Ann Dermatol.
2018 Feb;30(1):119-122. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.119.
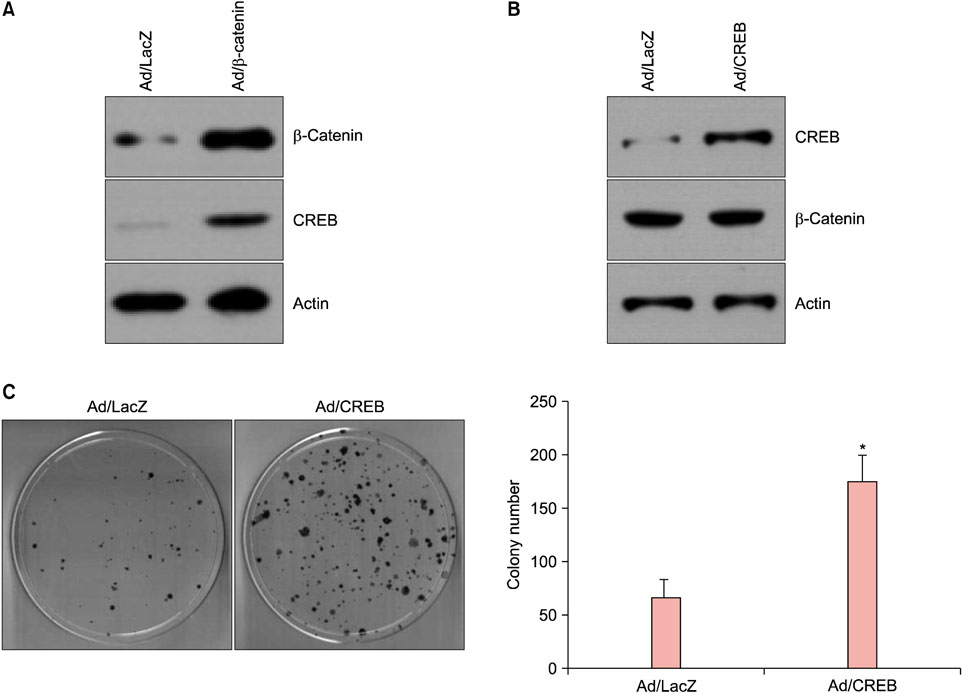
β-Catenin Regulates the Expression of cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein 1 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. cdkimd@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2399775
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.119
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001; 63:8–18.
Article2. Shin JM, Chang IK, Lee YH, Yeo MK, Kim JM, Sohn KC, et al. Potential role of S100A8 in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma differentiation. Ann Dermatol. 2016; 28:179–185.
Article3. Malanchi I, Peinado H, Kassen D, Hussenet T, Metzger D, Chambon P, et al. Cutaneous cancer stem cell maintenance is dependent on beta-catenin signalling. Nature. 2008; 452:650–653.
Article4. Condello S, Morgan CA, Nagdas S, Cao L, Turek J, Hurley TD, et al. β-Catenin-regulated ALDH1A1 is a target in ovarian cancer spheroids. Oncogene. 2015; 34:2297–2308.
Article5. Rheinwald JG, Beckett MA. Tumorigenic keratinocyte lines requiring anchorage and fibroblast support cultured from human squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1981; 41:1657–1663.6. Kim HK, Moon H, Lee KS, Moon HS, Kim BS, Kim DJ. Clonogenic assay of gastric adenocarcinoma stem cells. Korean J Intern Med. 1987; 2:163–169.7. Taipale J, Beachy PA. The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature. 2001; 411:349–354.
Article8. Hamburger AW, Salmon SE. Primary bioassay of human tumor stem cells. Science. 1977; 197:461–463.
Article9. Yang JS, Lavker RM, Sun TT. Upper human hair follicle contains a subpopulation of keratinocytes with superior in vitro proliferative potential. J Invest Dermatol. 1993; 101:652–659.
Article10. Bossis I, Voutetakis A, Bei T, Sandrini F, Griffin KJ, Stratakis CA. Protein kinase A and its role in human neoplasia: the Carney complex paradigm. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004; 11:265–280.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Beta-Catenin Downregulation Contributes to Epidermal Growth Factor-induced Migration and Invasion of MDAMB231 Cells
- Immunohistochemical Expression of Nuclear Retinoid Receptor and CREB(cAMP Response Element Binding Protein) in Lung Cancers
- Glutamine synthetase mediates sorafenib sensitivity in β-catenin-active hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- β-Catenin expression is associated with cell invasiveness in pancreatic cancer
- Expression of beta-catenin and Adenomatous Polyposis Coli(APC) Protein in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Laryngeal Cancers