J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2018 Jan;59(1):60-66. 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.1.60.
Comparison between Modified Bilateral Lateral Rectus Recession and Augmented Unilateral Recession-resection for Convergence Insufficiency Exotropia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. smile-ri@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2401679
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2018.59.1.60
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the surgical outcomes between modified bilateral lateral rectus muscle (BLR) recession and augmented unilateral recession-resection (R&R) for the convergence insufficiency intermittent exotropia (IXT).
METHODS
37 patients with convergence insufficiency IXT were divided into two groups: 13 patients (underwent BLR recession) and 24 patients (underwent unilateral R&R). Success was defined as within 10 prism diopters (PD) at distance and near, and within 10 PD of the difference between them at postoperative 12 months.
RESULTS
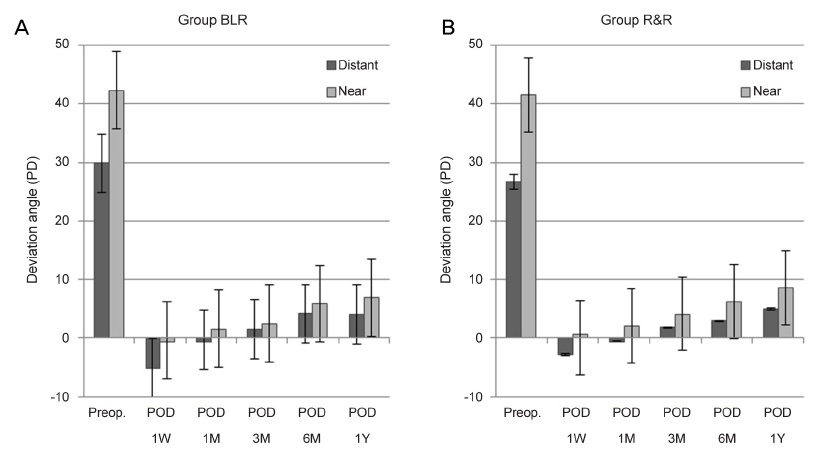
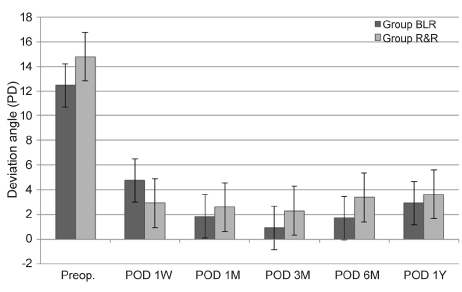
After the patch test, the preoperative distance deviation angle in the BLR group was 29.9 ± 8.4 PD, and the near deviation angle was 42.3 ± 9.7 PD; the difference between them was 12.5 ± 3.2 PD. In the R&R group, the preoperative distance deviation angle was 26.7 ± 5.8 PD, and the near deviation angle was 41.5 ± 7.4 PD; the difference between them was 14.8 ± 4.3 PD (p = 0.235, p = 0.987, and p = 0.123). At the 12-month follow-up in the BLR group, the distance angle was 3.8 ± 5.1 PD, and the near deviation angle was 4.9 ± 6.1 PD; the difference between them was 2.9 ± 5.9 PD. In the R&R group, the postoperative distance deviation angle was 4.7 ± 6.1 PD, and the near deviation angle was 7.9 ± 6.6 PD; the difference between them was 3.65 ± 5.1 PD (p = 0.708, p = 0.162, and p = 0.632, respectively). The surgical success rate did not differ significantly between groups at 12 months postoperatively (76.9%: BLR group and 70.8%: R&R group; p = 0.690).
CONCLUSIONS
Modified BLR recession showed a similar surgical success rate to augmented unilateral R&R, and was effective in reducing both distance and near exodeviation, and in decreasing the difference between distance and near deviation in convergence insufficiency IXT.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burian HM. Exodeviations: their classification, diagnosis and treatment. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966; 62:1161–1166.
Article2. Daum KM. Convergence insufficiency. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1984; 61:16–22.
Article3. Daum KM. Characteristics of convergence insufficiency. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1988; 65:426–438.
Article4. Birnbaum MH, Soden R, Cohen AH. Efficacy of vision therapy for convergence insufficiency in an adult male population. J Am Optom Assoc. 1999; 70:225–232.5. Choi DG, Rosenbaum AL. Medial rectus resection(s) with adjustable suture for intermittent exotropia of the convergence insufficiency type. J AAPOS. 2001; 5:13–17.
Article6. Choi MY, Hwang JM. The long-term result of slanted medial rectus resection in exotropia of the convergence insufficiency type. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:1279–1283.
Article7. Snir M, Axer-Siegel R, Shalev B, et al. Slanted lateral rectus recession for exotropia with convergence weakness. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:992–996.
Article8. von Noorden GK. Resection of both medial rectus muscles in organic convergence insufficiency. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976; 81:223–226.
Article9. Hermann JS. Surgical therapy for convergence insufficiency. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1981; 18:28–31.
Article10. Raab EL, Parks MM. Recession of the lateral recti. Effect of preoperative fusion and distance-near relationship. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975; 93:584–586.11. Ohtsuki H, Hasebe S, Kono R, et al. Prism adaptation response is useful for predicting surgical outcome in selected types of intermittent exotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 131:117–122.
Article12. Kushner BJ. Surgical pearls for the management of exotropia. Am Orthopt J. 1992; 42:65–71.
Article13. Kraft SP, Levin AV, Enzenauer RW. Unilateral surgery for exotropia with convergence weakness. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1995; 32:183–187.
Article14. Kushner BJ. Exotropic deviations: a functional classification and approach to treatment. Am Orthopt J. 1988; 38:81–93.
Article15. Chun BY, Kang KM. Early results of slanted recession of the lateral rectus muscle for intermittent exotropia with convergence insufficiency. J Ophthalmol. 2015; 2015:380467.
Article16. Yang HK, Hwang JM. Surgical outcomes in convergence insufficiency-type exotropia. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:1512–1517.
Article17. Cooper J. Major review: intermittent exotropia. Basic and divergence excess type. Binoc Vis Eye Muscle Surg Q. 1993; 8:185–216.18. Kushner BJ, Morton GV. Distant/near differences in intermittent exotropia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:478–486.19. Haldi BA. Surgical management of convergence insufficiency. Am Orthopt J. 1978; 28:106–109.
Article20. Kushner BJ. Selective surgery of intermittent exotropia based on distance/near differences. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:324–328.21. Scott AB. Strabismus muscle forces and innervation.In : Lenerstrand G, Bach-y-Rita P, editors. Basic Mechanism of Ocular Motility and Their Clinical Implications, Wenner-Gren Center International Symposium Series (Proceedings of the International Symposium held in Wenner-Gren Center, Stockholm, June 4-6, 1974). 1st ed. New York: Pergamon Press;1975. p. 181–191.22. Choi MY, Hyung SM, Hwang JM. Unilateral recession-resection in children with exotropia of the convergence insufficiency type. Eye (Lond). 2017; 21:344–347.
Article23. Kushner BJ. Insertion slanting strabismus surgical procedures. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011; 129:1620–1625.
Article24. Burian HM, Franceschetti AT. Evaluation of diagnostic methods for the classification of exodeviations. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1970; 68:56–71.
Article25. Kim SH, Kim SY, Kwon JY. Change of deviation angle after monocular occlusion in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1175–1182.26. Ruttum MS. Initial versus subsequent postoperative motor alignment in intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS. 1997; 1:88–91.
Article27. Raab EL, Parks MM. Recession of lateral recti. Early and late postoperative alignments. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969; 82:203–208.28. Ko KH, Min BM. Factors related to surgical results of intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1996; 37:179–184.29. Kim SJ. Comparison of surgical results between bilateral recession and unilateral recession-resection in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1992; 33:733–738.30. Keech RV, Stewart SA. The surgical overcorrection of intermittent exotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1990; 27:218–220.
Article31. Jang JH, Park JM, Lee SJ. Factors predisposing to consecutive esotropia after surgery to correct intermittent exotropia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250:1485–1490.
Article32. Lee EK, Yang HK, Hwang JM. Long-term outcome of prismatic correction in children with consecutive esotropia after bilateral lateral rectus recession. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015; 99:342–345.
Article33. Kim HJ, Choi DG. Consecutive esotropia after surgery for intermittent exotropia: the clinical course and factors associated with the onset. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014; 98:871–875.
Article34. Park HS, Kim JB, Seo MS, Park YG. A study on the consecutive esotropia after intermittent exotropia surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:1327–1334.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Bilateral Lateral Rectus Recession and Unilateral Recession-Resection in Large Angle Exotropia
- Comparison of Surgical Results Between Bilateral Recession and Unilateral Resection-Recession in Intermittent Exotropia
- Comparison of Surgical Results Between Bilateral Recession and Unilateral Recession-Resection in Intermittent Exotropia
- Comparison of the Change in Tension of Lateral Rectus Muscle between Bilateral Recession of Lateral Rectus Muscle and Unilateral Recession of Lateral Rectus Muscle and Resection of Medial Rectus Muscle in Rabbit
- Comparison of Surgical Results by Initial Postoperative Alignment Following Bilateral Lateral Rectus Recession and Unilateral Lateral Rectus Recession-Medial Rectus Resection in Intermittent Exotropes