Nat Prod Sci.
2017 Dec;23(4):227-234. 10.20307/nps.2017.23.4.227.
Induction of Apoptosis with Moringa oleifera Fruits in HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells Via Intrinsic Pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Natural Sciences, Duksung Women's University, Seoul 01369, Korea. hasook@duksung.ac.kr
- KMID: 2401572
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2017.23.4.227
Abstract
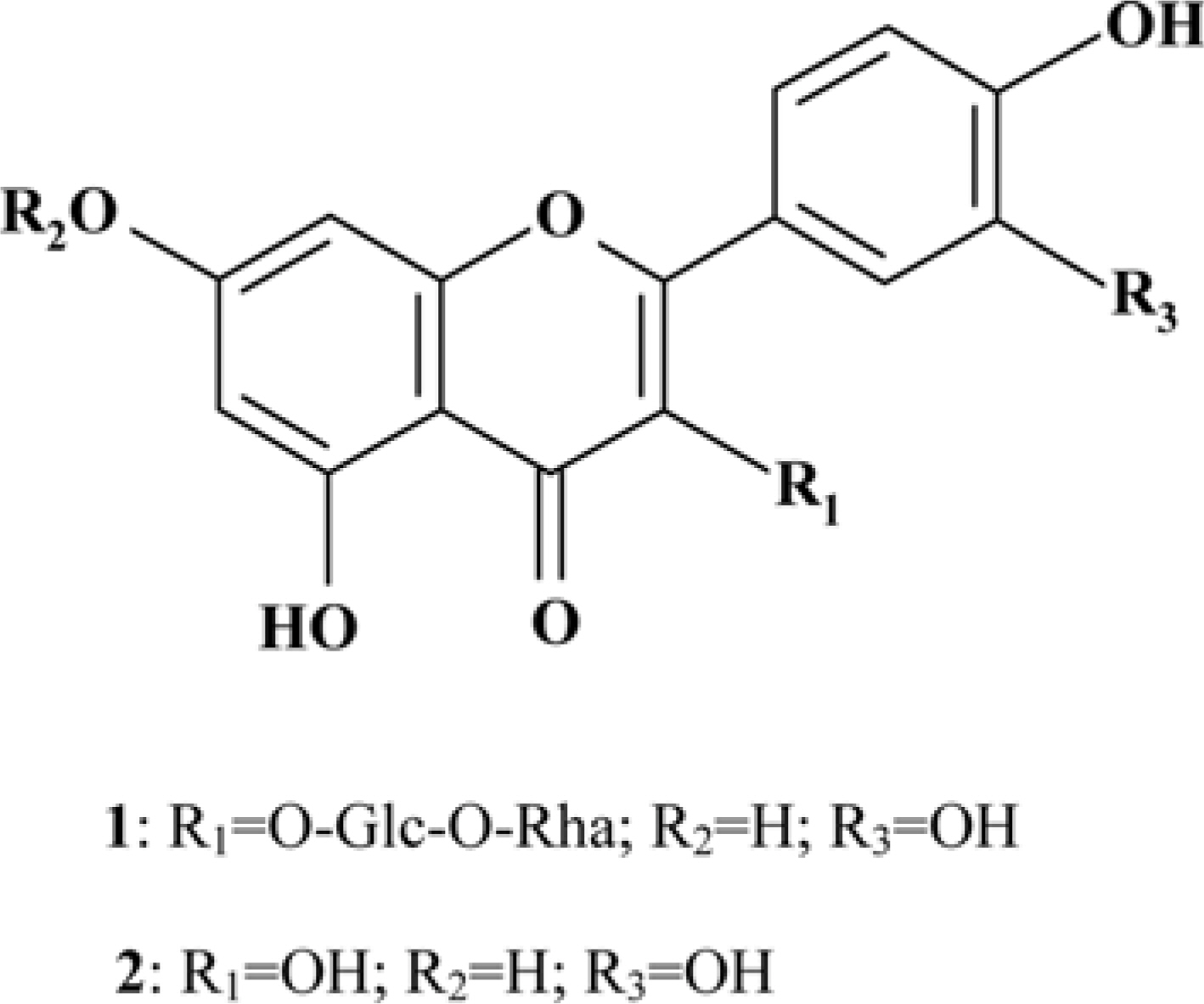
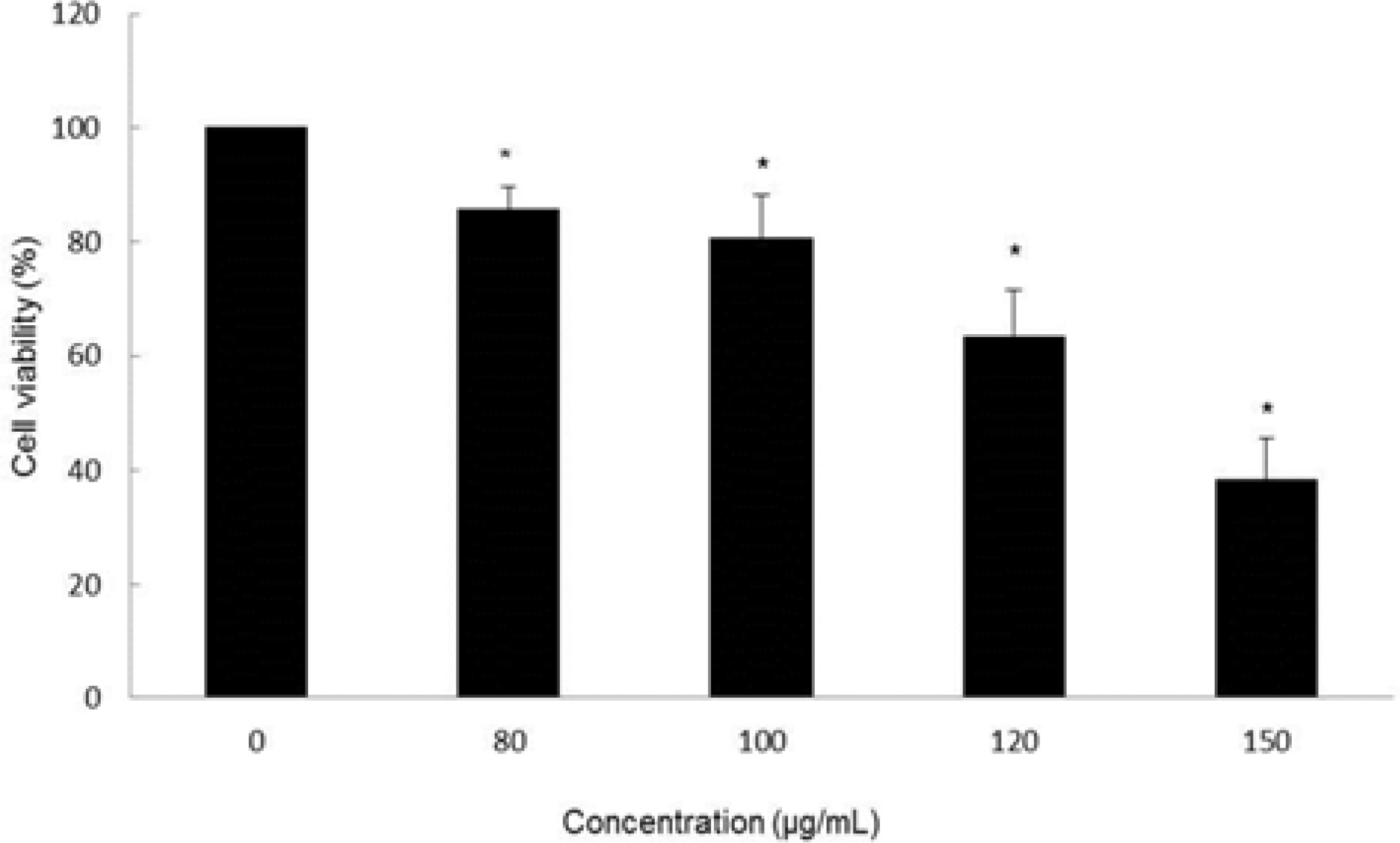
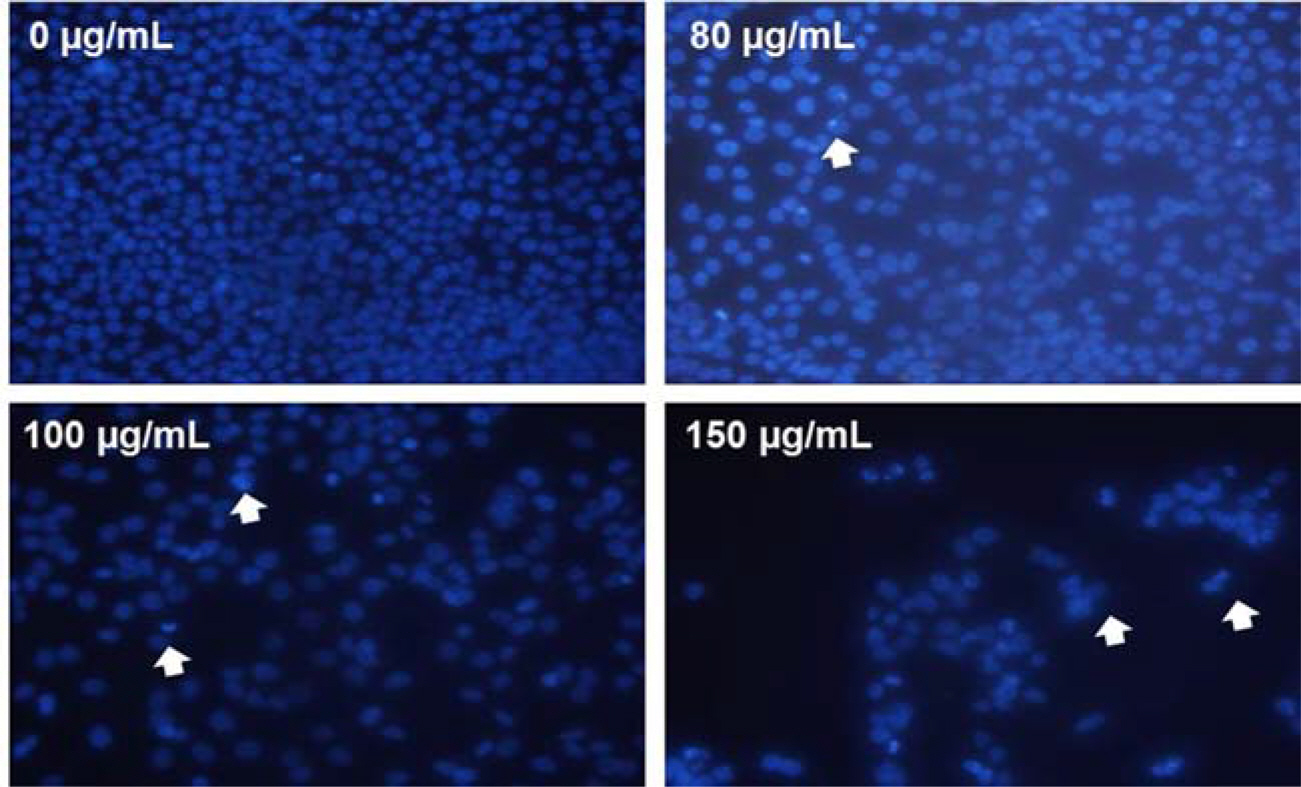
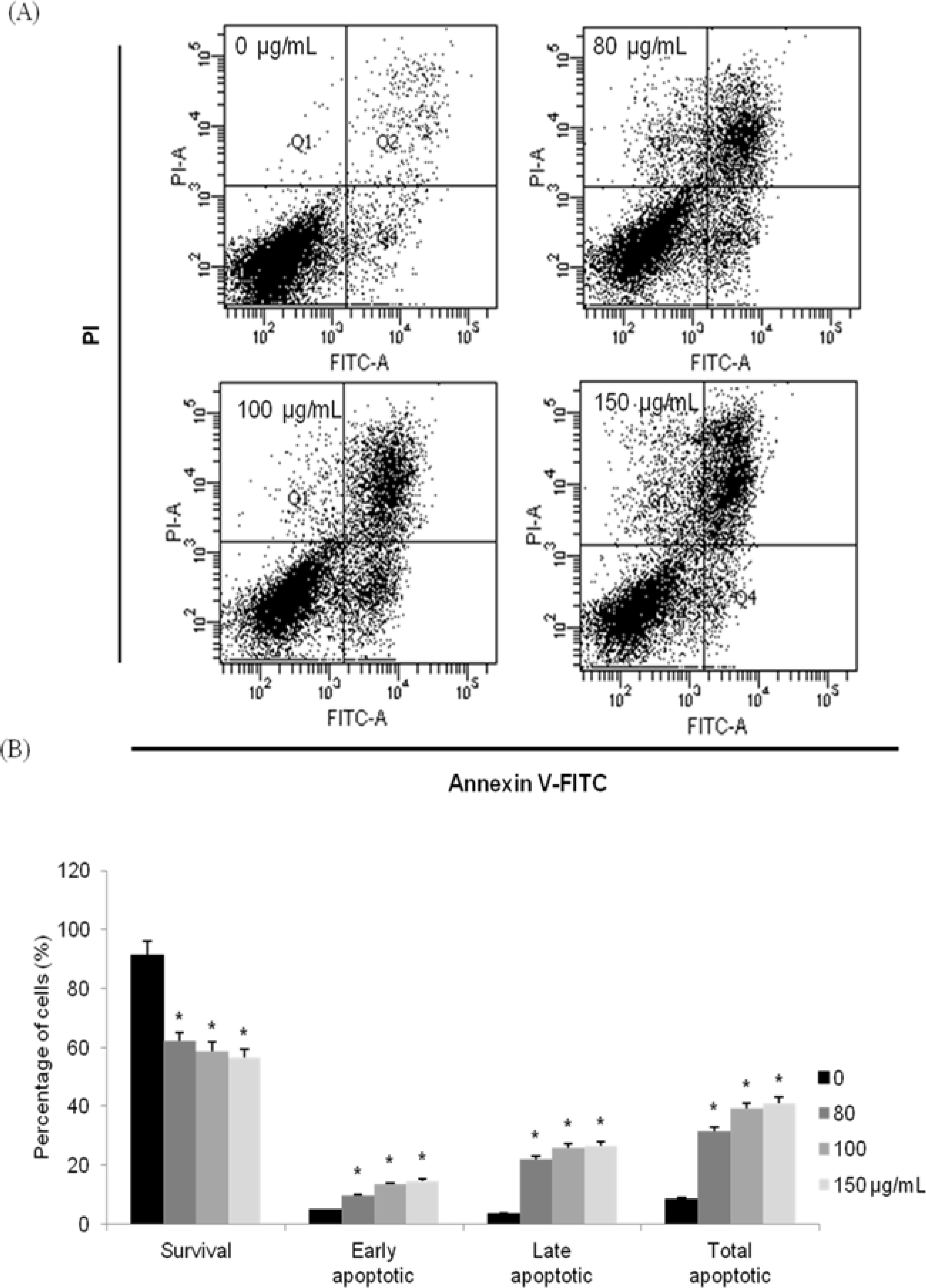
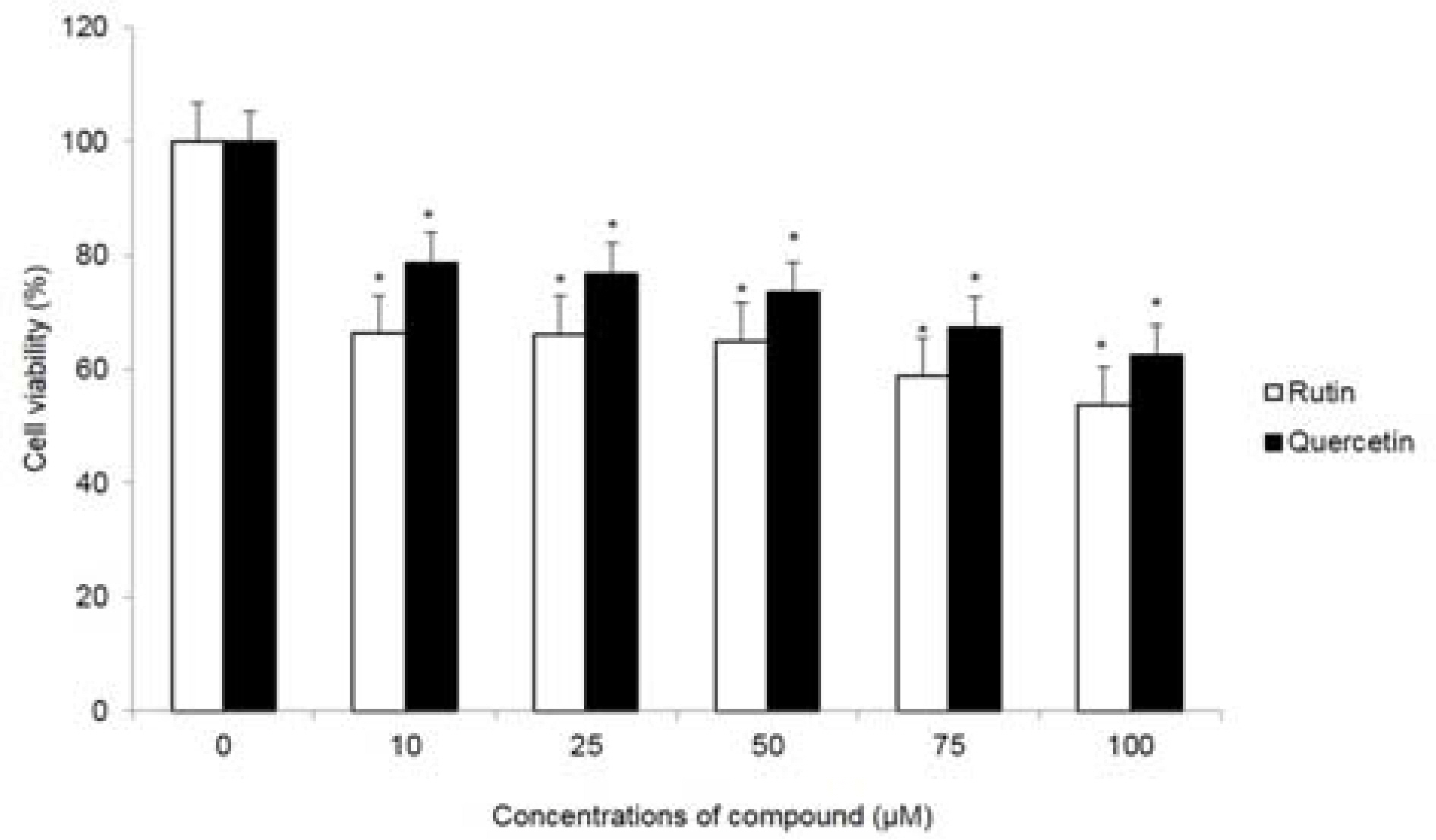
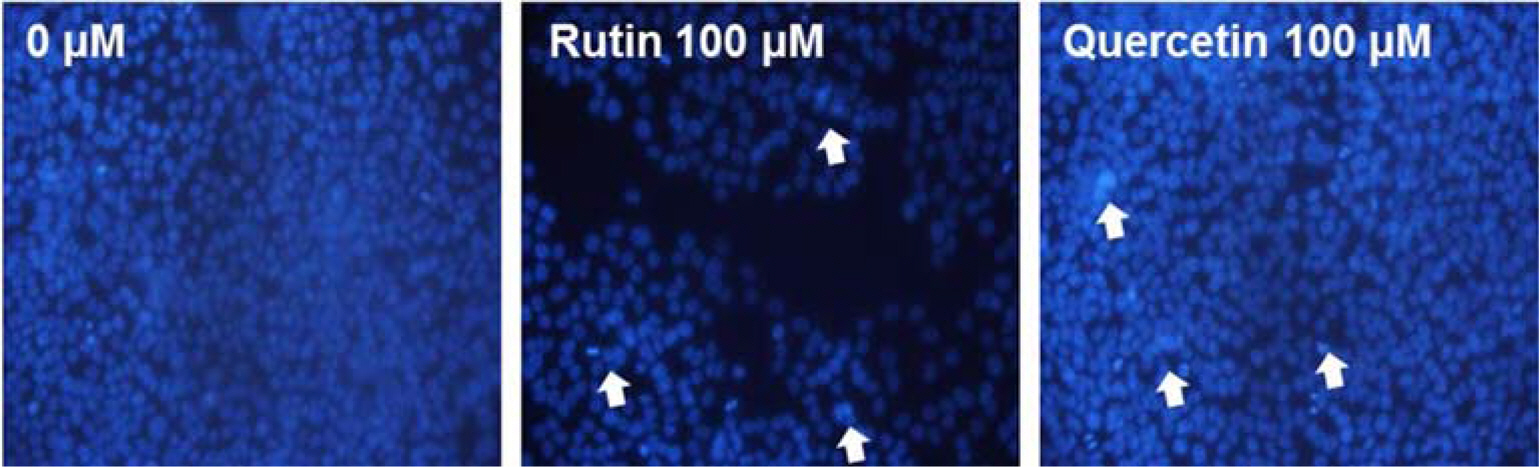
- Moringa oleifera Lam (M. oleifera, Moringaceae) is a tree of the Moringaceae family that can reach a height of between 5 and 10 m. The current paper presents cytotoxic effect of M. oleifera fruits and its flavonoids 1 and 2. The viability of HCT116 human colon cancer cells were 38.5% reduced by 150 µg/mL of ethanolic extracts in a concentration-dependent manner; in addition, we observed the apoptotic features of cell shrinkage and decreased cell size. Bcl-2 family proteins were regulated as determined by Western blotting analysis, suggesting that M. oleifera fruits and their flavonoids 1 and 2 induced apoptosis through an intrinsic pathway. Based on our findings, 70% ethanolic extracts of M. oleifera fruits and flavonoids 1 and 2 might be useful as cytotoxic agents in colorectal cancer therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
(1). Anwar F.., Latif S.., Ashraf M.., Gilani A. H.Phytother. Res. 2007. 21:17–25.(2). Bharali R.., Tabassum J.., Azad M. R.AsianPac. J. Cancer Prev. 2003. 4:131–139.(3). Guevara A. P.., Vargas C.., Sakurai H.., Fujiwara Y.., Hashimoto K.., Maoka T.., Kozuka M.., Ito Y.., Tokuda H.., Nishino H.Mutat. Res. 1999. 440:181–188.(4). Siddhuraju P.., Becker K. J.Agric. Food Chem. 2003. 51:2144–2155.(5). Sreelatha S.., Jeyachitra A.., Padma P. R.Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011. 49:1270–1275.(6). Budda S.., Butryee C.., Tuntipopipat S.., Rungsipipat A.., Wangnaithum S.., Lee J. S.., Kupradinun P. Asian. Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011. 12:3221–3228.(7). Stoha S. J.., Hartman M. J.Phytother. Res. 2015. 29:796–804.
Article(8). Krishnaswamy K.., Raghuramulu N.Indian J. Med. Res. 1998. 108:167–181.(9). Armstrong B.., Doll R.Int. J. Cancer. 1975. 15:617–631.(10). Voorrips L. E.., Goldbohm R. A.., Van Poppel G.., Sturmans F.., Hermus R. J.., Van den Brandt P. A.Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000. 152:1081–1092.
Article(11). Steller H.Science. 1995. 267:1445–1449.(12). Reed J. C.Cancer J. Sci. Am. 1998. 4:S8–S14.(13). Reed J. C.Oncology. 2004. 18:11–20.(14). Martinvalet D.., Zhu P.., Lieberman J.Immunity. 2005. 22:355–370.(15). Adams J. M.., Cory S.Science. 1998. 281:1322–1326.(16). Carmichael J.., DeGraff W. G.., Gazdar A. F.., Minna, J. D, Mitchell J. B.Cancer Res. 1987. 47:936–942.(17). Visagie M. H.., Joubert A. M.Mol. Cell Biochem. 2011. 357:343–352.(18). Ryu M. J.., Chung H. S.In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2015. 51:92–101.(19). Devisetti R.., Sreerama Y. N.., Bhattacharya S. J.Food Sci. Technol. 2016. 53:649–657.(20). Atawodi S. E.., Atawodi J. C.., Idakwo G. A.., Pfundstein B.., Haubner R.., Wurtele G.., Bartsch H.., Owen R. W. J.Med. Food. 2010. 13:710–716.(21). Verma A. R.., Vijayakumar M.., Mathela C. S.., Rao C. V.Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009. 47:2196–2201.(22). Manguro L. O.., Lemmen P.Nat. Prod. Res. 2007. 21:56–68.(23). Oboh G.., Ademiluyi A. O.., Ademosun A. O.., Olasehinde T. A.., Oyeleye S. I.., Boligon A. A.., Athayde M. L.Biochem. Res. Int. 2015. 2015:175950.(24). Karthivashan G.., Tangestani Fard M.., Arulselvan P.., Abas F.., Fakurazi S. J.Food Sci. 2013. 78:C1368–C1375.(25). Sahakitpichan P.., Mahidol C.., Disadee W.., Ruchirawat S.., Kanchanapoom T.Phytochemistry. 2011. 72:791–795.(26). Jintana T.., Naoto Y.., Perayot P.., Penpun W.., Tatsuro Y.., Naoki I.., Masami I.., Auayporn A.Trop. J. Pharm Res. 2017. 16:371–378.(27). Shin S. W.., Lee Y. H.., Moon S. R.., Koo I. H.., Hong H. J.., Shin E. J.., Lee M. Y.., Park J. H.., Chung H. S. J.Kor. Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2010. 53:716–723.(28). Findley H. W.., Gu L.., Yeager A. M.., Zhou M.Blood. 1997. 89:2986–2993.(29). Nagappan A.., Park K. I.., Park H. S.., Kim J. A.., Hong G. E.., Kang S. R.., Lee D. H.., Kim E. H.., Lee W. S.., Won C. K.., Kim G. S.Food Chem. 2012. 135:1920–1928.(30). Oliver F. J.., de la Rubia G.., Rolli V.., Ruiz-Ruiz M. C.., de Murcia G.., Murcia J. M. J.Biol. Chem. 1998. 273:33533–33539.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Induction of Apoptosis with Kigelia africana fruits in HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells via MAPKs Signaling Pathway
- Acute Pancreatitis Induced by Moringa Oleifera in a 48 years Old Korean Women: A Case Report
- Molecular docking of bioactive compounds derived from Moringa oleifera with p53 protein in the apoptosis pathway of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Cucurbitacin E’s Anti-Cancer Effects on HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells by Controlling Expression and Phosphorylation Levels of Caspase-9, eIF-2α, and ATF-4
- The Changes of Expression of Survivin by Butyrate in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells