Ann Dermatol.
2018 Feb;30(1):102-104. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.102.
Investigating Skin Penetration Following Needle-Free Injection Combined with Fractional Laser and Subcision
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. momo920@daum.net
- 2Department of Business and Technology Management, NYU Tandon School of Engineering, Brooklyn, NY, USA.
- KMID: 2399767
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.102
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
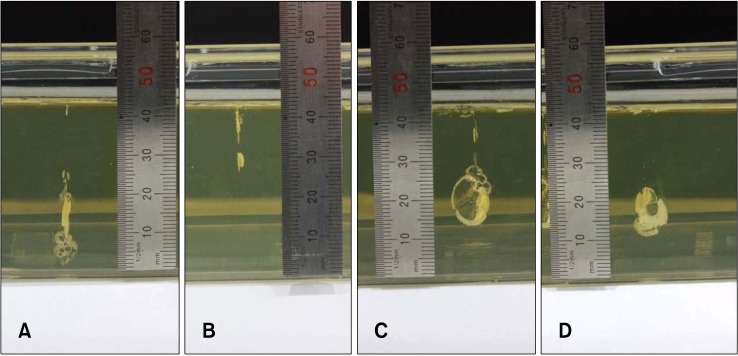
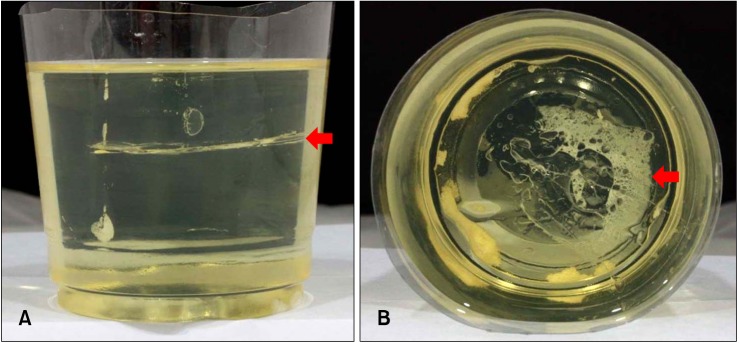
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levenberg A, Halachmi S, Arad-Cohen A, Ad-El D, Cassuto D, Lapidoth M. Clinical results of skin remodeling using a novel pneumatic technology. Int J Dermatol. 2010; 49:1432–1439. PMID: 21091682.
Article2. Seok J, Hong JY, Jang JH, Bae JH, Choi SY, Yoo KH, et al. The NEEDLELESS MICROJET: a novel device for hypertrophic scar remodelling on the forehead. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016; 30:e145–e146. PMID: 26537185.
Article3. Seok J, Kwon HJ, Choi SY, Yoo KH, Oh CT, Kim BJ. Successful treatment of thyroidectomy scar with a pneumatic needleless injector and silicone gel. Int Wound J. 2016; 13:1089–1090. PMID: 26991428.
Article4. Seok J, Choi SY, Park KY, Jang JH, Bae JH, Kim BJ, et al. Depressed scar after filler injection successfully treated with pneumatic needleless injector and radiofrequency device. Dermatol Ther. 2016; 29:45–47. PMID: 26301992.
Article5. Seok J, Oh CT, Kwon HJ, Kwon TR, Choi EJ, Choi SY, et al. Investigating skin penetration depth and shape following needle-free injection at different pressures: a cadaveric study. Lasers Surg Med. 2016; 48:624–628. PMID: 27075398.
Article6. Ding T, Zhang S, Fu Q, Xu Z, Wan M. Ultrasound line-byline scanning method of spatial-temporal active cavitation mapping for high-intensity focused ultrasound. Ultrasonics. 2014; 54:147–155. PMID: 23673346.
Article7. Stachowiak JC, Li TH, Arora A, Mitragotri S, Fletcher DA. Dynamic control of needle-free jet injection. J Control Release. 2009; 135:104–112. PMID: 19284969.
Article8. Kwon TR, Seok J, Jang JH, Kwon MK, Oh CT, Choi EJ, et al. Needle-free jet injection of hyaluronic acid improves skin remodeling in a mouse model. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016; 105:69–74. PMID: 27257030.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of an Atrophic Scar with Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser-assisted Poly-L-lactic Acid Delivery
- Utility of the stacking method for depressed scar improvement using a 1,064-nm, microlens array, picosecond-dominant laser in Republic of Korea: retrospective clinical study
- Treatment of an ear keloid refractory to intralesional triamcinolone injection monotherapy with fractional CO2 laser and triamcinolone combination therapy: a case report
- Successful Treatment of Post-operative Keloid with Combined Cryotherapy and Ablative Fractional CO2 Laser
- Efficacy of Early Application of Ablative Fractional CO2 Laser on Secondary Skin Contracture after Skin Graft