J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2018 Jan;56(1):25-30. 10.4047/jkap.2018.56.1.25.
Full mouth rehabilitation of mandibular edentulous patient using implant hybrid prosthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Republic of Korea. onsdo@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2402984
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2018.56.1.25
Abstract
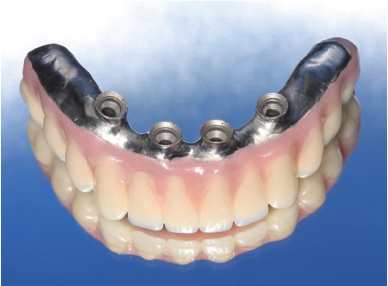
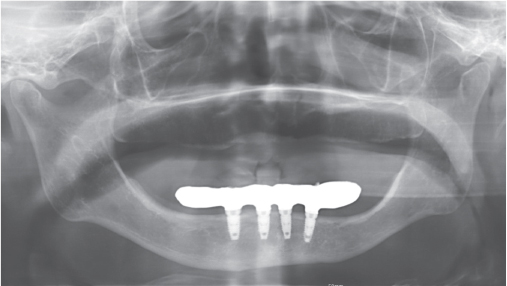
- In edentulous patients, the advantages of prosthodontic therapy using oral implants include both stability and comfort. Advantages suggested for this approach include the prevention of mandibular bone resorption and increased masticatory function. Implant hybrid prostheses place 4 to 6 implants between the mental foramens, and cantilevers are used to replace the posterior teeth at both ends. The 85 - year - old female patient visited our clinic with complete edentulism in the maxilla and mandible. This article reports a satisfactory clinical and esthetic outcome of full mouth rehabilitation using removable complete denture in the maxilla and implant hybrid prosthesis in the mandible.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tallgren A. The continuing reduction of the residual alveolar ridges in complete denture wearers: a mixed-longitudinal study covering 25 years. J Prosthet Dent. 1972; 27:120–132.
Article2. Cooper LF. The current and future treatment of edentulism. J Prosthodont. 2009; 18:116–122.
Article3. Misch CE. Contemporary implant dentistry. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby;2009. p. 94–101.4. Drago C, Gurney L. Maintenance of implant hybrid prostheses: clinical and laboratory procedures. J Prosthodont. 2013; 22:28–35.
Article5. Zitzmann NU, Marinello CP. A review of clinical and technical considerations for fixed and removable implant prostheses in the edentulous mandible. Int J Prosthodont. 2002; 15:65–72.6. Kwon T, Bain PA, Levin L. Systematic review of short- (5-10 years) and long-term (10 years or more) survival and success of full-arch fixed dental hybrid prostheses and supporting implants. J Dent. 2014; 42:1228–1241.
Article7. English CE. The mandibular overdenture supported by implants in the anterior symphysis: a prescription for implant placement and bar-prosthesis design. Dent Implantol Update. 1993; 4:9–14.8. Chung CH, Son MK. The classification and comparison of implant prosthesis according to types of retention. Part I: screw retained prosthesis vs cement retained prosthesis. J Korean Acad Oral Maxillofac Implantol. 2010; 14:138–151.9. Misch CE. Dental implant prosthetics. 1st ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby;2004. p. 414–416.10. Gracis S, Michalakis K, Vigolo P, Vult von Steyern P, Zwahlen M, Sailer I. Internal vs. external connections for abutments/reconstructions: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23:202–216.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Full mouth rehabilitation of fully edentulous patient using implant hybrid prosthesis
- Full mouth rehabilitation of mandibular edentulous patient using implant hybrid prosthesis
- Full mouth rehabilitation of fully edentulous patient with implant-supported fixed prosthesis preceding bone graft: A case report
- Full mouth rehabilitation of edentulous patient with fixed implant prosthesis
- Full mouth implant-supported fixed prosthesis restoration of an edentulous maxillary patient using computer-guided implant surgery