J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2017 Mar;24(1):55-58. 10.4184/jkss.2017.24.1.55.
First Coccygeal Vertebra Dislocation Treated by Open Reduction and Internal Fixation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea. 98tjddlr@naver.com
- KMID: 2402844
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2017.24.1.55
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Case report.
OBJECTIVES
To report the effectiveness of open reduction and internal (screw) fixation treatment performed to treat dislocation of the first coccygeal vertebra. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Most treatment methods for coccygeal dislocation were conservative treatment for acute coccygodynia and coccygectomy for chronic coccygodynia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
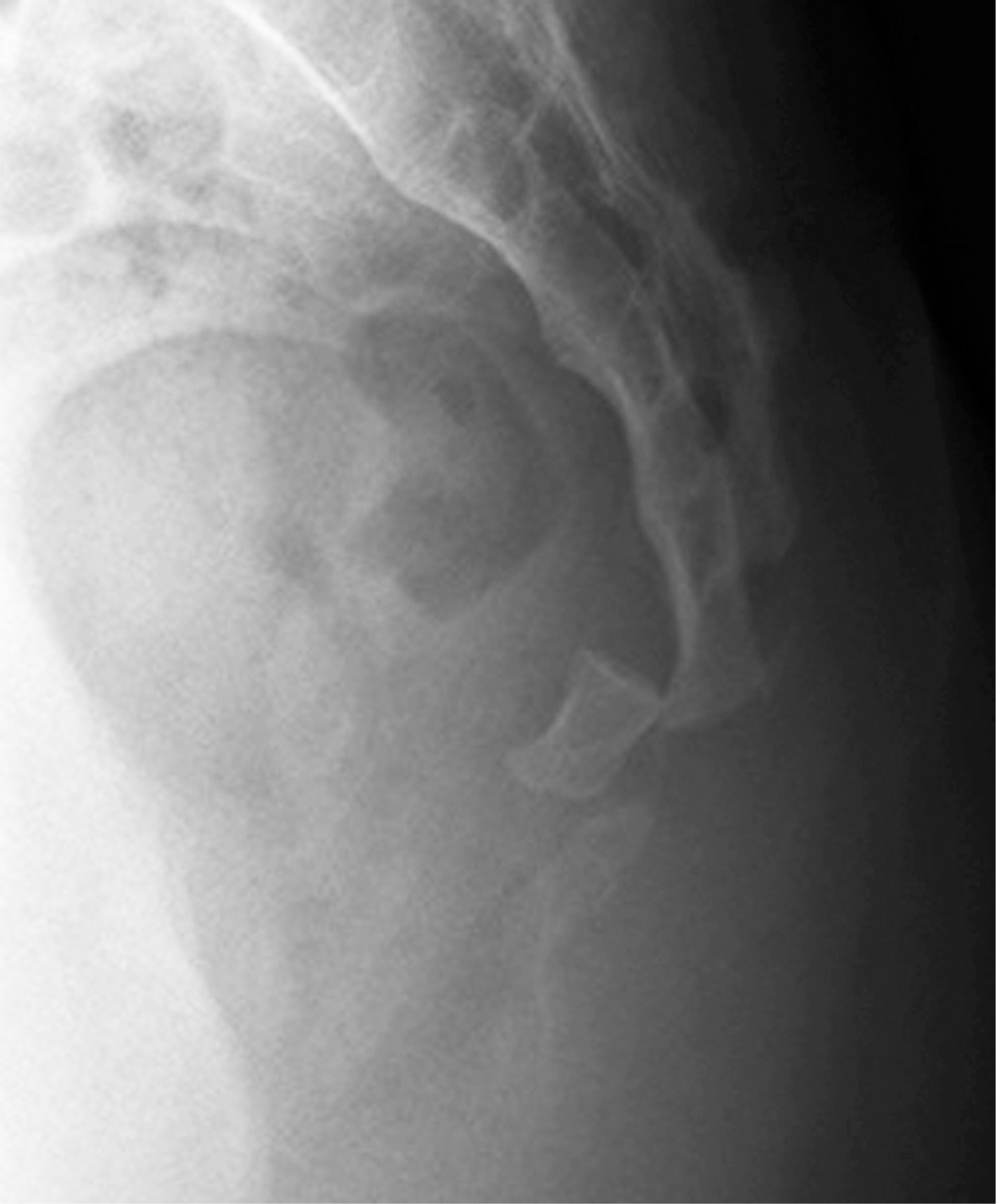
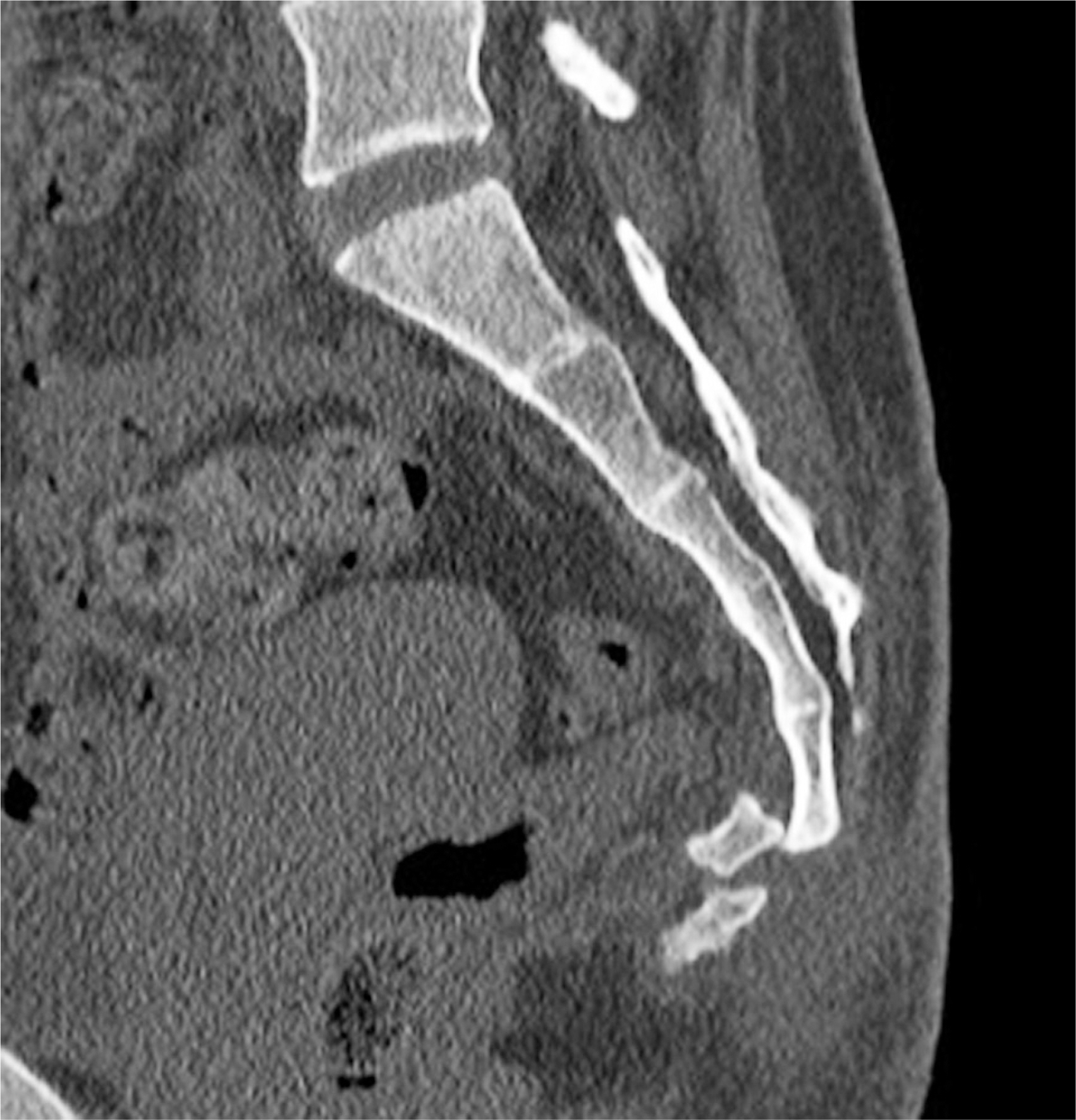
A 18-year-old female presented with severe coccygodynia due to a fall down the stairs. Computed tomography showed dislocation of the first coccygeal vertebra. We performed open reduction and internal fixation with a 4.0-mm shortthread cancellous screw with a washer, with no additional procedure for bone union.
RESULTS
Union was achieved 10 weeks postoperatively.
CONCLUSIONS
Open reduction and internal (screw) fixation can be a useful method for coccygeal vertebra dislocation.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Johnson PH. Coccygodynia. J Ark Med Soc. 1981; 77:421–4.2. Karadimas EJ, Trypsiannis G, Giannoudis PV. Surgical treatment of coccygodynia: an analytic review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2010; 20:698–705.
Article3. Maigne JY, Doursounian L, Chatellier G. Causes and mechanisms of common coccydynia: role of body mass index and coccygeal trauma. Spine. 2000; 25:3072–9.4. Perkins R, Schofferman J, Reynolds J. Coccygectomy for severe refractory sacrococcygeal joint pain. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003; 16:100–3.
Article5. Key J A. Operative treatment of coccygodynia. J Bone Joint Surg. 1937; 19:759–64.6. Ramieri A, Domenicucci M, Cellocco P, et al. Acute traumatic instability of the coccyx: results in 28 consecutive coccygectomies. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:939–44.
Article7. Bergkamp AB, Verhaar JA. Dislocation of the coccyx: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77:831–2.
Article8. Kim WY, Han CW, Kim YH. Joystick reduction and percutaneous pinning for an acutely anteriorly dislocated coccyx: a case report. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:388–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Treatment of Volar Iunate Dislocation and Perilunar Dislocation
- Carpometacarpal Joint Fracture Dislocation of Second to Fifth Finger
- Axial-Ulnar fracture-Dislocation of the Carpus : A Case Report
- An Isolated Fracture-Dislocation of the Cuboid: A Case of Report
- A Operative treatment of the three-part, four-part Fracture and Fracture dislocation in proximal humerus