J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Oct;32(10):1713-1716. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.10.1713.
Lead Poisoning at an Indoor Firing Range
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Aerospace Medical Center, Republic of Korea Air Force, Cheongju, Korea.
- 3Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. luvoem@gmail.com
- 4Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Aerospace Medical Research Center, Republic of Korea Air Force, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2400447
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.10.1713
Abstract
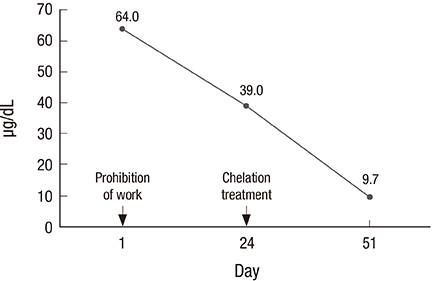
- In March 2014, a 39-year-old Korean male presented with a 6-month history of various nonspecific symptoms including dizziness, fatigue, asthenia, irritability, elevated blood pressure, palpitation, eyestrain, and tinnitus. His occupational history revealed that he had been working as an indoor firing range manager for 13 months; therefore, he was subjected to a blood lead level (BLL) test. The test results showed a BLL of 64 µg/dL; hence, he was diagnosed with lead poisoning and immediately withdrawn from work. As evident from the workplace environmental monitoring, the level of lead exposure in the air exceeded its limit (0.015-0.387 mg/m³). He received chelation treatment with calcium-disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (1 g/day) for 5 days without any adverse effects. In the follow-up results after 2 months, the BLL had decreased to 9.7 µg/dL and the symptoms resolved. This report represents the first occupational case of lead poisoning in firing ranges in Korea, and this necessitates institutional management to prevent the recurrence of poisoning through this route. Workplace environmental monitoring should be implemented for indoor firing ranges, and the workers should undergo regularly scheduled special health examinations. In clinical practice, it is essential to question the patient about his occupational history.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Song Y, Suh C, Kim SA, Kim N, Kim SM, Jeong SW, Kim SY, Kim KH, Kim JH, Son BC, et al. High lead exposure in two leaded bronze ingot foundry workers. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2014; 26:38.2. Kim JH, Kim EA, Koh DH, Byun K, Ryu HW, Lee SG. Blood lead levels of Korean lead workers in 2003–2011. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2014; 26:30.3. Ye HH, Jeong JU, Baek NJ, Choi CY, Jeon MJ, Sakong J. A case of lead poisoning due to a mixture of talisman ash. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2013; 25:37.4. Park WJ, Lee SH, Lee SH, Yoon HS, Moon JD. Occupational lead exposure from indoor firing ranges in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:497–501.5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US). Adult blood lead epidemiology & surveillance (ABLES) [Internet]. accessed on 24 July 2017. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/ABLES/description.html.6. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (US). OSHA lead standards [Internet]. accessed on 24 July 2017. Available at http://www.osha.gov/SLTC/lead.7. Korea Occupational Safety & Health Agency. Health care guidelines for lead-exposed workers (KOSHA GUIDE H-134-2013) [Internet]. accessed on 24 July 2017. Available at http://www.kosha.or.kr/www/boardView.do?contentId=352592&menuId=4828&boardType=A4.8. Gidlow DA. Lead toxicity. Occup Med (Lond). 2015; 65:348–356.9. Flora G, Gupta D, Tiwari A. Toxicity of lead: a review with recent updates. Interdiscip Toxicol. 2012; 5:47–58.10. Kim NH, Hyun YY, Lee KB, Chang Y, Ryu S, Oh KH, Ahn C. Environmental heavy metal exposure and chronic kidney disease in the general population. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:272–277.11. Lewis R, Kosnett MJ. Metals. In : LaDou J, Harrison R, editors. Current Occupational & Environmental Medicine. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill;2014. p. 463–485.12. Kim HC, Jang TW, Chae HJ, Choi WJ, Ha MN, Ye BJ, Kim BG, Jeon MJ, Kim SY, Hong YS. Evaluation and management of lead exposure. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2015; 27:30.13. Fischbein A, Hu H. Occupational and environmental exposure to lead. In : Rom WN, Markowitz S, editors. Environmental and Occupational Medicine. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2006. p. 954–990.14. Kim YS, Park JH, Hong JR, Gil HW, Yang JO, Lee EY, Hong SY. Influence of blood lead concentration on the nerve conduction velocity in patients with end-stage renal disease. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:290–294.15. D’souza HS, Dsouza SA, Menezes G, Venkatesh T. Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of lead poisoning in general population. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2011; 26:197–201.16. Beaucham C, Page E, Alarcon WA, Calvert GM, Methner M, Schoonover TM; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Indoor firing ranges and elevated blood lead levels - United States, 2002–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014; 63:347–351.17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Lead exposure from indoor firing ranges among students on shooting teams--Alaska, 2002–2004. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2005; 54:577–579.18. Valway SE, Martyny JW, Miller JR, Cook M, Mangione EJ. Lead absorption in indoor firing range users. Am J Public Health. 1989; 79:1029–1032.19. Landrigan PJ, McKinney AS, Hopkins LC, Rhodes WW Jr, Price WA, Cox DH. Chronic lead absorption. Result of poor ventilation in an indoor pistol range. JAMA. 1975; 234:394–397.20. Demmeler M, Nowak D, Schierl R. High blood lead levels in recreational indoor-shooters. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2009; 82:539–542.