J Clin Neurol.
2014 Jan;10(1):64-68.
Clinical and Molecular Study of the Extracellular Matrix Protein 1 Gene in a Spanish Family with Lipoid Proteinosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Virgen Macarena University Hospital Saville, Spain.
- 2Department of Neurology, Virgen Macarena University Hospital Saville, Spain.
- 3Department of Molecular Biology, Virgen Macarena University Hospital Saville, Spain. lucas@us.es
- 4Department of Dermatology, Virgen Macarena University Hospital Saville, Spain.
- 5Department of Pathology, Virgen Macarena University Hospital Saville, Spain.
- 6Instituto de Biomedicina de Sevilla (IBiS), Virgen del Rocio University Hospital, CSIC, Sevilla, Spain.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Lipoid proteinosis (LP) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a hoarse voice, variable scarring, and infiltration of the skin and mucosa. This disease is associated with mutations of the gene encoding extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1).
CASE REPORT
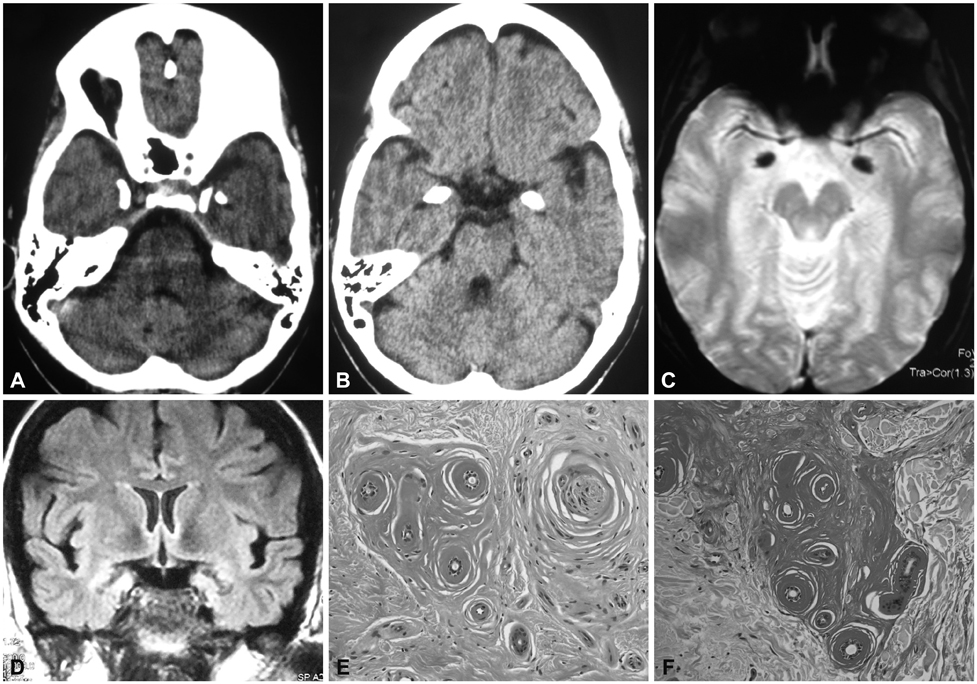
This was a clinical and molecular study of a new case of LP with a severe phenotype. A 35-year-old female born to nonconsanguineous parents developed dermatological and extracutaneous symptoms in her 9th month of life. The neurological abnormalities of the disease began to appear at the age of 19 years. Computed tomography revealed cranial calcifications.
CONCLUSIONS
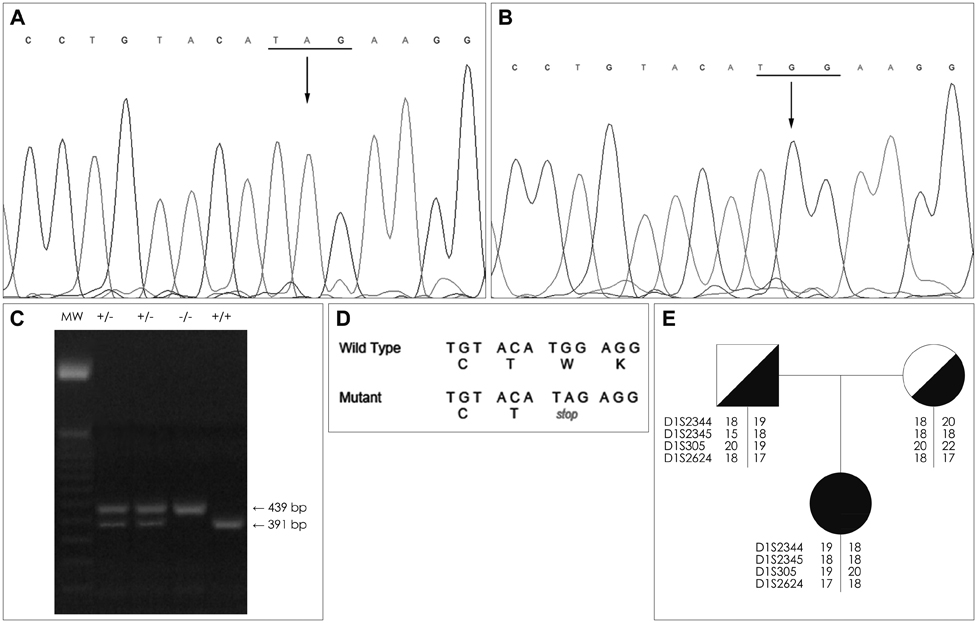
The diagnosis of LP was confirmed by histopathological findings and direct sequencing of ECM1. A new homozygous nonsense mutation was identified in exon 7 of ECM1, c.1076G>A (p.Trp359*). This mutation was not detected in 106 chromosomes of healthy individuals with a similar demographic origin. Microsatellite markers around ECM1 were used to construct the haplotype in both the parents and the patient. Reports on genotype-phenotype correlations in LP point to a milder phenotype in carriers of missense mutations in the Ecm1a isoform, whereas mutations in the Ecm1b isoform are thought to be associated with more severe phenotypes. The present findings in a Spanish patient carrying a truncating mutation in exon 7 revealed complete dermatological and neurological manifestations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hamada T. Lipoid proteinosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2002; 27:624–629.
Article2. Chan I, Liu L, Hamada T, Sethuraman G, McGrath JA. The molecular basis of lipoid proteinosis: mutations in extracellular matrix protein 1. Exp Dermatol. 2007; 16:881–890.
Article3. Horev L, Potikha T, Ayalon S, Molho-Pessach V, Ingber A, Gany MA, et al. A novel splice-site mutation in ECM-1 gene in a consanguineous family with lipoid proteinosis. Exp Dermatol. 2005; 14:891–897.
Article4. Smits P, Ni J, Feng P, Wauters J, Van Hul W, Boutaibi ME, et al. The human extracellular matrix gene 1 (ECM1): genomic structure, cDNA cloning, expression pattern, and chromosomal localization. Genomics. 1997; 45:487–495.
Article5. Kragh-Hansen U. Structure and ligand binding properties of human serum albumin. Dan Med Bull. 1990; 37:57–84.6. Smits P, Poumay Y, Karperien M, Tylzanowski P, Wauters J, Huylebroeck D, et al. Differentiation-dependent alternative splicing and expression of the extracellular matrix protein 1 gene in human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2000; 114:718–724.
Article7. Deckers MM, Smits P, Karperien M, Ni J, Tylzanowski P, Feng P, et al. Recombinant human extracellular matrix protein 1 inhibits alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization of mouse embryonic metatarsals in vitro. Bone. 2001; 28:14–20.
Article8. Sekiya I, Vuoristo JT, Larson BL, Prockop DJ. In vitro cartilage formation by human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma defines the sequence of cellular and molecular events during chondrogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99:4397–4402.
Article9. Hamada T, Wessagowit V, South AP, Ashton GH, Chan I, Oyama N, et al. Extracellular matrix protein 1 gene (ECM1) mutations in lipoid proteinosis and genotype-phenotype correlation. J Invest Dermatol. 2003; 120:345–350.
Article10. Fujimoto N, Terlizzi J, Aho S, Brittingham R, Fertala A, Oyama N, et al. Extracellular matrix protein 1 inhibits the activity of matrix metalloproteinase 9 through high-affinity protein/protein interactions. Exp Dermatol. 2006; 15:300–307.
Article11. Fujimoto N, Terlizzi J, Brittingham R, Fertala A, McGrath JA, Uitto J. Extracellular matrix protein 1 interacts with the domain III of fibulin-1C and 1D variants through its central tandem repeat 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 333:1327–1333.
Article12. Sercu S, Zhang M, Oyama N, Hansen U, Ghalbzouri AE, Jun G, et al. Interaction of extracellular matrix protein 1 with extracellular matrix components: ECM1 is a basement membrane protein of the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2008; 128:1397–1408.
Article13. Sung HJ, Johnson CE, Lessner SM, Magid R, Drury DN, Galis ZS. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 facilitates collagen remodeling and angiogenesis for vascular constructs. Tissue Eng. 2005; 11:267–276.
Article14. Nagy V, Bozdagi O, Matynia A, Balcerzyk M, Okulski P, Dzwonek J, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 is required for hippocampal late-phase long-term potentiation and memory. J Neurosci. 2006; 26:1923–1934.
Article15. Szklarczyk A, Lapinska J, Rylski M, McKay RD, Kaczmarek L. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 undergoes expression and activation during dendritic remodeling in adult hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:920–930.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lipoid Proteinosis
- Substrate-immobilized bone morphogenic protein-7 peptides on titanium surface support the expression of extracellular matrix proteins
- 14-3-3epsilon protein increases matrix metalloproteinase-2 gene expression via p38 MAPK signaling in NIH3T3 fibroblast cells
- Effects of Mutant Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein on the Synthesis of Extracellular Matrix in the Swarm Rat Chondrosarcoma Cell Line
- A Novel COMP Gene Mutation in a Korean Kindred with Multiple Epiphyseal Dysplasia