Ann Rehabil Med.
2017 Dec;41(6):1013-1018. 10.5535/arm.2017.41.6.1013.
Relationships Between Self-awareness and Clinical Diagnostic Findings of Abnormal Foot Arch Height in Koreans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hwanglee@skku.edu
- 2Department of Physical Therapy, Graduate School of Sahmyook University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2400286
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.6.1013
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To see how people think about their own feet, and evaluate whether there are correlations among self-awareness of the participants and clinical examination findings.
METHODS
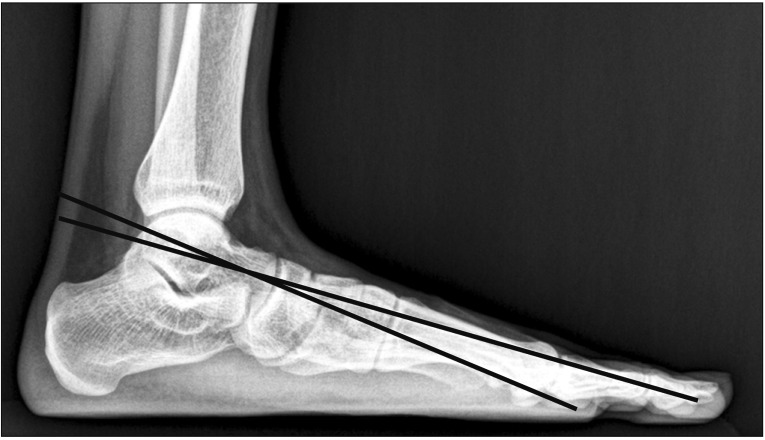
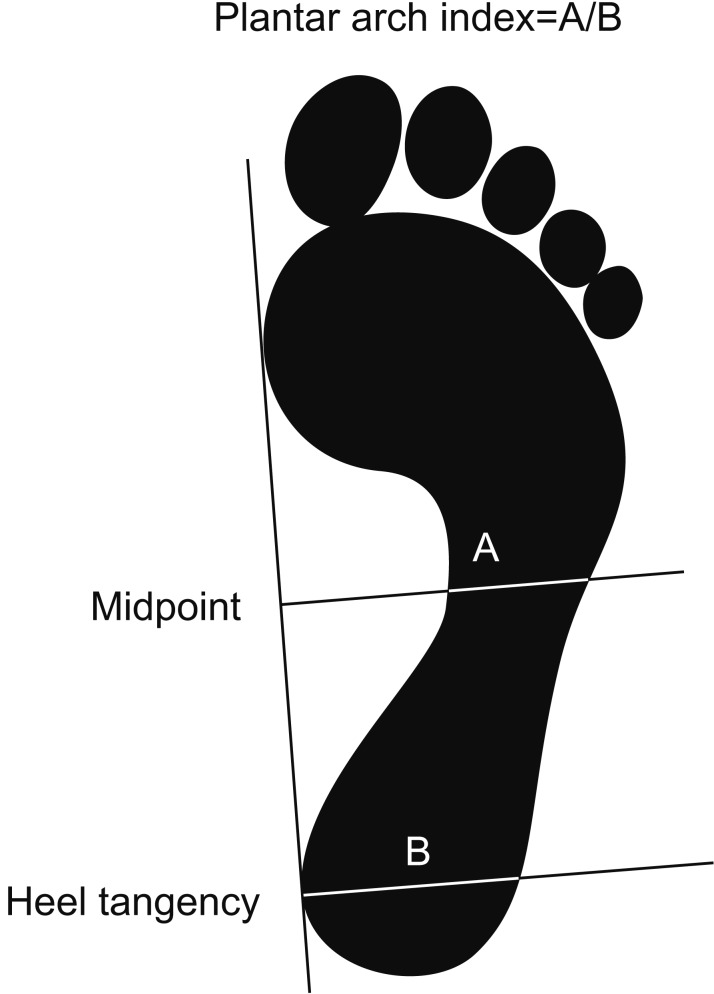
Adult twins and their families who participated in the Healthy Twin study from May 2008 to April 2010 were recruited. Participants were asked whether they thought their feet were normal, flat, or cavus. The lateral talometatarsal angles were measured on foot X-rays to determine the foot arch height. Using the podoscopic footprints taken with the podobaroscope, the Staheli arch index was also measured. Kappa statistics were used to calculate degree of agreement among the three measurement methods.
RESULTS
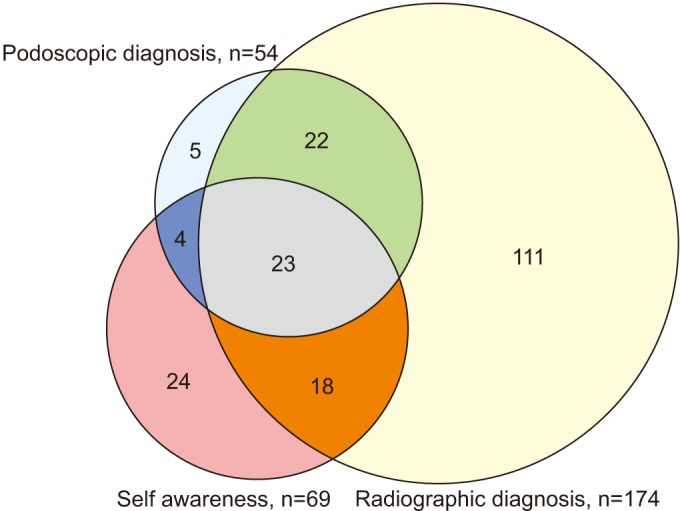
Self-awareness and radiographic findings were significantly different (Pearson chi-square test, p=0.000) and only slightly agreed (kappa measure of agreement=0.136, p=0.000). Self-awareness and podoscopy results revealed a significant difference (Pearson chi-square test, p=0.000), with only slight agreement (kappa measure of agreement=0.072, p=0.000).
CONCLUSION
There is significant disagreement between patients' perception of their feet and actual test results. Many people may have an incorrect assumption about their own foot conditions that may be reflected in improper management. Dissemination of accurate information about foot disorders by foot clinicians would be helpful.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arunakul M, Amendola A, Gao Y, Goetz JE, Femino JE, Phisitkul P. Tripod index: a new radiographic parameter assessing foot alignment. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34:1411–1420. PMID: 23657663.2. Dyal CM, Feder J, Deland JT, Thompson FM. Pes planus in patients with posterior tibial tendon insufficiency: asymptomatic versus symptomatic foot. Foot Ankle Int. 1997; 18:85–88. PMID: 9043880.
Article3. Clement DB, Taunton JE. A guide to the prevention of running injuries. Can Fam Physician. 1980; 26:543–548. PMID: 21293616.4. Lysholm J, Wiklander J. Injuries in runners. Am J Sports Med. 1987; 15:168–171. PMID: 3578639.
Article5. Williams DS, McClay IS. Measurements used to characterize the foot and the medial longitudinal arch: reliability and validity. Phys Ther. 2000; 80:864–871. PMID: 10960934.
Article6. Halabchi F, Mazaheri R, Mirshahi M, Abbasian L. Pediatric flexible flatfoot; clinical aspects and algorithmic approach. Iran J Pediatr. 2013; 23:247–260. PMID: 23795246.7. Dunn JE, Link CL, Felson DT, Crincoli MG, Keysor JJ, McKinlay JB. Prevalence of foot and ankle conditions in a multiethnic community sample of older adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2004; 159:491–498. PMID: 14977645.
Article8. Harris RI, Beath T. Hypermobile flat-foot with short tendo achillis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1948; 30A:116–140. PMID: 18921631.
Article9. Harris EJ, Vanore JV, Thomas JL, Kravitz SR, Mendelson SA, Mendicino RW, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of pediatric flatfoot. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2004; 43:341–373. PMID: 15605048.
Article10. Menz HB, Fotoohabadi MR, Wee E, Spink MJ. Visual categorisation of the arch index: a simplified measure of foot posture in older people. J Foot Ankle Res. 2012; 5:10. PMID: 22524253.
Article11. Lee JS, Kim KB, Jeong JO, Kwon NY, Jeong SM. Correlation of foot posture index with plantar pressure and radiographic measurements in pediatric flatfoot. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015; 39:10–17. PMID: 25750866.
Article12. Lee TH, Chay SW, Kim HJ. Diagnosis of flatfoot deformity. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2016; 20:1–5.
Article13. Murley GS, Menz HB, Landorf KB. A protocol for classifying normal- and flat-arched foot posture for research studies using clinical and radiographic measurements. J Foot Ankle Res. 2009; 2:22. PMID: 19575811.
Article14. Younger AS, Sawatzky B, Dryden P. Radiographic assessment of adult flatfoot. Foot Ankle Int. 2005; 26:820–825. PMID: 16221454.
Article15. Kim SB, Yoon K, Park HS, Kwak H, Ha NJ, Park JS. Radiologic measurement of flatfoot. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2000; 24:995–1001.17. Pita-Fernandez S, Gonzalez-Martin C, Seoane-Pillado T, Lopez-Calvino B, Pertega-Diaz S, Gil-Guillen V. Validity of footprint analysis to determine flatfoot using clinical diagnosis as the gold standard in a random sample aged 40 years and older. J Epidemiol. 2015; 25:148–154. PMID: 25382154.18. Sung J, Cho SI, Lee K, Ha M, Choi EY, Choi JS, et al. Healthy Twin: a twin-family study of Korea: protocols and current status. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2006; 9:844–848. PMID: 17254419.19. Coughlin MJ, Kaz A. Correlation of Harris mats, physical exam, pictures, and radiographic measurements in adult flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 2009; 30:604–612. PMID: 19589305.
Article20. Staheli LT, Chew DE, Corbett M. The longitudinal arch. A survey of eight hundred and eighty-two feet in normal children and adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69:426–428. PMID: 3818704.21. Chuckpaiwong B, Nunley JA 2nd, Queen RM. Correlation between static foot type measurements and clinical assessments. Foot Ankle Int. 2009; 30:205–212. PMID: 19321096.
Article22. Kim JS, Lee YS. Causal relationship between military activities and musculoskeletal injuries. J Korea Inst Mil Sci Technol. 2008; 11:142–147.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Change of Foot Measurements with Weight Bearing by 3-D Foot Scanner
- A Study on Changes of the Foot Shape with the Weight Loading by One Foot
- The Role of Transverse Arch in Foot Stiffness and Its Clinical Implications
- Diagnostic measurements of flatfoot
- The Height and Volume of Medial Longitudinal Arch in Normal and Painful Feet