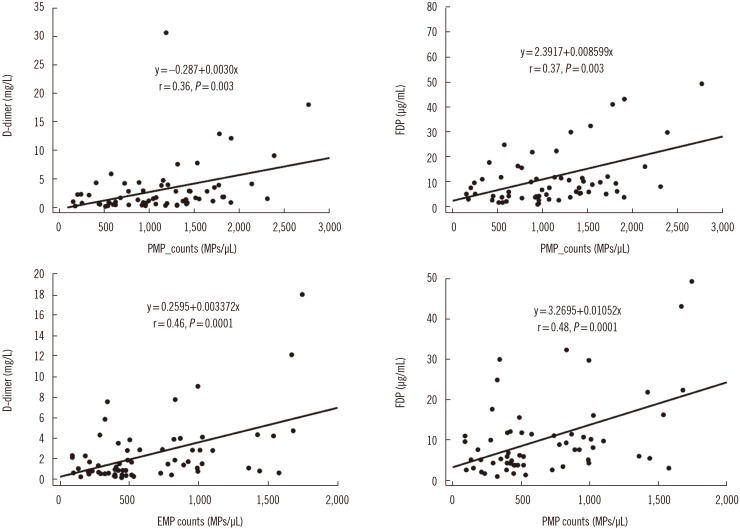
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chew HK, Wun T, Harvey D, Zhou H, White RH. Incidence of venous thromboembolism and its effect on survival among patients with common cancers. Arch Intern Med. 2006; 166:458–464. PMID: 16505267.2. Sorensen HT, Mellemkjaer L, Olsen JH, Baron JA. Prognosis of cancers associated with venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:1846–1850. PMID: 11117976.3. Thaler J, Ay C, Weinstabl H, Dunkler D, Simanek R, Vormittag R, et al. Circulating procoagulant microparticles in cancer patients. Ann Hematol. 2011; 90:447–453. PMID: 20981426.4. Biro E, Sturk-Maquelin KN, Vogel GM, Meuleman DG, Smit MJ, Hack CE, et al. Human cell-derived microparticles promote thrombus formation in vivo in a tissue factor-dependent manner. J Thromb Haemost. 2003; 1:2561–2568. PMID: 14738565.5. Zhang X, McGeoch SC, Johnstone AM, Holtrop G, Sneddon AA, MacRury SM, et al. Platelet-derived microparticle count and surface molecule expression differ between subjects with and without type 2 diabetes, independently of obesity status. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014; 37:455–463. PMID: 24097206.6. Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007; 39:175–191. PMID: 17695343.7. Tesselaar ME, Romijn FP, van der Linden IK, Bertina RM, Osanto S. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity in cancer patients with and without thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7:1421–1423. PMID: 19500241.8. Manly DA, Wang J, Glover SL, Kasthuri R, Liebman HA, Key NS, et al. Increased microparticle tissue factor activity in cancer patients with Venous Thromboembolism. Thromb Res. 2010; 125:511–512. PMID: 19854471.9. Beer JH, Haeberli A, Vogt A, Woodtli K, Henkel E, Furrer T, et al. Coagulation markers predict survival in cancer patients. Thromb Haemost. 2002; 88:745–749. PMID: 12428088.10. Thaler J, Ay C, Mackman N, Metz-Schimmerl S, Stift J, Kaider A, et al. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity in patients with pancreatic cancer: correlation with clinicopathological features. Eur J Clin Invest. 2013; 43:277–285. PMID: 23398637.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Absorption Study of Genistein Using Solid Lipid Microparticles and Nanoparticles: Control of Oral Bioavailability by Particle Sizes
- Association between vascular access failure and microparticles in hemodialysis patients
- A Case of Systemic Chemetherapy in Advanced Seminoma
- Three Cases of Synchronous Solid Tumor and Multiple Myeloma
- Preparation of Collagen Modified Hyaluronan Microparticles as Antibiotics Carrier