J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2017 Dec;25(4):131-137. 10.4250/jcu.2017.25.4.131.
Outcomes of Left Ventricular Function According to Treatment Response for a Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. kittysooni@chamc.co.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Laboratory Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2399414
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2017.25.4.131
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
To evaluate the outcomes of left ventricular (LV) function according to treatment response for a hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus (hsPDA) in preterm infants.
METHODS
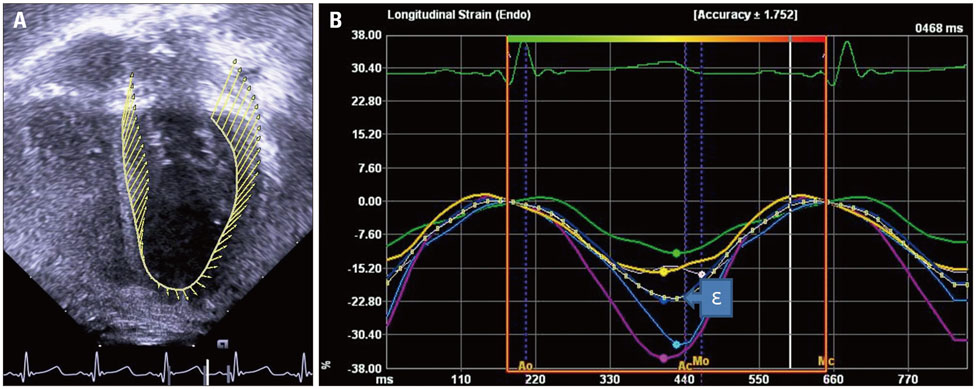
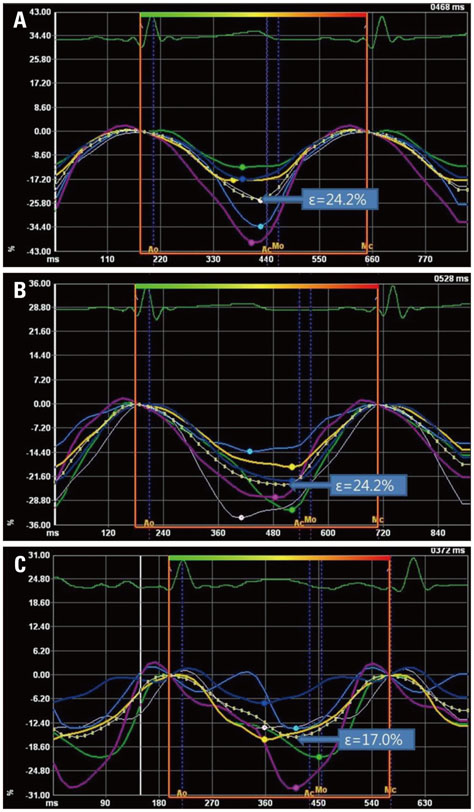
Echocardiograms of 21 preterm infants born at gestational age < 31 weeks obtained at term-equivalent age were retrospectively studied. Among preterm infants with a hsPDA, 9 underwent ligation after failure of pharmacological closure (ligation group) and 6 experienced successful pharmacological closure (medication group). Six preterm infants without hsPDA (no-hsPDA group) were studied as controls. LV peak longitudinal systolic strain (ε) of each infant was retrospectively obtained from echocardiograms using velocity vector imaging, along with neonatal outcomes.
RESULTS
Pharmacological closures were attempted at postnatal day 2-3. In the ligation group, the median postnatal age at ligation was 20 days. In the ligation group, LV peak longitudinal systolic ε was significantly decreased at term-equivalent age compared to the other groups. Between the medication and no-hsPDA groups, LV peak longitudinal systolic ε did not differ significantly. Among the neonatal outcomes, infants who experienced necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) showed significantly decreased LV peak longitudinal systolic ε compared to the infants who did not experience NEC .
CONCLUSION
We speculate that in preterm infants with an hsPDA, in cases of medical treatment failure, early PDA ligation at less than 20 days of postnatal age would be beneficial for preserving LV systolic function.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Noori S, McCoy M, Friedlich P, Bright B, Gottipati V, Seri I, Sekar K. Failure of ductus arteriosus closure is associated with increased mortality in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2009; 123:e138–e144.2. Clyman RI, Couto J, Murphy GM. Patent ductus arteriosus: are current neonatal treatment options better or worse than no treatment at all? Semin Perinatol. 2012; 36:123–129.3. Benitz WE. Committee on Fetus and Newborn, American Academy of Pediatrics. Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2016; 137:e20153730.4. Sung SI, Chang YS, Chun JY, Yoon SA, Yoo HS, Ahn SY, Park WS. Mandatory closure versus nonintervention for patent ductus arteriosus in very preterm infants. J Pediatr. 2016; 177:66–71.e1.5. El-Khuffash A, Weisz DE, McNamara PJ. Reflections of the changes in patent ductus arteriosus management during the last 10 years. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2016; 101:F474–F478.6. James AT, Corcoran JD, Breatnach CR, Franklin O, Mertens L, El-Khuffash A. Longitudinal assessment of left and right myocardial function in preterm infants using strain and strain rate imaging. Neonatology. 2016; 109:69–75.7. Czernik C, Rhode S, Helfer S, Schmalisch G, Bührer C, Schmitz L. Development of left ventricular longitudinal speckle tracking echocardiography in very low birth weight infants with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia during the neonatal period. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e106504.8. Bensley JG, Stacy VK, De Matteo R, Harding R, Black MJ. Cardiac remodelling as a result of pre-term birth: implications for future cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2010; 31:2058–2066.9. Haque U, Stiver C, Rivera BK, Richards B, Ma N, Cua CL, Smith CV, Backes CH. Right ventricular performance using myocardial deformation imaging in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol. 2017; 37:81–87.10. Nestaas E, Støylen A, Brunvand L, Fugelseth D. Longitudinal strain and strain rate by tissue Doppler are more sensitive indices than fractional shortening for assessing the reduced myocardial function in asphyxiated neonates. Cardiol Young. 2011; 21:1–7.11. Pirat B, Khoury DS, Hartley CJ, Tiller L, Rao L, Schulz DG, Nagueh SF, Zoghbi WA. A novel feature-tracking echocardiographic method for the quantitation of regional myocardial function: validation in an animal model of ischemia-reperfusion. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:651–659.12. Sosenko IR, Fajardo MF, Claure N, Bancalari E. Timing of patent ductus arteriosus treatment and respiratory outcome in premature infants: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr. 2012; 160:929–935.e1.13. Liebowitz M, Koo J, Wickremasinghe A, Allen IE, Clyman RI. Effects of prophylactic indomethacin on vasopressor-dependent hypotension in extremely preterm infants. J Pediatr. 2017; 182:21–27.e2.14. Jhaveri N, Moon-Grady A, Clyman RI. Early surgical ligation versus a conservative approach for management of patent ductus arteriosus that fails to close after indomethacin treatment. J Pediatr. 2010; 157:381–387.e1.15. Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978; 92:529–534.16. Palleri E, Aghamn I, Bexelius TS, Bartocci M, Wester T. The effect of gestational age on clinical and radiological presentation of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2017; [Epub]. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.09.018.17. Sehgal A, Malikiwi A, Paul E, Tan K, Menahem S. Right ventricular function in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: association with respiratory sequelae. Neonatology. 2016; 109:289–296.18. Mourani PM, Sontag MK, Younoszai A, Ivy DD, Abman SH. Clinical utility of echocardiography for the diagnosis and management of pulmonary vascular disease in young children with chronic lung disease. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:317–325.19. Lopez L, Colan SD, Frommelt PC, Ensing GJ, Kendall K, Younoszai AK, Lai WW, Geva T. Recommendations for quantification methods during the performance of a pediatric echocardiogram: a report from the Pediatric Measurements Writing Group of the American Society of Echocardiography Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease Council. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010; 23:465–495. quiz 576-7.20. Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, Lancellotti P, Muraru D, Picard MH, Rietzschel ER, Rudski L, Spencer KT, Tsang W, Voigt JU. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015; 28:1–39.e14.21. Voigt JU, Pedrizzetti G, Lysyansky P, Marwick TH, Houle H, Baumann R, Pedri S, Ito Y, Abe Y, Metz S, Song JH, Hamilton J, Sengupta PP, Kolias TJ, d'Hooge J, Aurigemma GP, Thomas JD, Badano LP. Definitions for a common standard for 2D speckle tracking echocardiography: consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/Industry Task Force to standardize deformation imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015; 28:183–193.22. Kutty S, Padiyath A, Li L, Peng Q, Rangamani S, Schuster A, Danford DA. Functional maturation of left and right atrial systolic and diastolic performance in infants, children, and adolescents. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2013; 26:398–409.e2.23. El-Khuffash AF, Jain A, McNamara PJ. Ligation of the patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: understanding the physiology. J Pediatr. 2013; 162:1100–1106.24. Levy PT, Machefsky A, Sanchez AA, Patel MD, Rogal S, Fowler S, Yaeger L, Hardi A, Holland MR, Hamvas A, Singh GK. Reference ranges of left ventricular strain measures by two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2016; 29:209–225.e6.25. El-Khuffash AF, Jain A, Dragulescu A, McNamara PJ, Mertens L. Acute changes in myocardial systolic function in preterm infants undergoing patent ductus arteriosus ligation: a tissue Doppler and myocardial deformation study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2012; 25:1058–1067.26. McNamara PJ, Stewart L, Shivananda SP, Stephens D, Sehgal A. Patent ductus arteriosus ligation is associated with impaired left ventricular systolic performance in premature infants weighing less than 1000 g. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 140:150–157.27. Schubert U, Müller M, Abdul-Khaliq H, Norman M. Preterm birth is associated with altered myocardial function in infancy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2016; 29:670–678.28. Dogan V, Öcal B, Orun UA, Ozgur S, Yılmaz O, Keskin M, Ceylan O, Karademir S, Şenocak F. Strain and strain rate echocardiography findings in children with asymptomatic congenital aortic stenosis. Pediatr Cardiol. 2013; 34:1152–1158.29. Nestaas E, Støylen A, Brunvand L, Fugelseth D. Tissue Doppler derived longitudinal strain and strain rate during the first 3 days of life in healthy term neonates. Pediatr Res. 2009; 65:357–362.30. Pena JL, da Silva MG, Faria SC, Salemi VM, Mady C, Baltabaeva A, Sutherland GR. Quantification of regional left and right ventricular deformation indices in healthy neonates by using strain rate and strain imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009; 22:369–375.31. Perk G, Tunick PA, Kronzon I. Non-Doppler two-dimensional strain imaging by echocardiography--from technical considerations to clinical applications. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007; 20:234–243.32. Dandel M, Hetzer R. Echocardiographic strain and strain rate imaging--clinical applications. Int J Cardiol. 2009; 132:11–24.33. Rowland DG, Gutgesell HP. Noninvasive assessment of myocardial contractility, preload, and afterload in healthy newborn infants. Am J Cardiol. 1995; 75:818–821.34. Noori S, Friedlich P, Seri I, Wong P. Changes in myocardial function and hemodynamics after ligation of the ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 2007; 150:597–602.35. Schena F, Francescato G, Cappelleri A, Picciolli I, Mayer A, Mosca F, Fumagalli M. Association between hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2015; 166:1488–1492.36. Hagadorn JI, Brownell EA, Trzaski JM, Johnson KR, Lainwala S, Campbell BT, Herbst KW. Trends and variation in management and outcomes of very low-birth-weight infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatr Res. 2016; 80:785–792.37. Clyman RI. Recommendations for the postnatal use of indomethacin: an analysis of four separate treatment strategies. J Pediatr. 1996; 128(5 Pt 1):601–607.38. Sehgal A, Doctor T, Menahem S. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors in preterm infants with patent ductus arteriosus: effects on cardiac and vascular indices. Pediatr Cardiol. 2014; 35:1429–1436.39. El-Khuffash A, Higgins M, Walsh K, Molloy EJ. Quantitative assessment of the degree of ductal steal using celiac artery blood flow to left ventricular output ratio in preterm infants. Neonatology. 2008; 93:206–212.40. Dollberg S, Lusky A, Reichman B. Patent ductus arteriosus, indomethacin and necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants: a population-based study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005; 40:184–188.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Patent Ductus Arteriosus on Right Ventricle in Premature Infants: by M-mode and Doppler Echocardiography
- Indomethacin therapy in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus
- Risk Factors of Failure of Ibuprofen Treatment in Preterm Infants with Hemodynamically Significant Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Clinical and Echocardiographic Studies of Ventricular Septal Defect and Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Nonsurgical closure of patent ductus arteriosus with the rashkind PDA occluder system