Ann Rehabil Med.
2017 Dec;41(6):998-1004. 10.5535/arm.2017.41.6.998.
Long-Term Efficacy of Rehabilitation Following Arthroscopic Synovectomy in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated With Biologic Agents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Medical Center East, Tokyo, Japan. kambe.katsuaki@twmu.ac.jp
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Medical Center East, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2400284
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.6.998
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the long-term efficacy of rehabilitation following arthroscopic synovectomy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic agents.
METHODS
Arthroscopic synovectomy was performed in 29 joints of 17 patients, which were divided into two groups. Group 1 included arthroscopic synovectomy plus rehabilitation for 19 joints in 10 patients, and group 2 included arthroscopic synovectomy without rehabilitation for 10 joints in 7 patients. The Disease Activity Score C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP), Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and Functional Independence Measure (FIM) values (motor subscale) at 9.7 years after arthroscopic synovectomy were evaluated to identify the clinical factors related to outcomes.
RESULTS
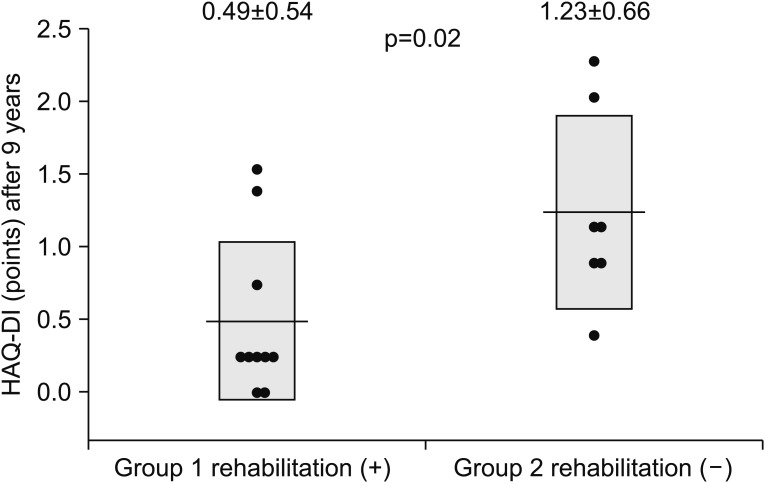
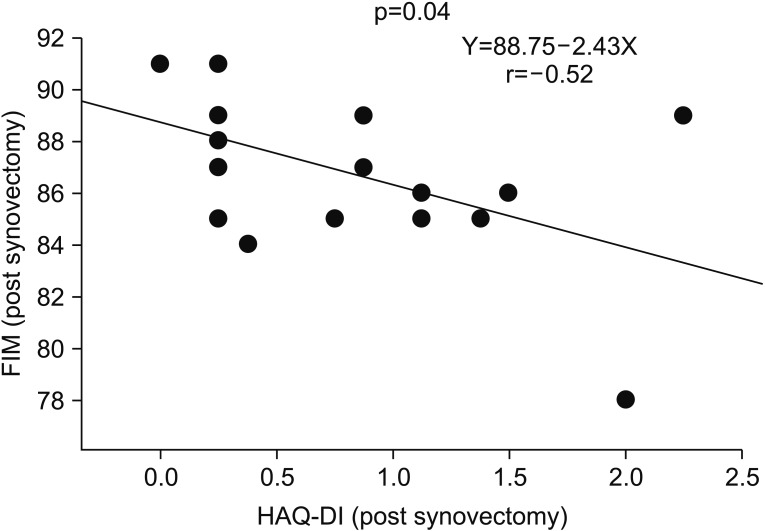
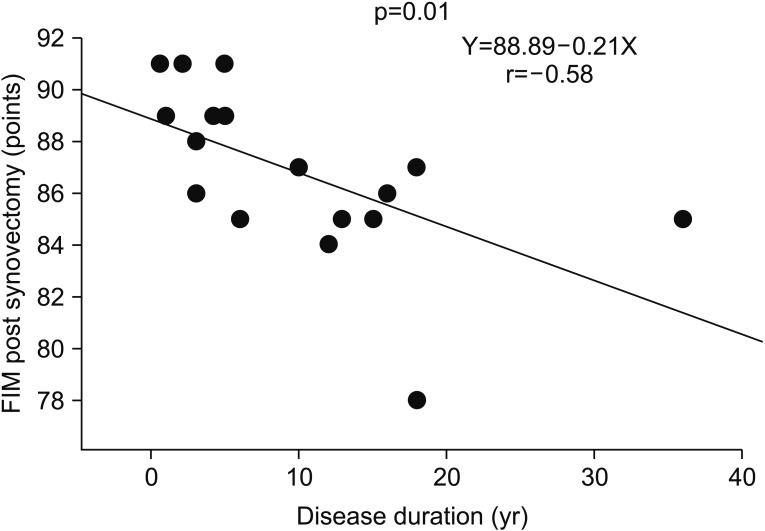
The increase in FIM score was significant in group 1 (p=0.05). HAQ-DI at 9 years was significantly decreased in group 1 (p=0.02). Therefore, arthroscopic synovectomy with rehabilitation was significant in improving FIM and HAQ-DI scores over a long period. Multiple regression analysis of FIM scores at 9 years indicated that rehabilitation (p=0.03) and disease duration (p=0.02) were significantly related to outcomes. FIM score at 9 years was significantly negatively correlated with disease duration (p=0.01, r=−0.58, Y=88.89-0.21X).
CONCLUSION
Rehabilitation following arthroscopic synovectomy was effective in achieving high FIM scores over time in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Luqmani R, Hennell S, Estrach C, Basher D, Birrell F, Bosworth A, et al. British Society for Rheumatology and British Health Professionals in Rheumatology guideline for the management of rheumatoid arthritis (after the first 2 years). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009; 48:436–439. PMID: 19174570.
Article2. Forestier R, Andre-Vert J, Guillez P, Coudeyre E, Lefevre-Colau MM, Combe B, et al. Non-drug treatment (excluding surgery) in rheumatoid arthritis: clinical practice guidelines. Joint Bone Spine. 2009; 76:691–698. PMID: 19945896.
Article3. Vliet Vlieland TP, Zwinderman AH, Vandenbroucke JP, Breedveld FC, Hazes JM. A randomized clinical trial of in-patient multidisciplinary treatment versus routine out-patient care in active rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996; 35:475–482. PMID: 8646440.4. Jacobsson LT, Frithiof M, Olofsson Y, Runesson I, Strombeck B, Wikstrom I. Evaluation of a structured multidisciplinary day care program in rheumatoid arthritis. A similar effect in newly diagnosed and longstanding disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998; 27:117–124. PMID: 9572637.5. Tijhuis GJ, Zwinderman AH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC, Vlieland PM. Two-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of a clinical nurse specialist intervention, inpatient, and day patient team care in rheumatoid arthritis. J Adv Nurs. 2003; 41:34–43. PMID: 12519286.
Article6. Christie A, Jamtvedt G, Dahm KT, Moe RH, Haavardsholm EA, Hagen KB. Effectiveness of nonpharmacological and nonsurgical interventions for patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an overview of systematic reviews. Phys Ther. 2007; 87:1697–1715. PMID: 17906290.
Article7. Momsen AM, Rasmussen JO, Nielsen CV, Iversen MD, Lund H. Multidisciplinary team care in rehabilitation: an overview of reviews. J Rehabil Med. 2012; 44:901–912. PMID: 23026978.
Article8. Lard LR, Visser H, Speyer I, vander Horst-Bruinsma IE, Zwinderman AH, Breedveld FC, et al. Early versus delayed treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of two cohorts who received different treatment strategies. Am J Med. 2001; 111:446–451. PMID: 11690569.
Article9. Landewe RB, Boers M, Verhoeven AC, Westhovens R, van de Laar MA, Markusse HM, et al. COBRA combination therapy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: long-term structural benefits of a brief intervention. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:347–356. PMID: 11840436.10. Krishnan E, Fries JF. Reduction in long-term functional disability in rheumatoid arthritis from 1977 to 1998: a longitudinal study of 3035 patients. Am J Med. 2003; 115:371–376. PMID: 14553872.11. Uhlig T, Kvien TK. Is rheumatoid arthritis really getting less severe? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009; 5:461–464. PMID: 19648945.
Article12. Krishnan E, Lingala B, Bruce B, Fries JF. Disability in rheumatoid arthritis in the era of biological treatments. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71:213–218. PMID: 21953343.
Article13. Kanbe K, Inoue K. Efficacy of arthroscopic synovectomy for the effect attenuation cases of infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 25:877–881. PMID: 16374576.
Article14. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31:315–324. PMID: 3358796.
Article15. Steinbrocker O, Traeger CH, Batterman RC. Therapeutic criteria in rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Med Assoc. 1949; 140:659–662. PMID: 18150288.
Article16. Bruce B, Fries JF. The Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005; 23(5 Suppl 39):S14–S18.17. Hamilton BB, Granger CV, Sherwin FS, Zielezny M, Tashman JS. A uniform national data system for medical rehabilitation. In : Fuhrer MJ, editor. Rehabilitation outcomes: analysis and measurement. Baltimore: Paul H. Brookes Publishing;1987.18. Meesters J, Verhoef J, Tijhuis G, Vliet Vlieland T. Functional disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis admitted for multidisciplinary rehabilitation from 1992 to 2009. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013; 52:1879–1883. PMID: 23861533.
Article19. Klokkerud M, Hagen KB, Kjeken I, Bremander A, Horslev-Petersen K, Vlieland TV, et al. Development of a framework identifying domains and elements of importance for arthritis rehabilitation. J Rehabil Med. 2012; 44:406–413. PMID: 22549648.
Article20. Brenda Z, Romanowski W, Bienkowski P, Lorenc R. Procedure for rehabilitation of the knee following synovectomy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis at the Poznan Rheumatological Center in Srema. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2000; 2:74–77.